1、[LG] Consistency Models
2、[CV] Human Motion Diffusion as a Generative Prior
3、[LG] Dropout Reduces Underfitting
4、[CL] Google USM: Scaling Automatic Speech Recognition Beyond 100 Languages
5、[RO] Efficient Solution to 3D-LiDAR-based Monte Carlo Localization with Fusion of Measurement Model Optimization via Importance Sampling
[LG] Understanding the Diffusion Objective as a Weighted Integral of ELBOs
[CV] 3D generation on ImageNet
[CL] UDAPDR: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation via LLM Prompting and Distillation of Rerankers
[LG] Modern Bayesian Experimental Design
摘要:一致性模型、人体运动扩散作为生成式先验、用Dropout减轻欠拟合、将自动语音识别扩展到超过100种语言、基于重要性采样融合测量模型优化的3D-LiDAR蒙特卡罗定位方法、将扩散目标理解为ELBO的加权积分、ImageNet上的3D生成、基于LLM的无监督域自适应算法及重排序器蒸馏、现代贝叶斯实验设计
1、[LG] Consistency Models
Y Song, P Dhariwal, M Chen, I Sutskever
[OpenAI]
一致性模型
要点:
-
一致性模型是一种新的生成模型,支持快速的单步生成和少步采样; -
在没有对抗性训练的情况下实现了较高的样本质量,并允许进行零样本数据编辑; -
可作为蒸馏预训练扩散模型的一种方式来训练,也可以作为独立的生成模型来训练; -
广泛的实验表面,一致性模型在标准基准上优于现有的扩散模型的蒸馏技术和单步非对抗生成模型。
一句话总结:
一致性模型是一个新的生成模型族,无需对抗训练就能实现高样本质量,支持快速单步生成,并可进行零样本数据编辑。
Diffusion models have made significant breakthroughs in image, audio, and video generation, but they depend on an iterative generation process that causes slow sampling speed and caps their potential for real-time applications. To overcome this limitation, we propose consistency models, a new family of generative models that achieve high sample quality without adversarial training. They support fast one-step generation by design, while still allowing for few-step sampling to trade compute for sample quality. They also support zero-shot data editing, like image inpainting, colorization, and super-resolution, without requiring explicit training on these tasks. Consistency models can be trained either as a way to distill pre-trained diffusion models, or as standalone generative models. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that they outperform existing distillation techniques for diffusion models in one- and few-step generation. For example, we achieve the new state-of-the-art FID of 3.55 on CIFAR-10 and 6.20 on ImageNet 64×64 for one-step generation. When trained as standalone generative models, consistency models also outperform single-step, non-adversarial generative models on standard benchmarks like CIFAR-10, ImageNet 64×64 and LSUN 256×256.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.01469
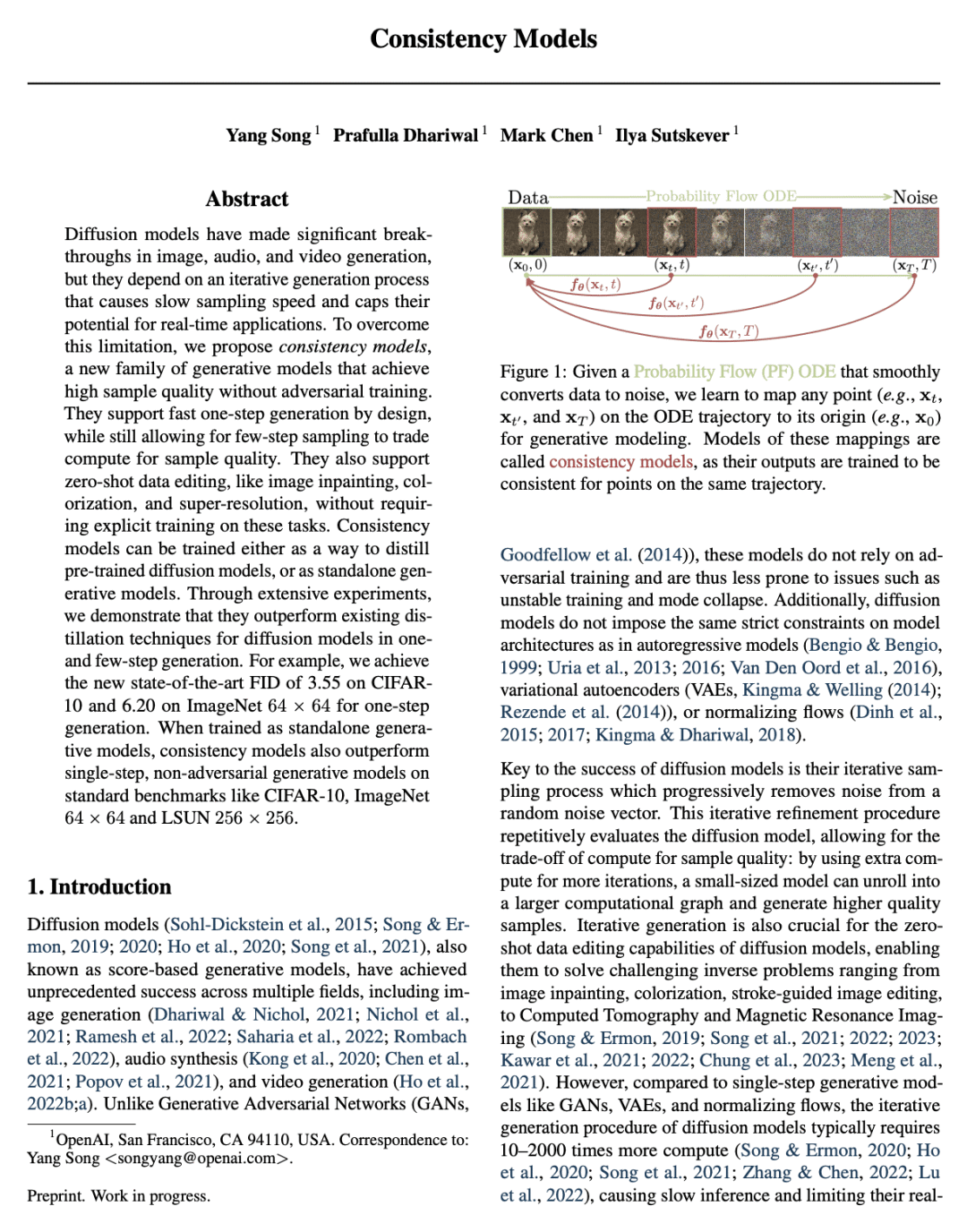
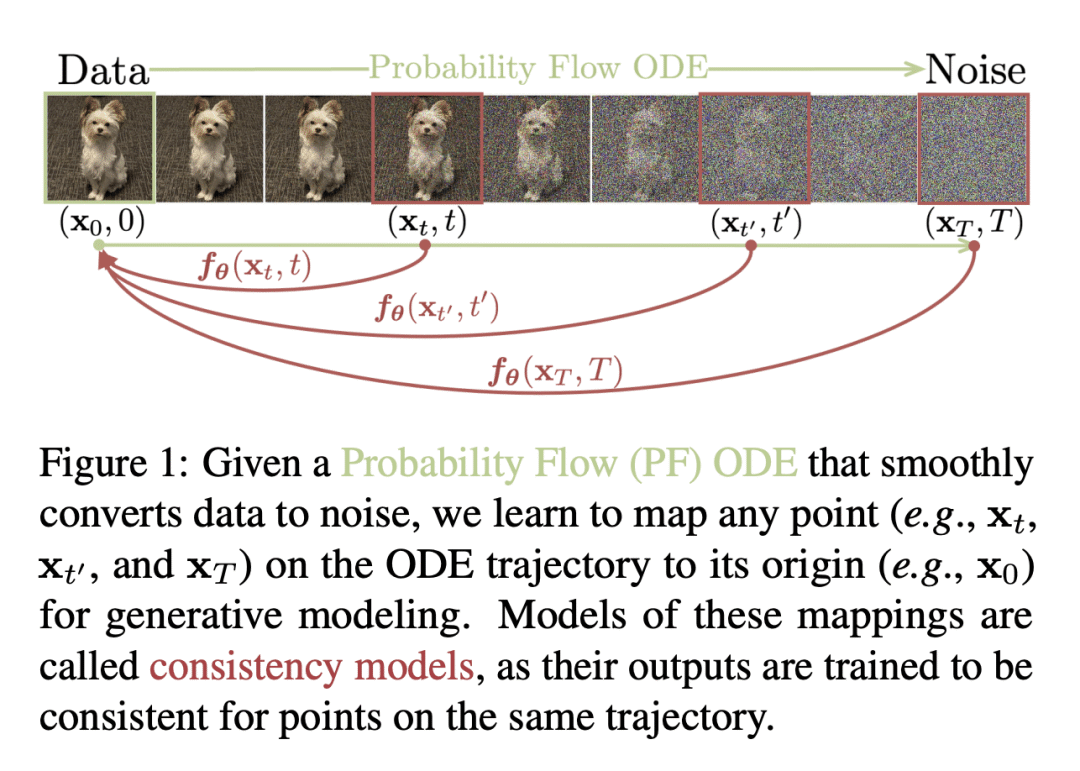
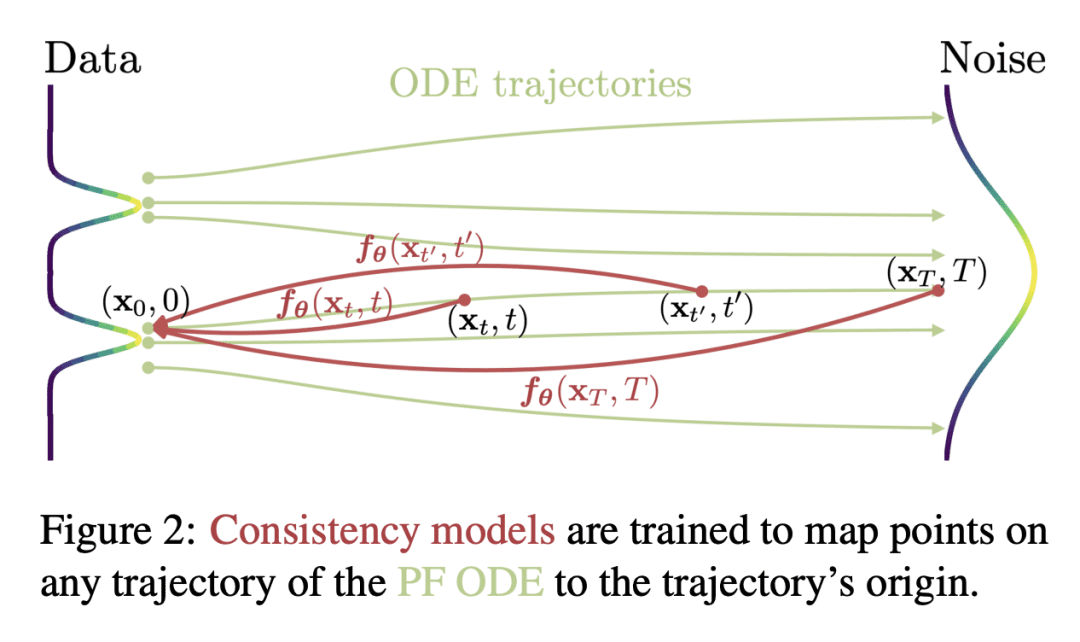
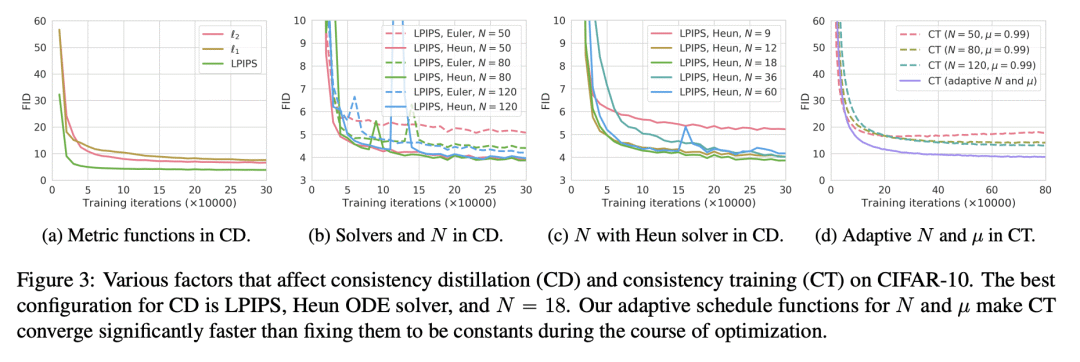
2、[CV] Human Motion Diffusion as a Generative Prior
Y Shafir, G Tevet, R Kapon, A H. Bermano
[Tel-Aviv University]
人体运动扩散作为生成式先验
要点:
-
提出用预训练的基于扩散的模型作为生成的先验,以缓解数据的低可用性,并在运动生成中实现更精细的生成任务; -
所提方法对微调是有效的,在少样本,甚至零样本设置下,能生成长达10分钟的提示间隔的动画,并具有有意义和可控的过渡; -
提出 ComMDM,一个轻量的通信块,在双人生成动作中注入互动,其性能总是优于为该任务设计和训练的SOTA模型; -
文中描述的技术,包括 DiffusionBlending、DoubleTake和ComMDM,可用于人体运动扩散以外的其他领域,在思想和方法的交叉渗透方面具有广阔的前景。
一句话总结:
即使在数据有限的情况下,基于扩散的运动模型也可以作为运动生成和控制的生成性先验,所提出的技术显示了有希望的结果。
In recent months, we witness a leap forward as denoising diffusion models were introduced to Motion Generation. Yet, the main gap in this field remains the low availability of data. Furthermore, the expensive acquisition process of motion biases the already modest data towards short single-person sequences. With such a shortage, more elaborate generative tasks are left behind. In this paper, we show that this gap can be mitigated using a pre-trained diffusion-based model as a generative prior. We demonstrate the prior is effective for fine-tuning, in a few-, and even a zero-shot manner. For the zero-shot setting, we tackle the challenge of long sequence generation. We introduce DoubleTake, an inference-time method with which we demonstrate up to 10-minute long animations of prompted intervals and their meaningful and controlled transition, using the prior that was trained for 10-second generations. For the few-shot setting, we consider two-person generation. Using two fixed priors and as few as a dozen training examples, we learn a slim communication block, ComMDM, to infuse interaction between the two resulting motions. Finally, using fine-tuning, we train the prior to semantically complete motions from a single prescribed joint. Then, we use our DiffusionBlending to blend a few such models into a single one that responds well to the combination of the individual control signals, enabling fine-grained joint- and trajectory-level control and editing. Using an off-the-shelf state-of-the-art (SOTA) motion diffusion model as a prior, we evaluate our approach for the three mentioned cases and show that we consistently outperform SOTA models that were designed and trained for those tasks.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.01418
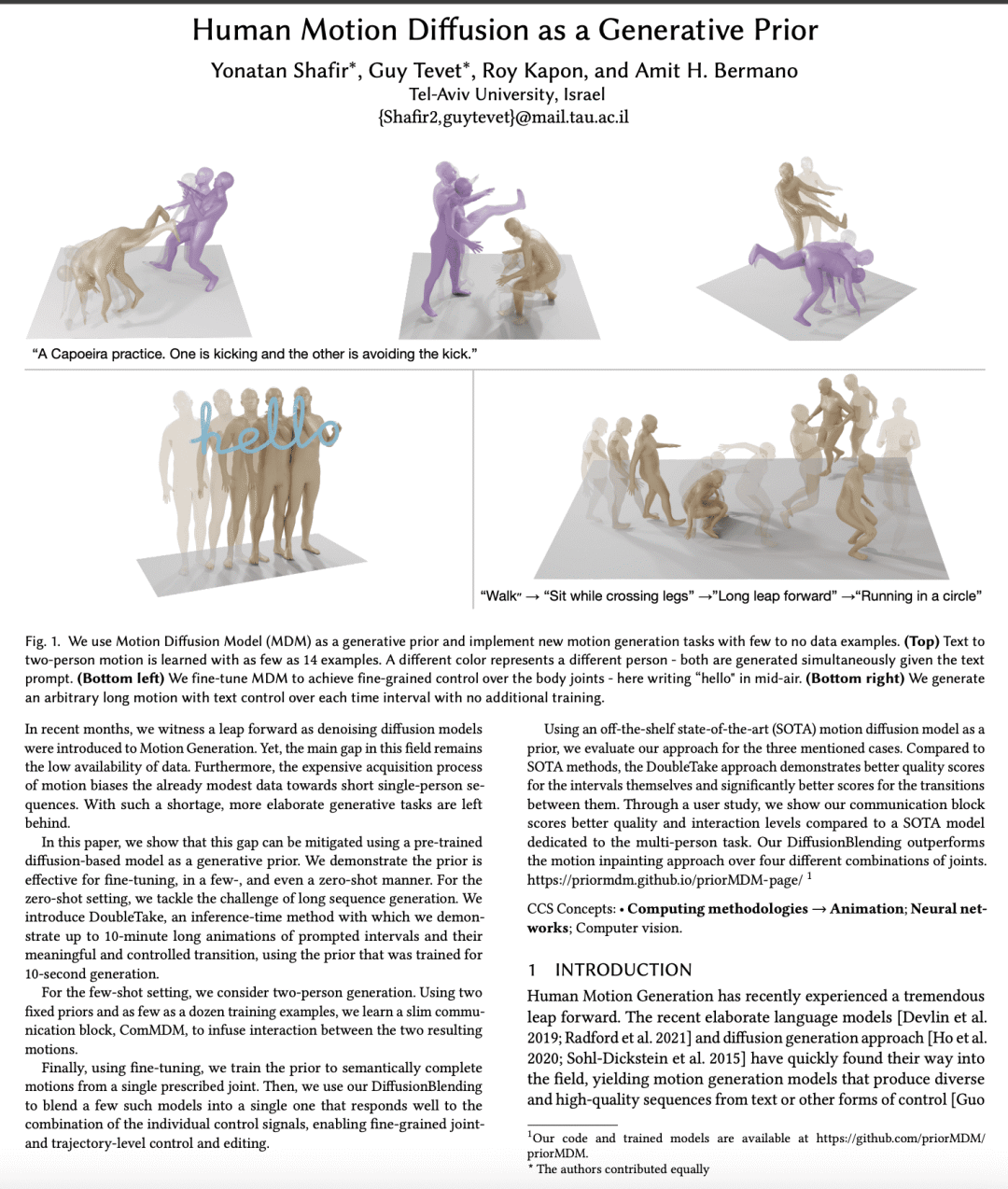
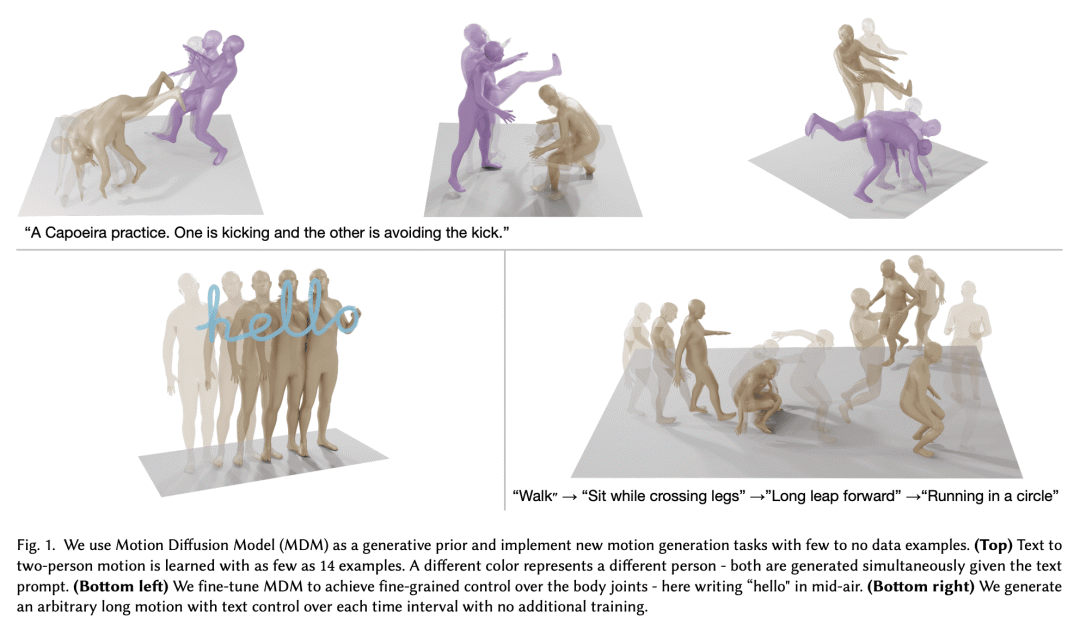

3、[LG] Dropout Reduces Underfitting
Z Liu, Z Xu, J Jin, Z Shen, T Darrell
[Meta AI & UC Berkeley]
用Dropout减轻欠拟合
要点:
-
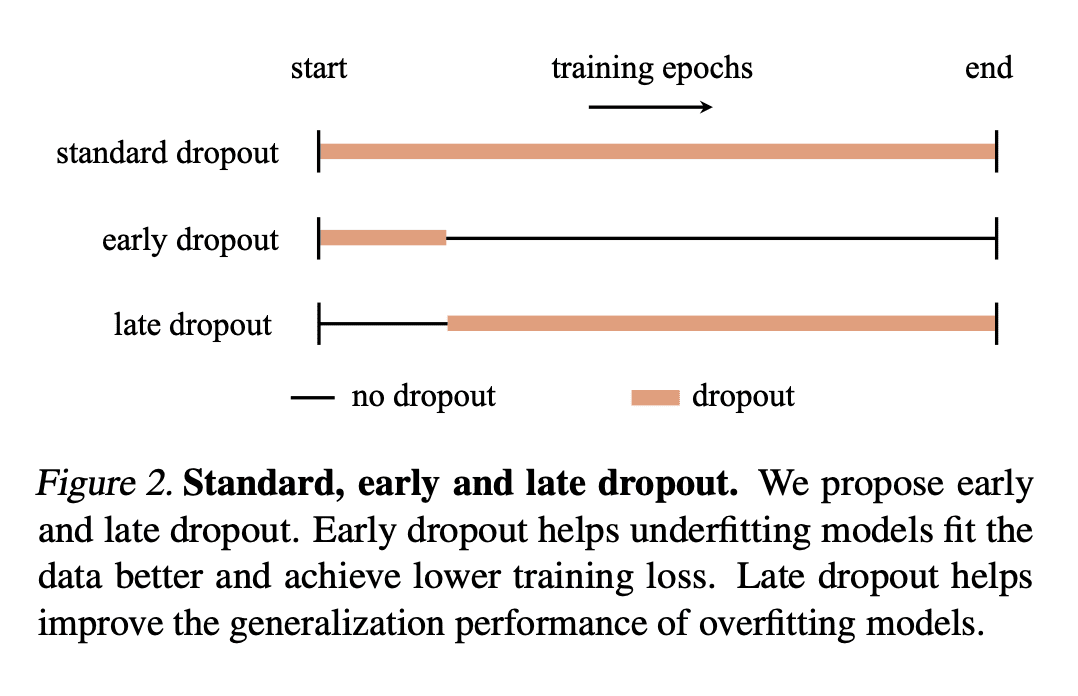
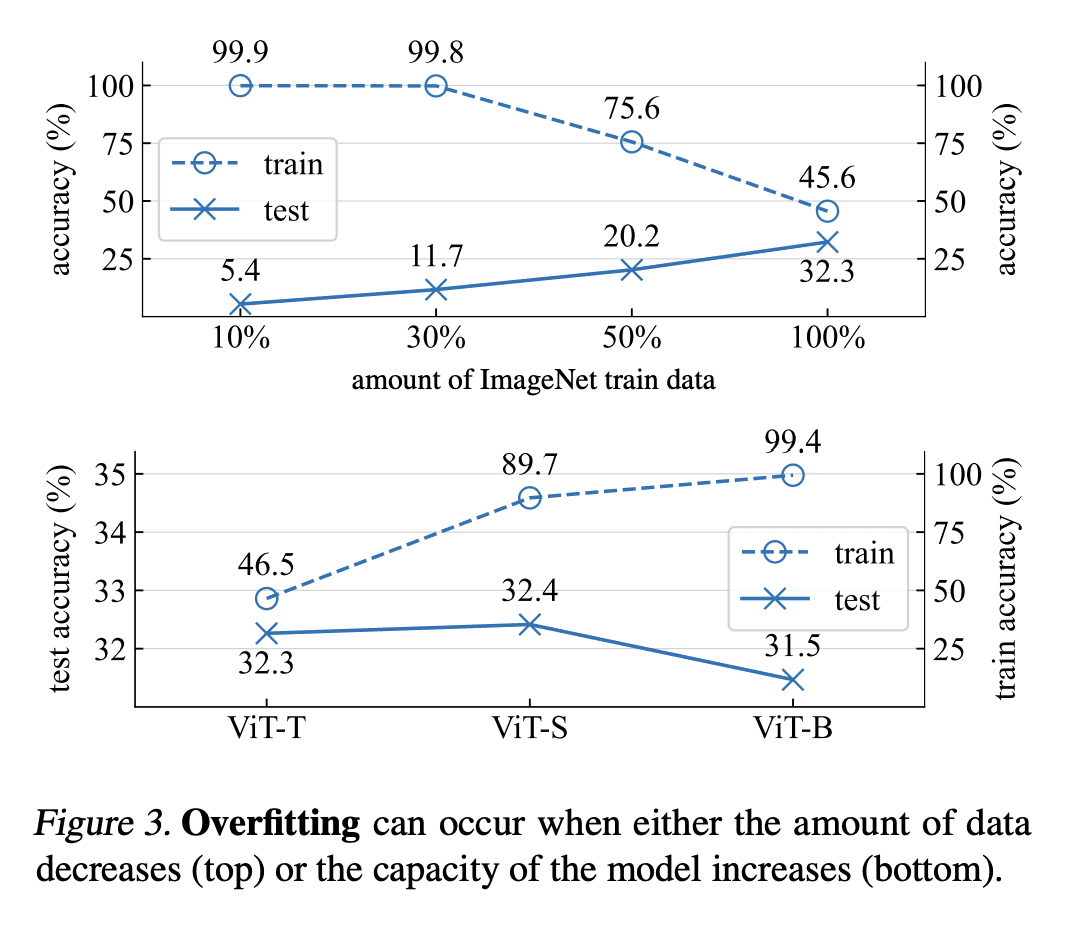
在训练开始时用 Dropout 正则化也可以减轻欠拟合; -
Early dropout 可以帮助欠拟合模型更好地拟合,late dropout 可以提高过拟合模型的泛化程度; -
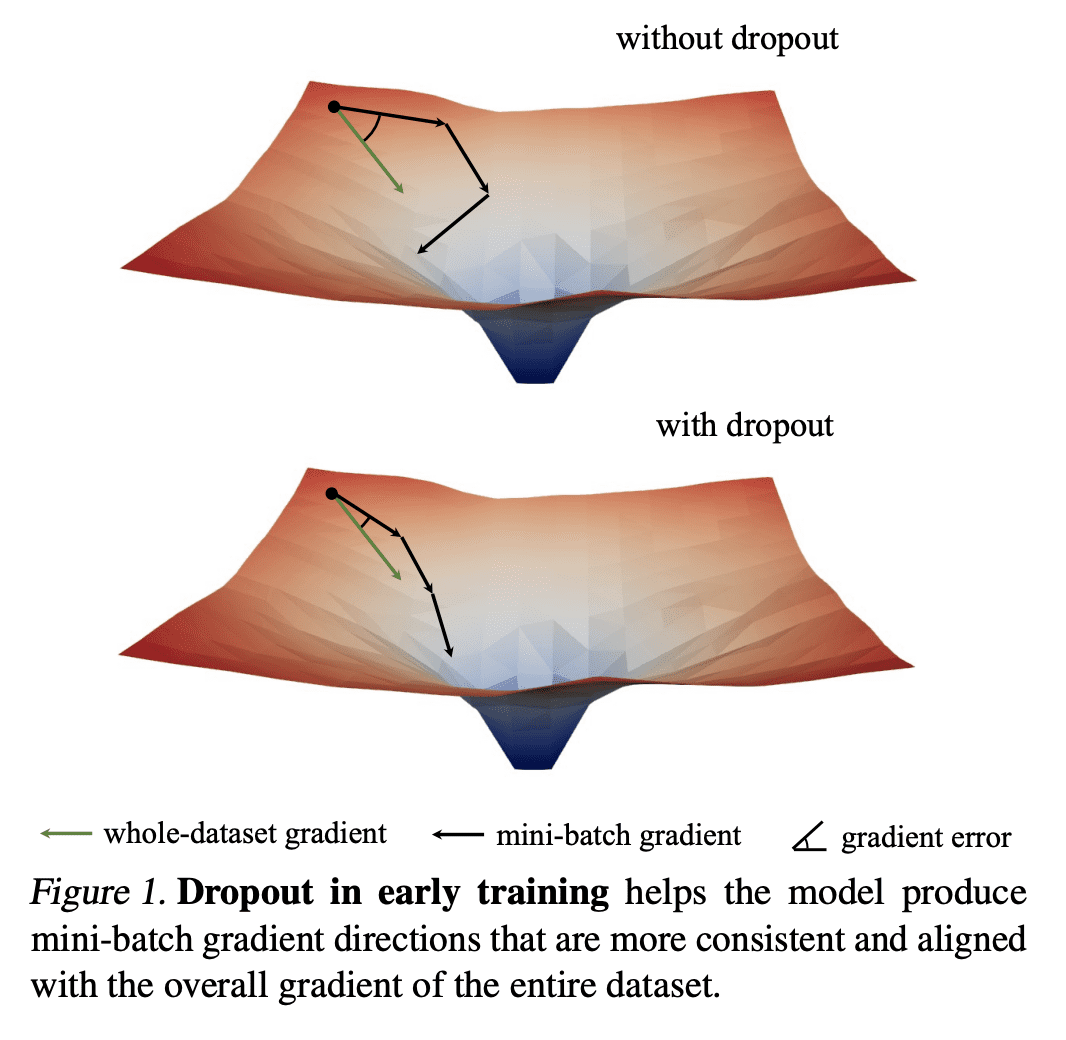
Dropout 减少了小批量梯度的方向性差异,并使小批量梯度与整个数据集的梯度保持一致,抵制了 SGD 的随机性; -
与没采用 dropout 的模型相比,采用了 early dropout 的模型实现了较低的最终训练损失,在各种视觉任务上提高了泛化精度。
一句话总结:
研究表明,dropout 可缓解训练开始时的欠拟合,提高泛化精度,从而提出了面向欠拟合模型的 early dropout 和面向过拟合模型的 late dropout。
Introduced by Hinton et al. in 2012, dropout has stood the test of time as a regularizer for preventing overfitting in neural networks. In this study, we demonstrate that dropout can also mitigate underfitting when used at the start of training. During the early phase, we find dropout reduces the directional variance of gradients across mini-batches and helps align the mini-batch gradients with the entire dataset’s gradient. This helps counteract the stochasticity of SGD and limit the influence of individual batches on model training. Our findings lead us to a solution for improving performance in underfitting models – early dropout: dropout is applied only during the initial phases of training, and turned off afterwards. Models equipped with early dropout achieve lower final training loss compared to their counterparts without dropout. Additionally, we explore a symmetric technique for regularizing overfitting models – late dropout, where dropout is not used in the early iterations and is only activated later in training. Experiments on ImageNet and various vision tasks demonstrate that our methods consistently improve generalization accuracy. Our results encourage more research on understanding regularization in deep learning and our methods can be useful tools for future neural network training, especially in the era of large data. Code is available at this https URL .
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.01500

4、[CL] Google USM: Scaling Automatic Speech Recognition Beyond 100 Languages
Y Zhang, W Han, J Qin, Y Wang, A Bapna…
[Google]
Google USM: 将自动语音识别扩展到超过100种语言
要点:
-
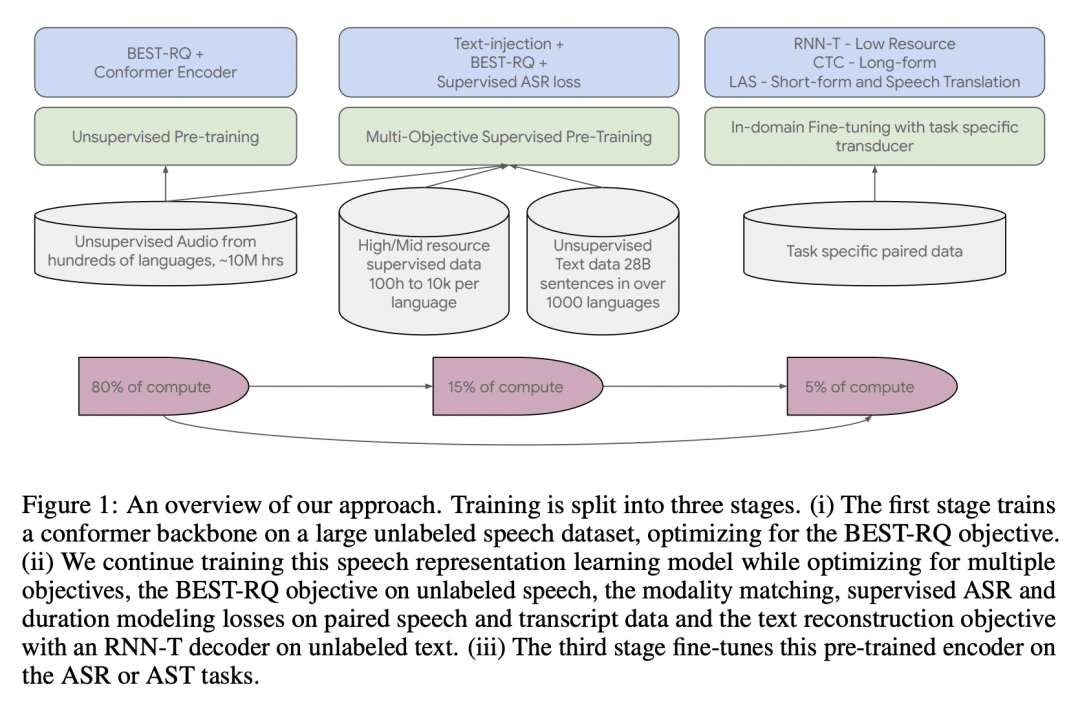
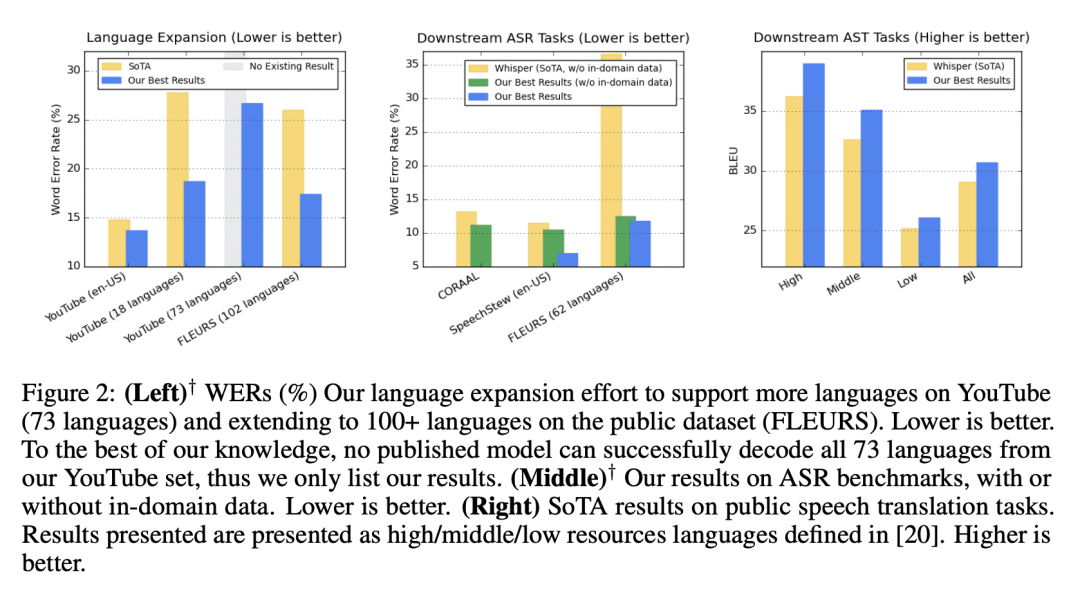
USM是一种单一的模型,通过在一个大型未标记多语言数据集上进行预训练,并在一个较小的已标记数据集上进行微调,在100多种语言中进行自动与语音识别(ASR); -
与母语人士合作,确定数百种长尾语言的无监督数据,可提高低资源语言的识别性能; -
域内数据对于优化特定域的ASR性能是最好的; -
下游任务的最佳转换器取决于任务。
一句话总结:
通用语音模型(USM)是一种大规模的单独模型,对100多种语言中实现自动语音识别(ASR),通过在大型未标记多语言数据集上进行预训练和在较小的已标记数据集上进行微调,达到最先进的性能。
We introduce the Universal Speech Model (USM), a single large model that performs automatic speech recognition (ASR) across 100+ languages. This is achieved by pre-training the encoder of the model on a large unlabeled multilingual dataset of 12 million (M) hours spanning over 300 languages, and fine-tuning on a smaller labeled dataset. We use multilingual pre-training with random-projection quantization and speech-text modality matching to achieve state-of-the-art performance on downstream multilingual ASR and speech-to-text translation tasks. We also demonstrate that despite using a labeled training set 1/7-th the size of that used for the Whisper model, our model exhibits comparable or better performance on both in-domain and out-of-domain speech recognition tasks across many languages.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.01037


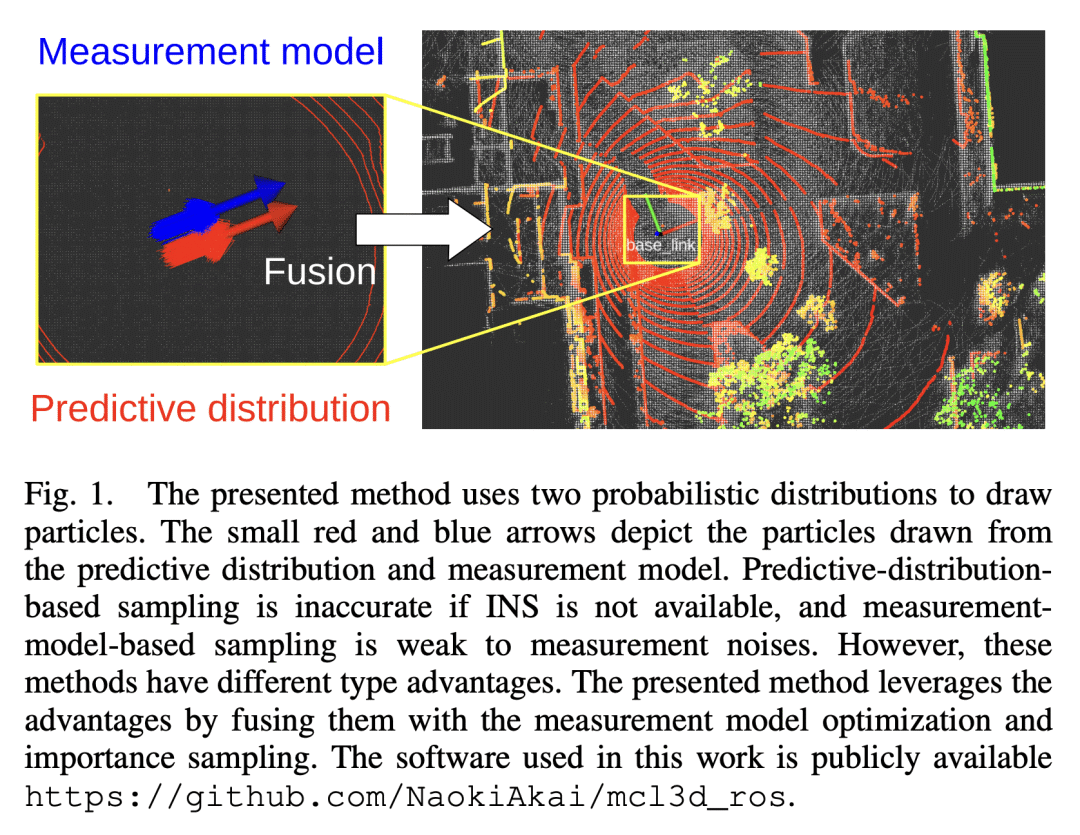
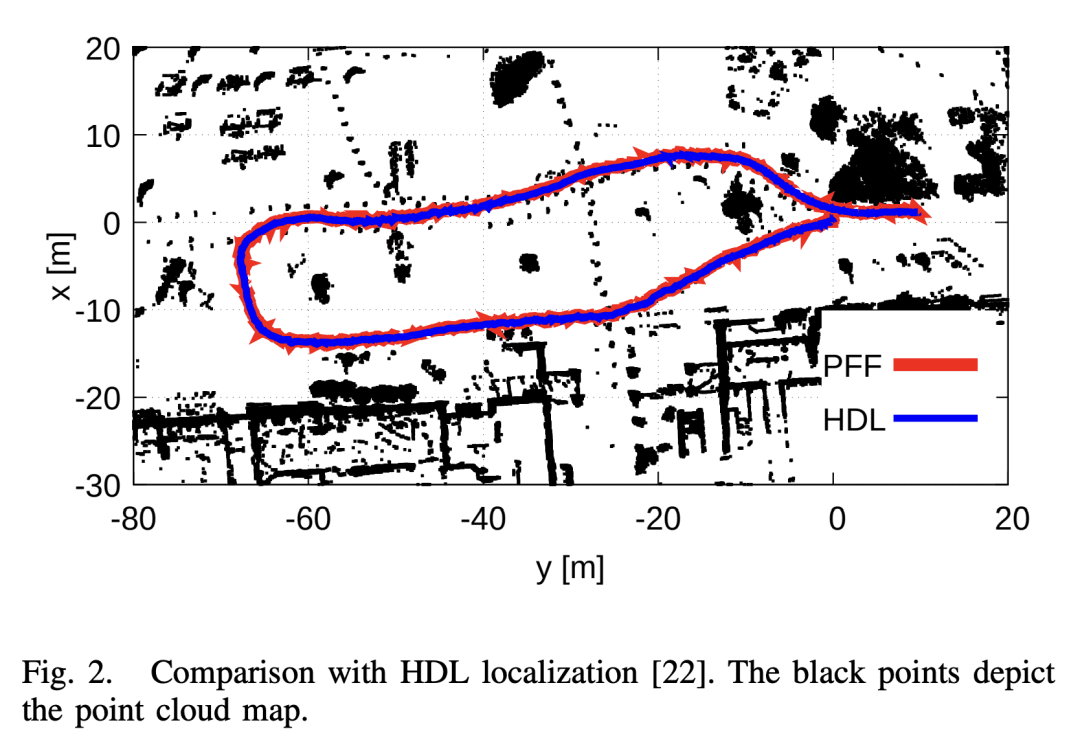
5、[RO] Efficient Solution to 3D-LiDAR-based Monte Carlo Localization with Fusion of Measurement Model Optimization via Importance Sampling
N Akai
[Nagoya University]
基于重要性采样融合测量模型优化的3D-LiDAR蒙特卡罗定位方法
要点:
-
如果粒子在真实值附近被精确采样,MCL 就能鲁棒地工作,所提出的融合方法结合了 MCL 和扫描匹配的优点,同时减轻了它们的缺点; -
通过数值微分的测量模型优化和正态分布近似的使用,可以在没有 INS 和任何加速技术(如GPU)的情况下围绕真实值进行有效的粒子采样; -
所提出的方法可以在单个 CPU 线程上准确地进行定位,除了一些近似值之外,没有任何启发式技术; -
第一次在没有 INS 和加速技术的情况下实现基于 3D-LiDAR 的 MCL 的研究,所提出的方法服从于严格的概率论方式。
一句话总结:
提出一种有效的解决方案,通过重要性采样对测量模型的优化进行融合,实现基于 3D-LiDAR 的蒙特卡洛定位。
This paper presents an efficient solution to 3D-LiDAR-based Monte Carlo localization (MCL). MCL robustly works if particles are exactly sampled around the ground truth. An inertial navigation system (INS) can be used for accurate sampling, but many particles are still needed to be used for solving the 3D localization problem even if INS is available. In particular, huge number of particles are necessary if INS is not available and it makes infeasible to perform 3D MCL in terms of the computational cost. Scan matching (SM), that is optimization-based localization, efficiently works even though INS is not available because SM can ignore movement constraints of a robot and/or device in its optimization process. However, SM sometimes determines an infeasible estimate against movement. We consider that MCL and SM have complemental advantages and disadvantages and propose a fusion method of MCL and SM. Because SM is considered as optimization of a measurement model in terms of the probabilistic modeling, we perform measurement model optimization as SM. The optimization result is then used to approximate the measurement model distribution and the approximated distribution is used to sample particles. The sampled particles are fused with MCL via importance sampling. As a result, the advantages of MCL and SM can be simultaneously utilized while mitigating their disadvantages. Experiments are conducted on the KITTI dataset and other two open datasets. Results show that the presented method can be run on a single CPU thread and accurately perform localization even if INS is not available.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.00216


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
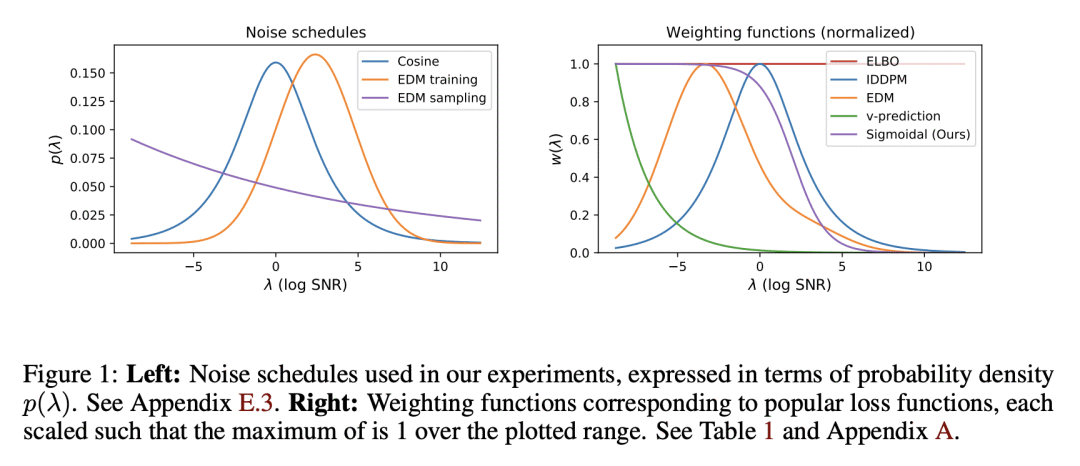
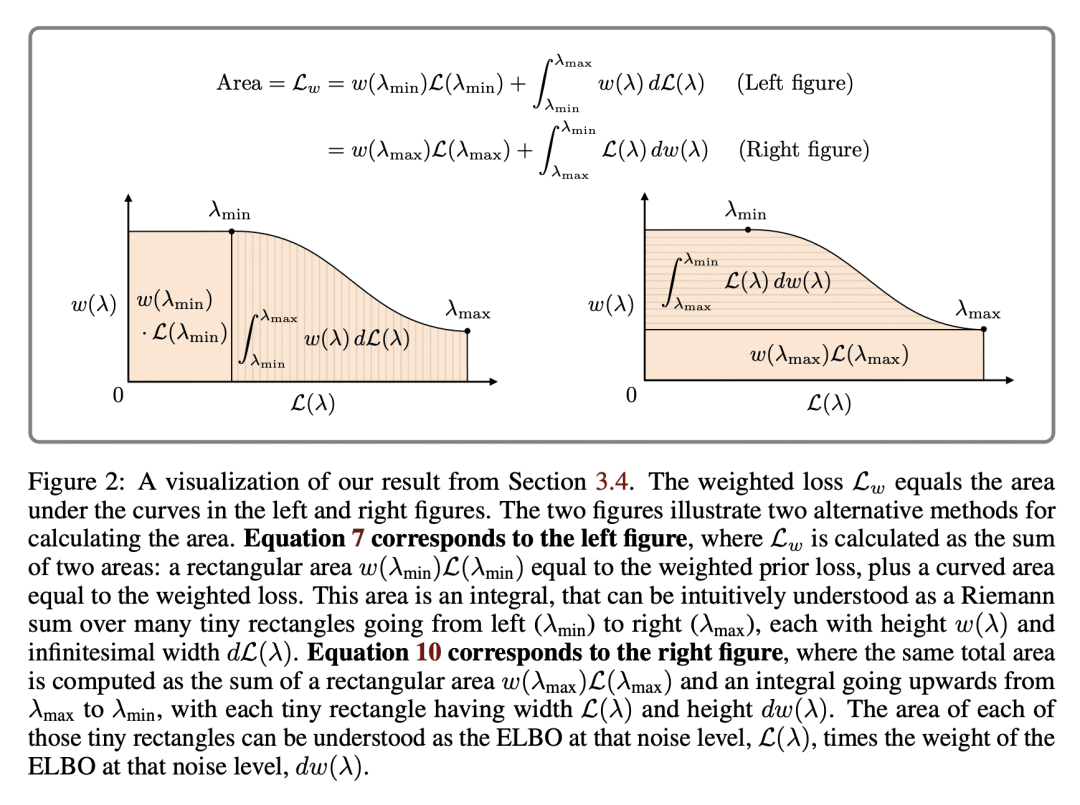
[LG] Understanding the Diffusion Objective as a Weighted Integral of ELBOs
D P. Kingma, R Gao
[Google]
将扩散目标理解为ELBO的加权积分
要点:
-
加权扩散损失推广了文献中的扩散模型,可解释为 ELBO 目标下的加权积分,每个噪声水平有一个ELBO; -
如果加权函数是单调的,那么加权损失就对应于噪声扰动数据的 ELBO 最大化,也就是最大似然目标; -
新发现的单调加权和有数据增强的 ELBO 之间的等价关系,使得扩散模型与其他基于似然的模型可以直接比较; -
单调加权的表现与已发表的最佳结果具有竞争性,为该领域的未来研究提供了一个有希望的途径。
一句话总结:
加权扩散损失相当于 ELBO 目标的加权积分,如果加权函数是单调的,就是一个基于似然的目标。
Diffusion models in the literature are optimized with various objectives that are special cases of a weighted loss, where the weighting function specifies the weight per noise level. Uniform weighting corresponds to maximizing the ELBO, a principled approximation of maximum likelihood. In current practice diffusion models are optimized with non-uniform weighting due to better results in terms of sample quality. In this work we expose a direct relationship between the weighted loss (with any weighting) and the ELBO objective.We show that the weighted loss can be written as a weighted integral of ELBOs, with one ELBO per noise level. If the weighting function is monotonic, then the weighted loss is a likelihood-based objective: it maximizes the ELBO under simple data augmentation, namely Gaussian noise perturbation. Our main contribution is a deeper theoretical understanding of the diffusion objective, but we also performed some experiments comparing monotonic with non-monotonic weightings, finding that monotonic weighting performs competitively with the best published results.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.00848

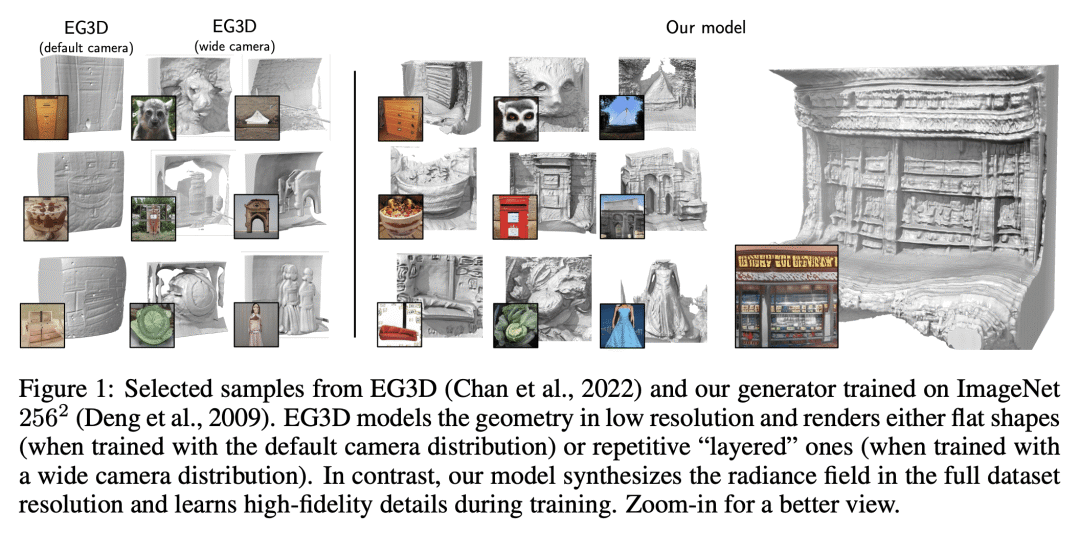
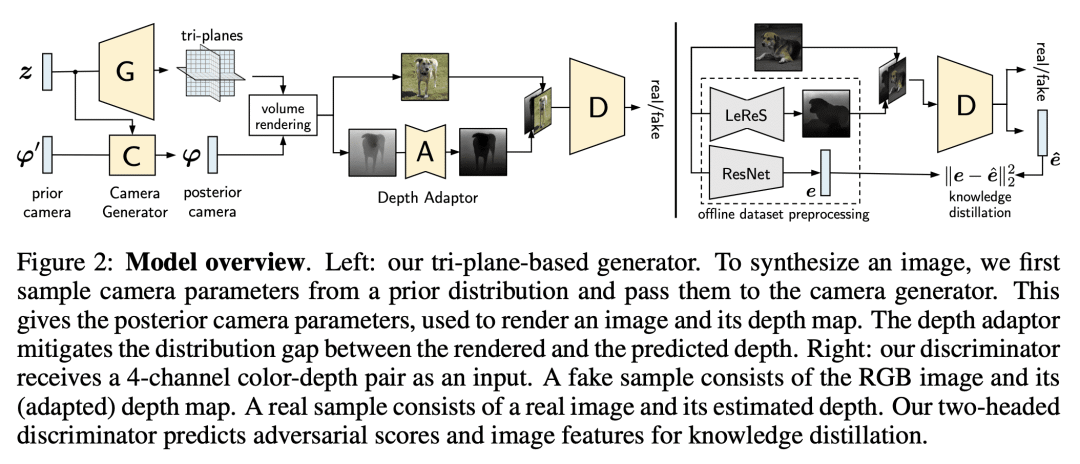
[CV] 3D generation on ImageNet
I Skorokhodov, A Siarohin, Y Xu, J Ren, H Lee, P Wonka, S Tulyakov
[Snap Inc & KAUST & CUHK]
ImageNet上的3D生成
要点:
-
基于通用先验的3D生成器(3DGP)可用于像 ImageNet 这样的真实场景多类别数据集; -
该模型包含了一个现成的深度估计器、一个具有新的正则化方案的灵活的相机模型,以及一个基于蒸馏技术的判别器,用于稳定训练和快速收敛; -
3DGP 在四个数据集的纹理和几何质量方面都优于最近的先进技术; -
仍有局限性,如粘连背景、与 2D 生成器相比视觉质量较差,以及没有可靠的生成几何体的定量测量。
一句话总结:
提出一种用于真实场景多类别数据集(如ImageNet)的基于通用先验的3D生成器(3DGP),可提高纹理和几何质量,并以非精确单目深度和潜在特征表示指导几何。
Existing 3D-from-2D generators are typically designed for well-curated single-category datasets, where all the objects have (approximately) the same scale, 3D location, and orientation, and the camera always points to the center of the scene. This makes them inapplicable to diverse, in-the-wild datasets of non-alignable scenes rendered from arbitrary camera poses. In this work, we develop a 3D generator with Generic Priors (3DGP): a 3D synthesis framework with more general assumptions about the training data, and show that it scales to very challenging datasets, like ImageNet. Our model is based on three new ideas. First, we incorporate an inaccurate off-the-shelf depth estimator into 3D GAN training via a special depth adaptation module to handle the imprecision. Then, we create a flexible camera model and a regularization strategy for it to learn its distribution parameters during training. Finally, we extend the recent ideas of transferring knowledge from pre-trained classifiers into GANs for patch-wise trained models by employing a simple distillation-based technique on top of the discriminator. It achieves more stable training than the existing methods and speeds up the convergence by at least 40%. We explore our model on four datasets: SDIP Dogs 256×256, SDIP Elephants 256×256, LSUN Horses 256×256, and ImageNet 256×256, and demonstrate that 3DGP outperforms the recent state-of-the-art in terms of both texture and geometry quality. Code and visualizations: this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.01416


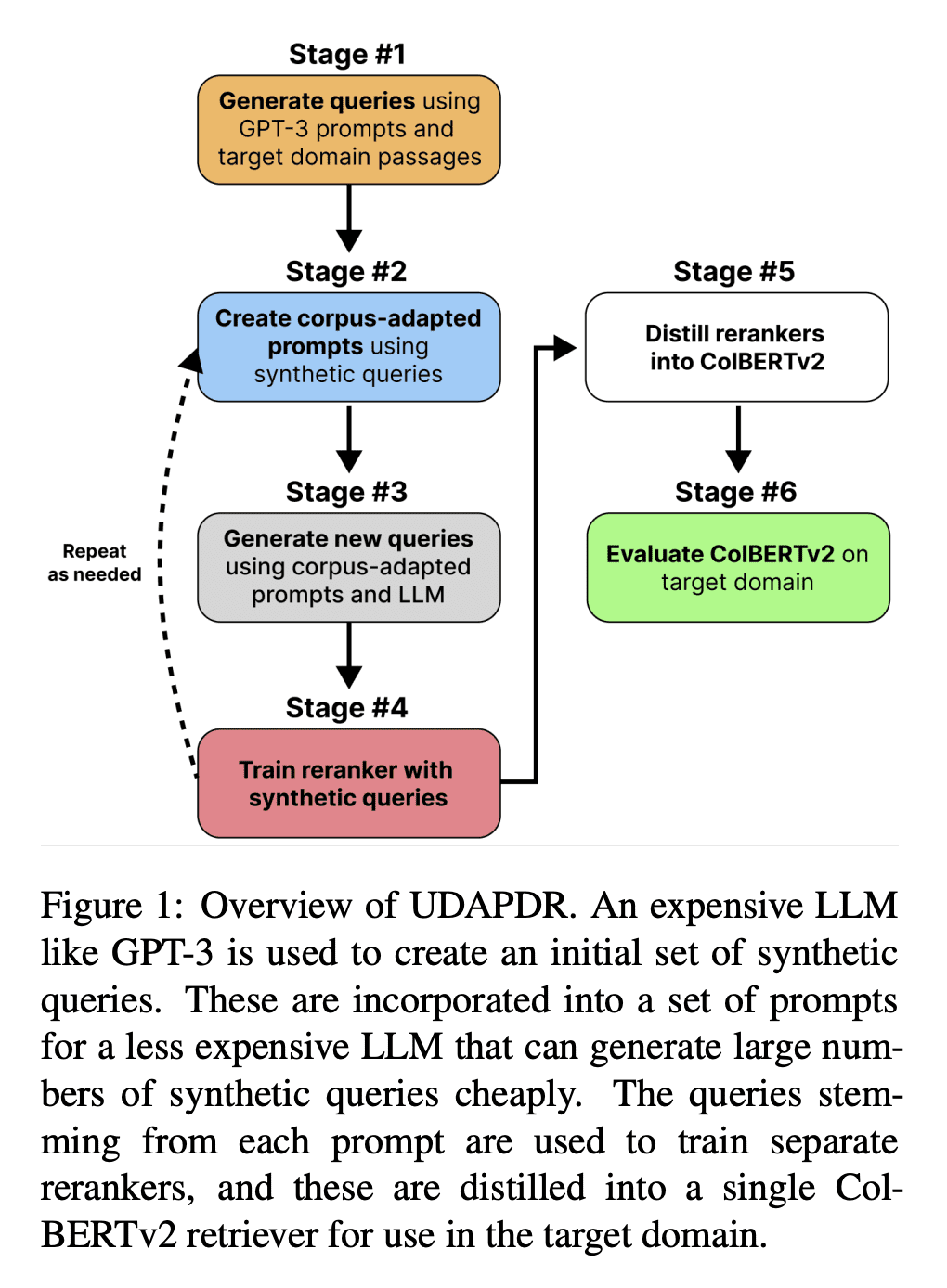
[CL] UDAPDR: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation via LLM Prompting and Distillation of Rerankers
J Saad-Falcon, O Khattab, K Santhanam, R Florian, M Franz, S Roukos, A Sil, M A Sultan, C Potts
[Stanford University]
UDAPDR: 基于 LLM 的无监督域自适应算法及重排序器蒸馏
要点:
-
UDAPDR 用大型语言模型产生的合成查询来微调多段落检索器,并将其蒸馏成一个高效的检索器,供目标域使用; -
只需要几千合成查询就能有效,并与各种LLM兼容; -
UDAPDR 提高了各种数据集在零样本下的检索精度,包括 LoTTE、NQ 和 SQuAD; -
在降低查询延迟的同时,保留了排序器的精度收益,使其成为信息检索任务的一个有竞争力的选择。
一句话总结:
UDAPDR 是一种用于神经信息检索(IR)的无监督域适应方法,用大型语言模型生成的合成查询,以提高零样本检索精度,并减少查询延迟。
Many information retrieval tasks require large labeled datasets for fine-tuning. However, such datasets are often unavailable, and their utility for real-world applications can diminish quickly due to domain shifts. To address this challenge, we develop and motivate a method for using large language models (LLMs) to generate large numbers of synthetic queries cheaply. The method begins by generating a small number of synthetic queries using an expensive LLM. After that, a much less expensive one is used to create large numbers of synthetic queries, which are used to fine-tune a family of reranker models. These rerankers are then distilled into a single efficient retriever for use in the target domain. We show that this technique boosts zero-shot accuracy in long-tail domains, even where only 2K synthetic queries are used for fine-tuning, and that it achieves substantially lower latency than standard reranking methods. We make our end-to-end approach, including our synthetic datasets and replication code, publicly available on Github.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.00807
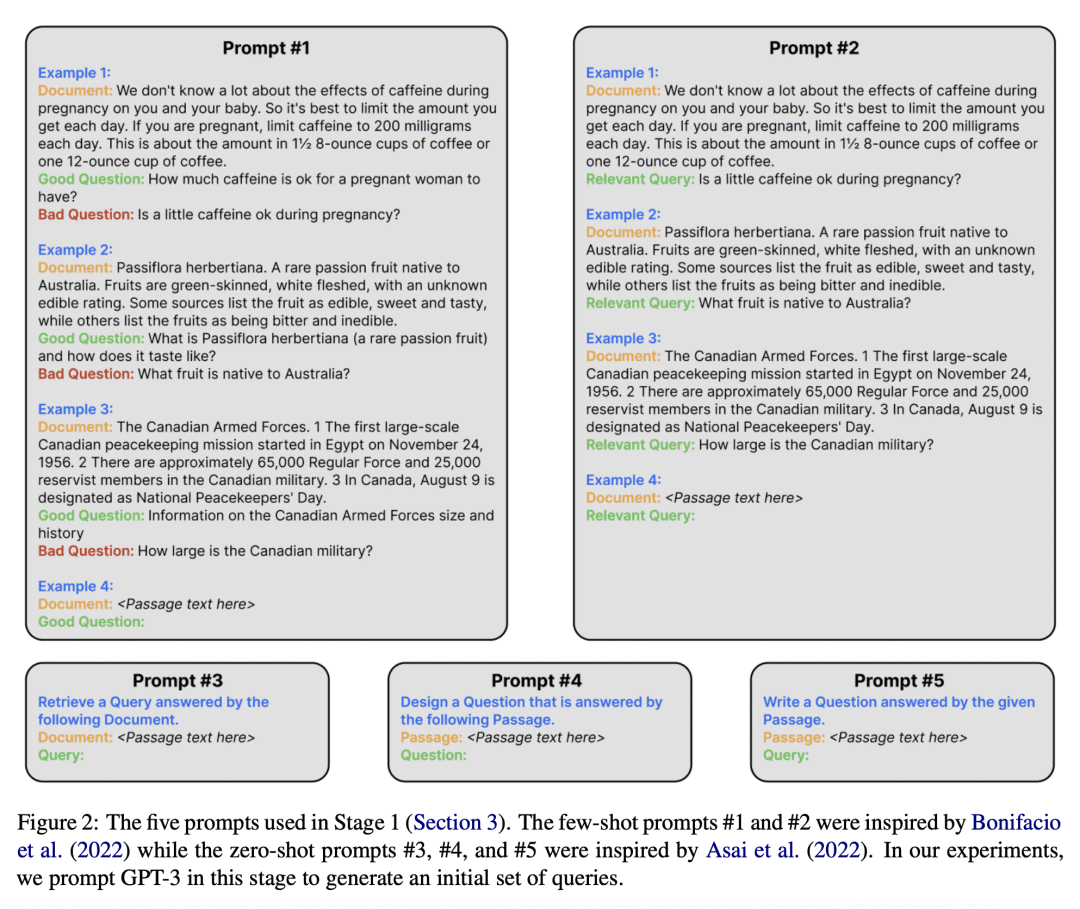

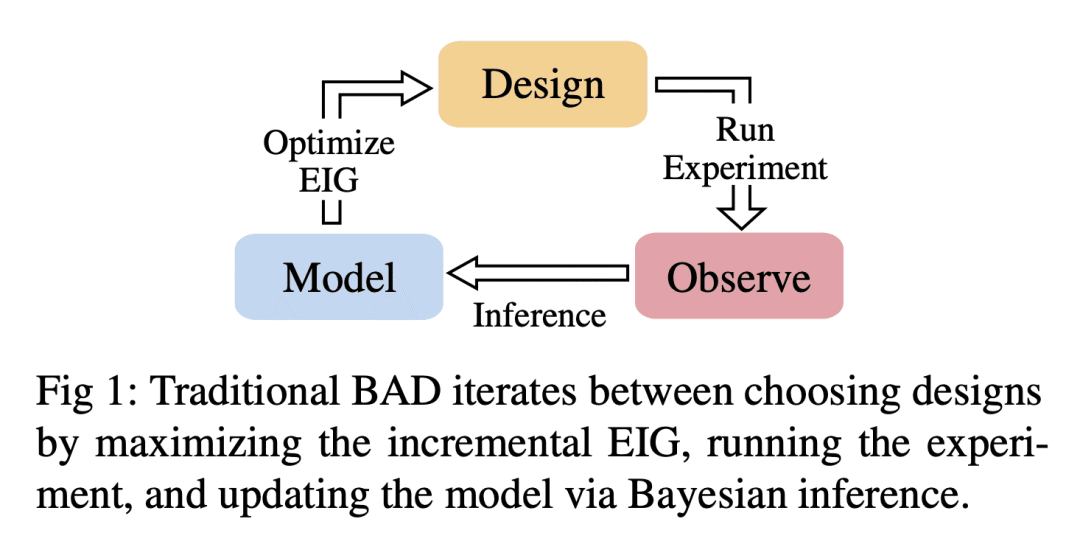
[LG] Modern Bayesian Experimental Design
T Rainforth, A Foster, D R Ivanova, F B Smith
[University of Oxford & Microsoft Research AI4Science]
现代贝叶斯实验设计
要点:
-
贝叶斯实验设计(BED)是一个优化实验设计的强大框架; -
BED 一直受到计算挑战的阻碍,但最近的进展已经解决了这些挑战; -
这些进展为有效利用BED开辟了新的机会; -
该领域的未来发展需要进一步改善BED的实际使用。
一句话总结:
贝叶斯实验设计(BED)为优化实验设计提供了一个强大的框架,但其计算方面的挑战阻碍了其实际应用。最近的进展解决了这些挑战,为有效利用BED开辟了新的机会。
Bayesian experimental design (BED) provides a powerful and general framework for optimizing the design of experiments. However, its deployment often poses substantial computational challenges that can undermine its practical use. In this review, we outline how recent advances have transformed our ability to overcome these challenges and thus utilize BED effectively, before discussing some key areas for future development in the field.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.14545





 ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง
ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง


