✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab完整代码及仿真定制内容点击👇
🔥 内容介绍
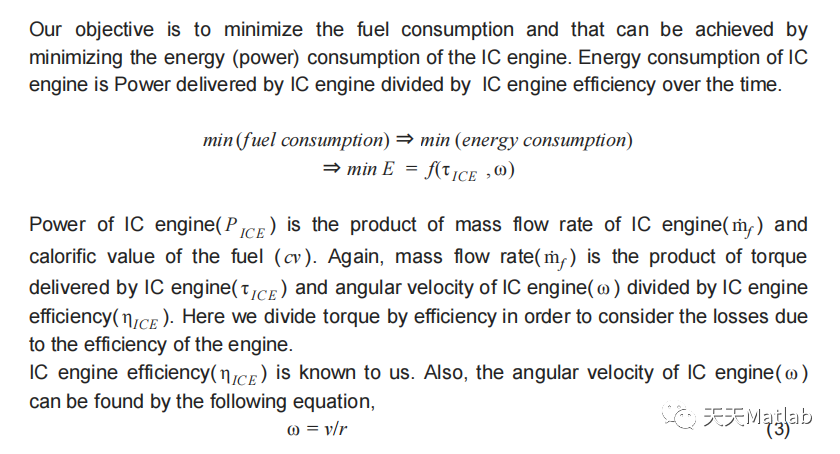
There are about 1.2 billion active vehicle on the road whose number is set to increase to about 2 billion by 2035. To meet stringent emission norms, environmental and energy concerns, vehicles have to reduce their CO2 emissions. Hybrid Electric Vehicles contributes to fuel savings and emission reduction aims, which ultimately reduces energy consumption. The aim of this project is to develop efficient powertrain control for hybrid vehicles to reduce energy consumption though heavy traffic. The project involves optimization of two subsystems, namely the IC engine and electric motor. The approach is to reduce fuel consumption by switching between electric drive and internal combustion engine during traffic scenario. The change in acceleration helps to find the velocity which in turn determines the position of the following vehicle which is also dependent on the vehicle ahead of the following vehicle. This calculation considers the efficiency of electric drive and internal combustion engine as well at different velocities.
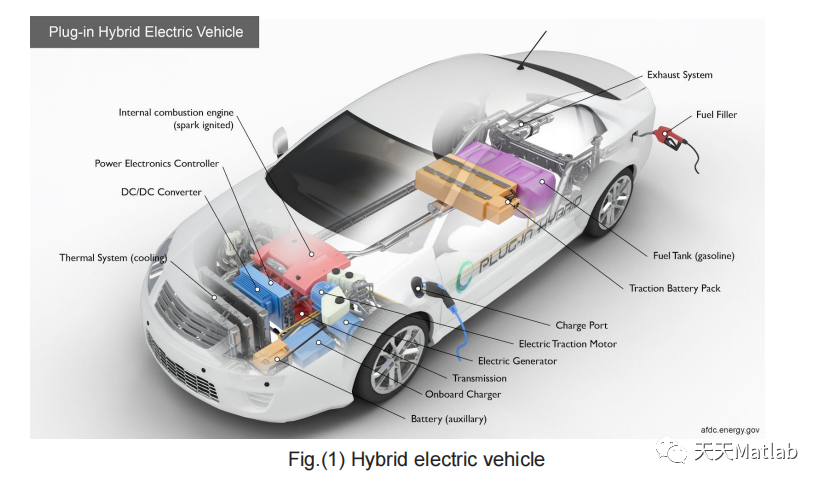
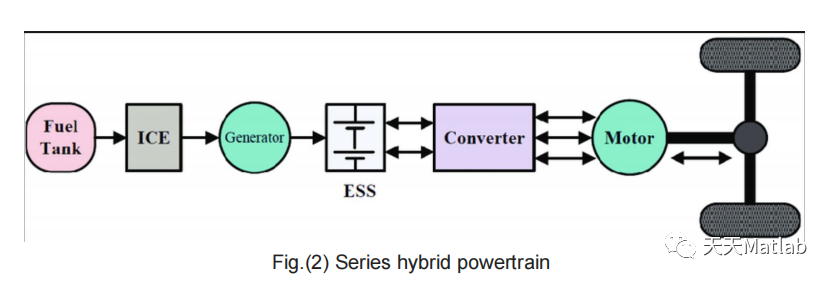
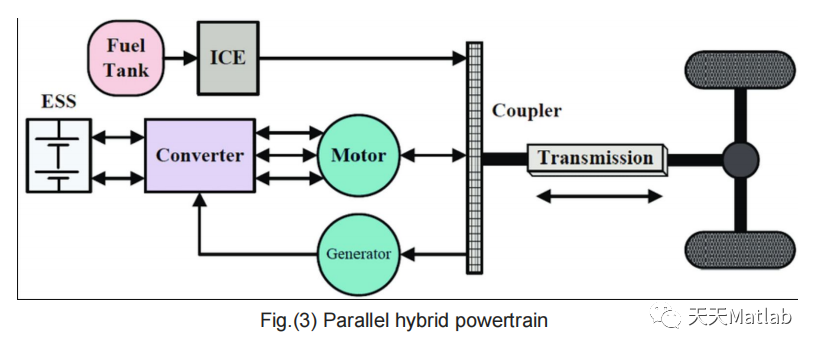
We have considered parallel configuration of the drivetrain in the hybrid electric vehicle. In this configuration, both electric motor and IC engine are mechanically coupled to drive the wheels



📣 部分代码
clear;clc;close all%% Data% load('enginedata.mat');% % Data from (TOYOTA PRIUS): https://media.toyota.co.uk/wp-content/files_mf/1329489972120216MTOYOTAPRIUSTECHNICALSPECIFICATIONS.pdfVehicle_length = 4.48; % meterVehicle_mass = 1805; % kgGear_ratio = 2.683; % Forward Gear RatioDifferential_drive_ratio = 3.267; % Differential Gear RatioWheel_radius = 0.3175; % m => 12.5 inch tire radius (195/65r15 tire);Max_power = 73000; % watt% Assumptions:time = 1:100;random_values = 0.2*rand(length(time),1) + 0.6; % limiting range of random variablesRoad_length = 500; % meterVehicle_safe_distance = 3.0 ; % meterVehicle_max_velocity = 29.057; % m/s => 65 mphEngine_efficiency = 0.80;%% PDE model for Vehicle DensityRoad_density_max = Road_length / (Vehicle_length + Vehicle_safe_distance);Road_density_random = random_values * Road_density_max;velocity_vehicle = Vehicle_max_velocity * (1 - (Road_density_random / Road_density_max));%% Vehicle ModelingNet_Gear_ratio = Gear_ratio * Differential_drive_ratio;Wheel_rpm = (velocity_vehicle*60)./(2*pi*Wheel_radius);Engine_rpm = Wheel_rpm * Net_Gear_ratio;Engine_torque = Max_power ./ Wheel_rpm;Wheel_torque = Engine_torque .* Net_Gear_ratio * 0.5;%% Optimization% Polynomial derived from curve fitting app using given engine data% X axis: eng_consum_spd% Y axis: eng_consum_trq% Z axis: eng_fuel_map_gpkWh% Polynomial order: (5,5)p00 = 976.7;p10 = -12.14;p01 = -3.574;p20 = 0.1646;p11 = -0.02367;p02 = 0.01739;p30 = -0.0009203;p21 = 0.000117;p12 = 4.708e-06;p03 = -2.651e-05;p40 = 2.344e-06;p31 = -2.78e-07;p22 = -4.89e-09;p13 = 6.132e-10;p04 = 1.604e-08;p50 = -2.234e-09;p41 = 2.812e-10;p32 = -4.378e-11;p23 = 2.251e-11;p14 = -6.75e-12;p05 = -1.881e-12;% x0 = [Engine_rpm(1) Engine_torque(1)];x0 =[100 100];bsfc = @(x) (1.5*(p00 + p10*x(1) + p01*x(2) + p20*x(1)^2 + p11*x(1)*x(2) + p02*x(2)^2 + p30*x(1)^3 + p21*x(1)^2*x(2) ... + p12*x(1)*x(2)^2 + p03*x(2)^3 + p40*x(1)^4 + p31*x(1)^3*x(2) + p22*x(1)^2*x(2)^2 ... + p13*x(1)*x(2)^3 + p04*x(2)^4 + p50*x(1)^5 + p41*x(1)^4*x(2) + p32*x(1)^3*x(2)^2 ... + p23*x(1)^2*x(2)^3 + p14*x(1)*x(2)^4 + p05*x(2)^5));dl_0 = 0;df_0 = 0;dt = 1;for i = time dl(i) = velocity_vehicle(i)*dt + dl_0; % Distance(position) of Leading Vehicle dl_0 = dl(i); endfor j = timeLB = [min(Engine_rpm) min(Engine_torque)];UB = 8*[Engine_rpm(j) Engine_torque(j)];A = [-dl(j) df_0; dl(j) -df_0];B = [-3; 5]; %[Safe_Distance; max_allowed_distance_for_following_purpose]x = fmincon(bsfc,x0,A,B,[],[],LB,UB);x1(j) = x(1);x2(j) = x(2);mf(j) = abs(bsfc(x))/(3.6e9*Engine_efficiency)*0.8;vel(j) = ((x2(j)./Net_Gear_ratio)*(2*pi/60))*(Wheel_radius);df(j) = vel(j)*dt + df_0; % Distance(position) of following vehicledf_0 = df(j);x0=x;endfigure(1);hold on;% subplot(2,1,1);plot(time,mf)xlabel("Time (sec)");ylabel("Mass flow rate (Kg/s)");hold off;figure(2)hold on;% subplot(2,1,2);plot(time,vel)xlabel("Time (sec)");ylabel("Our Vehicle Optimized Velocity (m/s)");hold off;cyc_mph(:,1) = time;cyc_mph(:,2) = vel;cd ECMS;save('cyc_mph.mat','cyc_mph')% ans = fMPG(4);
⛳️ 运行结果
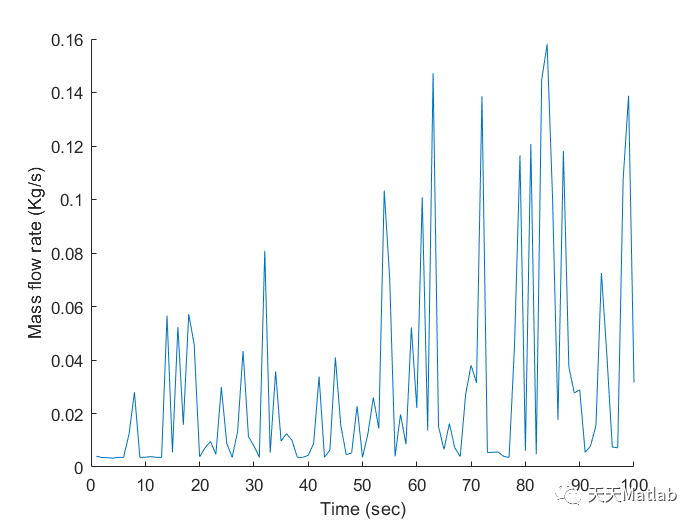
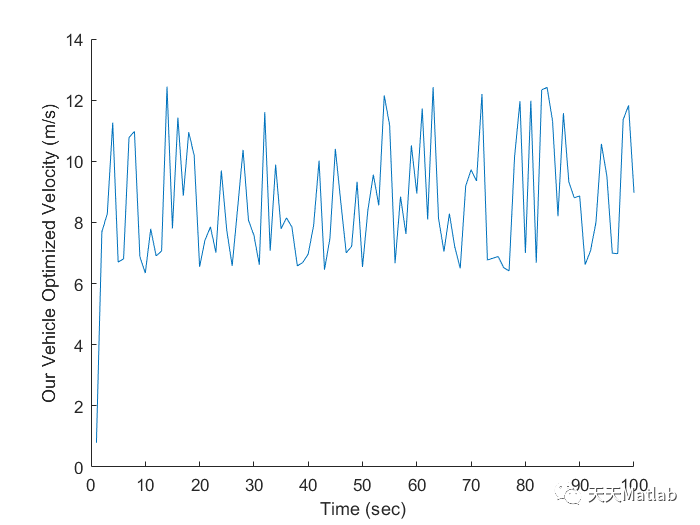
🔗 参考文献
🎈 部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
🎁 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
👇 私信完整代码和数据获取及论文数模仿真定制
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化
2 机器学习和深度学习方面
卷积神经网络(CNN)、LSTM、支持向量机(SVM)、最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)、极限学习机(ELM)、核极限学习机(KELM)、BP、RBF、宽度学习、DBN、RF、RBF、DELM、XGBOOST、TCN实现风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
2.图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
3 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、车辆协同无人机路径规划、天线线性阵列分布优化、车间布局优化
4 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配、无人机安全通信轨迹在线优化
5 无线传感器定位及布局方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化
6 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化
7 电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置
8 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长
9 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合



 ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง
ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง


