1、[CV] Single Motion Diffusion
2、[CL] MarioGPT: Open-Ended Text2Level Generation through Large Language Models
3、[AS] AV-data2vec: Self-supervised Learning of Audio-Visual Speech Representations with Contextualized Target Representations
4、[LG] Symbolic Physics Learner: Discovering governing equations via Monte Carlo tree search
5、[CL] Is ChatGPT a General-Purpose Natural Language Processing Task Solver?
[CL] Gradient-Based Automated Iterative Recovery for Parameter-Efficient Tuning
[LG] Cross-Modal Fine-Tuning: Align then Refine
[CL] Task-Specific Skill Localization in Fine-tuned Language Models
[CV] Contour-based Interactive Segmentation
摘要:单运动扩散模型、基于大型语言模型的开放式文本到关卡生成、基于上下文目标表示的视觉-听觉语音表示自监督学习、符号物理学习器、ChatGPT是通用NLP任务处理器吗、面向参数高效调优的基于梯度的自动迭代恢复、跨模态微调、微调语言模型特定任务技能定位、基于轮廓的交互式分割
1、[CV] Single Motion Diffusion
S Raab, I Leibovitch, G Tevet, M Arar, A H. Bermano, D Cohen-Or
[Tel-Aviv University]
单运动扩散模型
要点:
-
单运动扩散模型(SinMDM)是一个旨在学习单个运动序列的内部模式并合成忠实于它的任意长度运动的模型,在可用数据实例有限的领域特别有用; -
使用扩散模型和专门为从单一输入运动中学习的任务而设计的去噪网络,其基于 Transformer 的架构可避免过拟合并鼓励运动多样性; -
SinMDM 可用于各种情况,包括空间和时间上的夹杂、运动扩展、风格迁移和人群动画,并且在质量和时空效率上都优于现有方法。 -
该模型的先天局限性,是所有学习单个实例模型所共有的,即合成分布外的能力有限,而基于扩散的方法的主要局限是推理时间相对较长。
一句话总结:
单运动扩散模型(SinMDM)利用扩散模型和去噪网络,以有限数据合成生物的逼真动画,性能优于现有方法,并能完成各种运动操作任务。
Synthesizing realistic animations of humans, animals, and even imaginary creatures, has long been a goal for artists and computer graphics professionals. Compared to the imaging domain, which is rich with large available datasets, the number of data instances for the motion domain is limited, particularly for the animation of animals and exotic creatures (e.g., dragons), which have unique skeletons and motion patterns. In this work, we present a Single Motion Diffusion Model, dubbed SinMDM, a model designed to learn the internal motifs of a single motion sequence with arbitrary topology and synthesize motions of arbitrary length that are faithful to them. We harness the power of diffusion models and present a denoising network designed specifically for the task of learning from a single input motion. Our transformer-based architecture avoids overfitting by using local attention layers that narrow the receptive field, and encourages motion diversity by using relative positional embedding. SinMDM can be applied in a variety of contexts, including spatial and temporal in-betweening, motion expansion, style transfer, and crowd animation. Our results show that SinMDM outperforms existing methods both in quality and time-space efficiency. Moreover, while current approaches require additional training for different applications, our work facilitates these applications at inference time. Our code and trained models are available at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05905
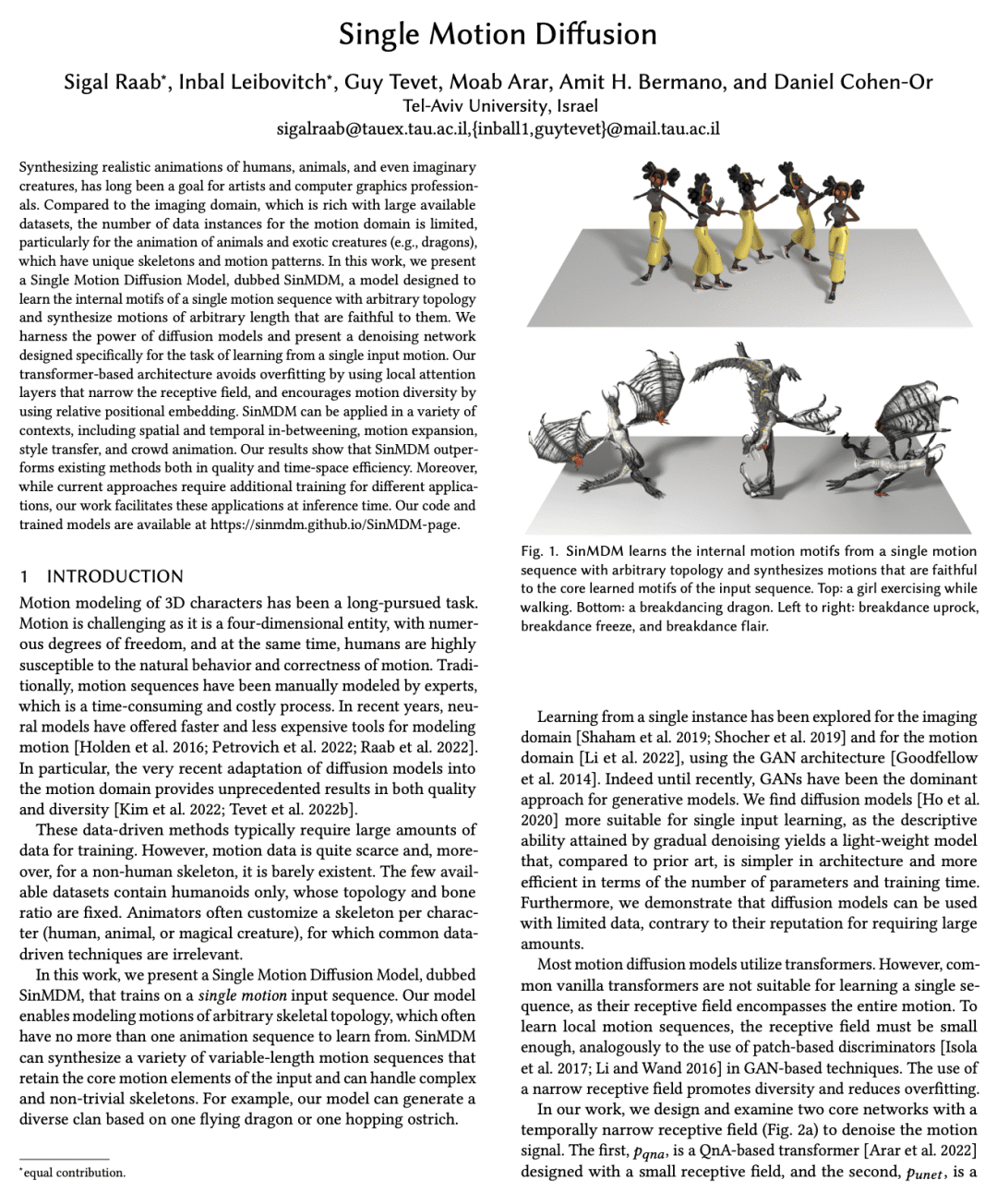

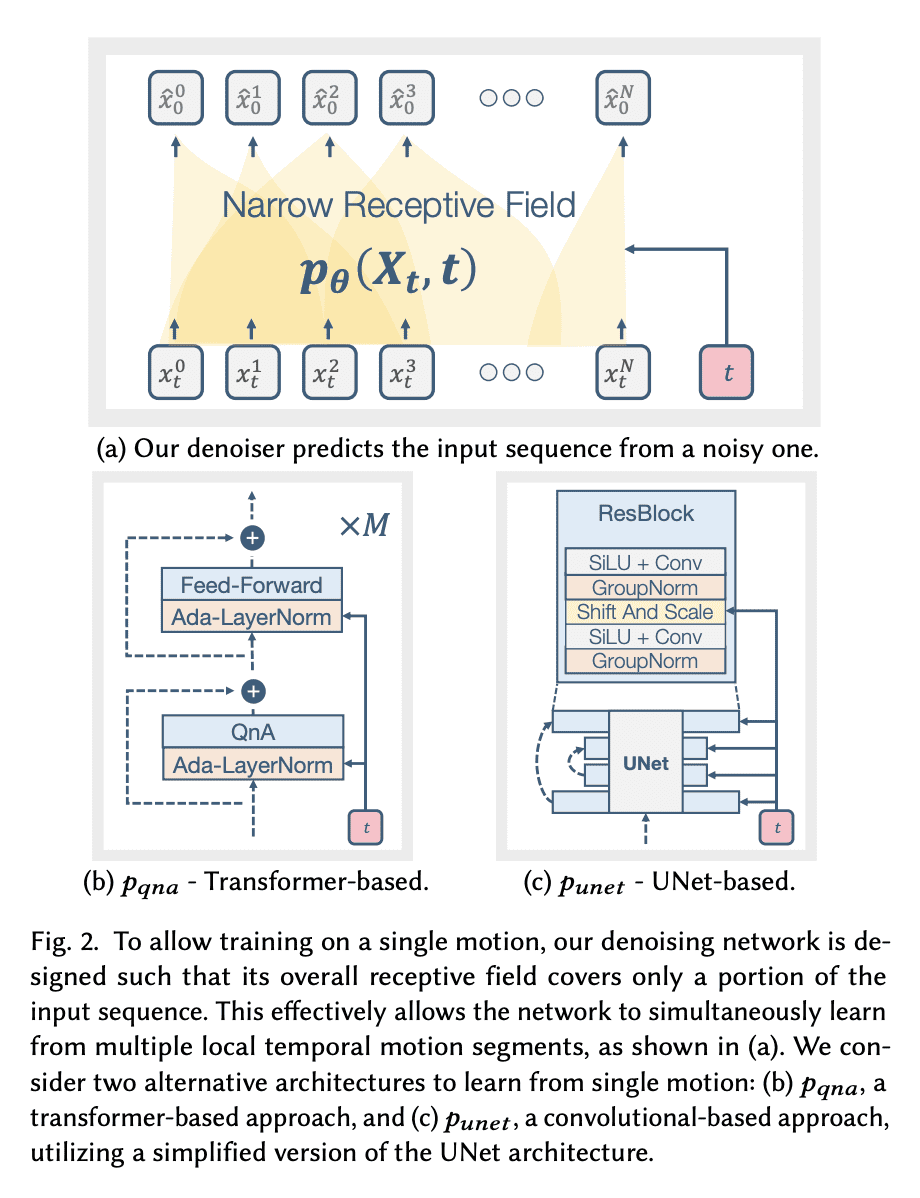
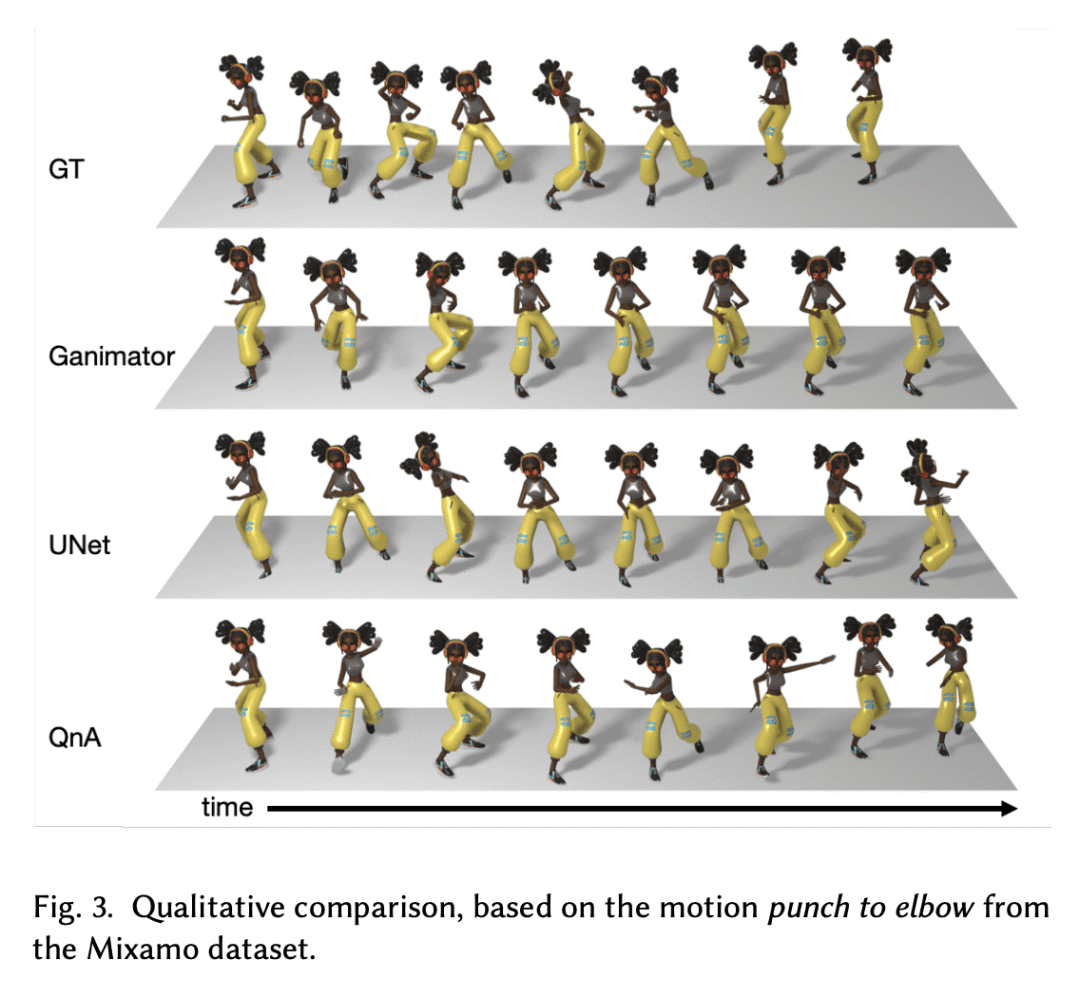
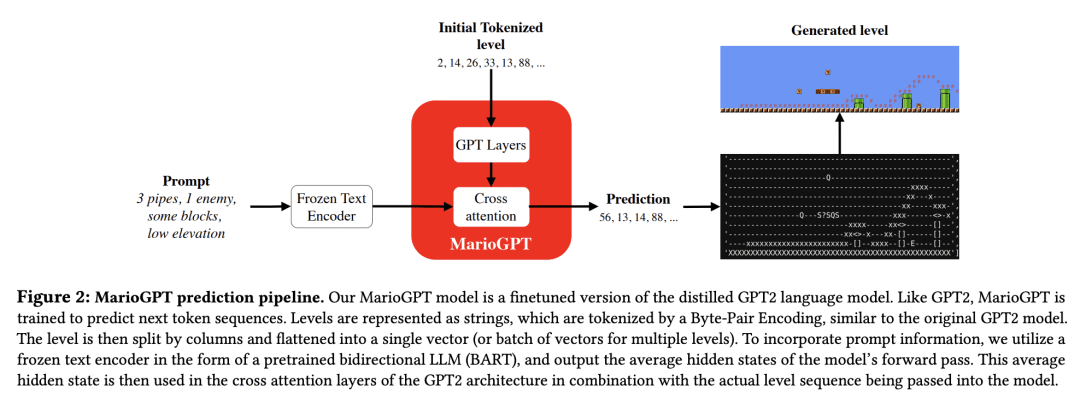
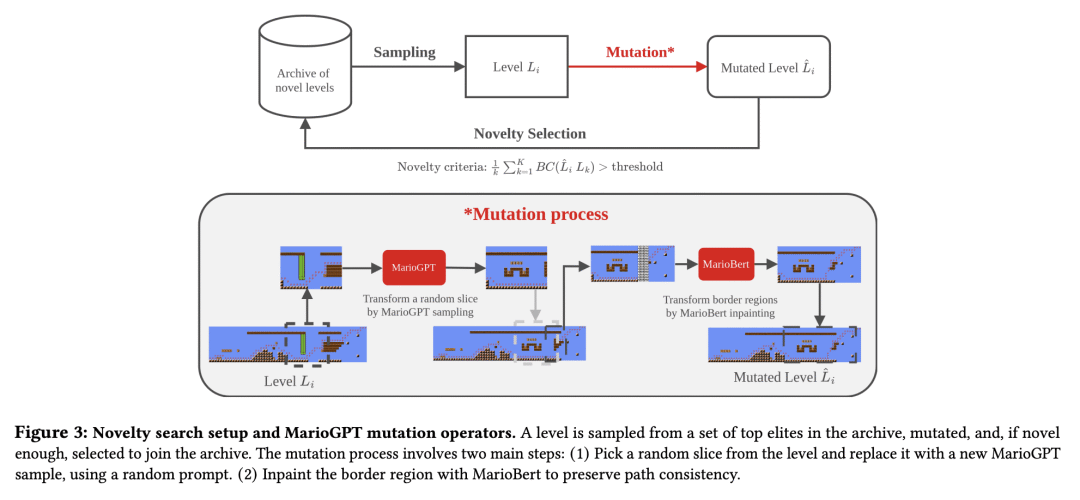
2、[CL] MarioGPT: Open-Ended Text2Level Generation through Large Language Models
S Sudhakaran, M González-Duque, C Glanois, M Freiberger, E Najarro, S Risi
[IT University of Copenhagen]
MarioGPT: 基于大型语言模型的开放式Text2Level生成
要点:
-
MarioGPT 是一个微调的GPT-2模型,通过自然语言提示生成超级马里奥兄弟的关卡; -
该模型可预测玩家的互动,生成多样化和可玩的环境,并减少对昂贵的外部主体互动的需求; -
将 MarioGPT 与新颖性搜索等多样性驱动算法相结合,可以实现开放式和功能性的内容生成; -
将 GPT-n 这样的大型语言模型用于 PCG 方法,为未来研究开辟了新的方向。
一句话总结:
MarioGPT 是一个经过微调的 GPT-2 模型,可以根据自然语言提示生成超级马里奥兄弟的关卡,并且可以与新奇性搜索相结合,以开放的方式产生多样化的关卡。
Procedural Content Generation (PCG) algorithms provide a technique to generate complex and diverse environments in an automated way. However, while generating content with PCG methods is often straightforward, generating meaningful content that reflects specific intentions and constraints remains challenging. Furthermore, many PCG algorithms lack the ability to generate content in an open-ended manner. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown to be incredibly effective in many diverse domains. These trained LLMs can be fine-tuned, re-using information and accelerating training for new tasks. In this work, we introduce MarioGPT, a fine-tuned GPT2 model trained to generate tile-based game levels, in our case Super Mario Bros levels. We show that MarioGPT can not only generate diverse levels, but can be text-prompted for controllable level generation, addressing one of the key challenges of current PCG techniques. As far as we know, MarioGPT is the first text-to-level model. We also combine MarioGPT with novelty search, enabling it to generate diverse levels with varying play-style dynamics (i.e. player paths). This combination allows for the open-ended generation of an increasingly diverse range of content.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05981

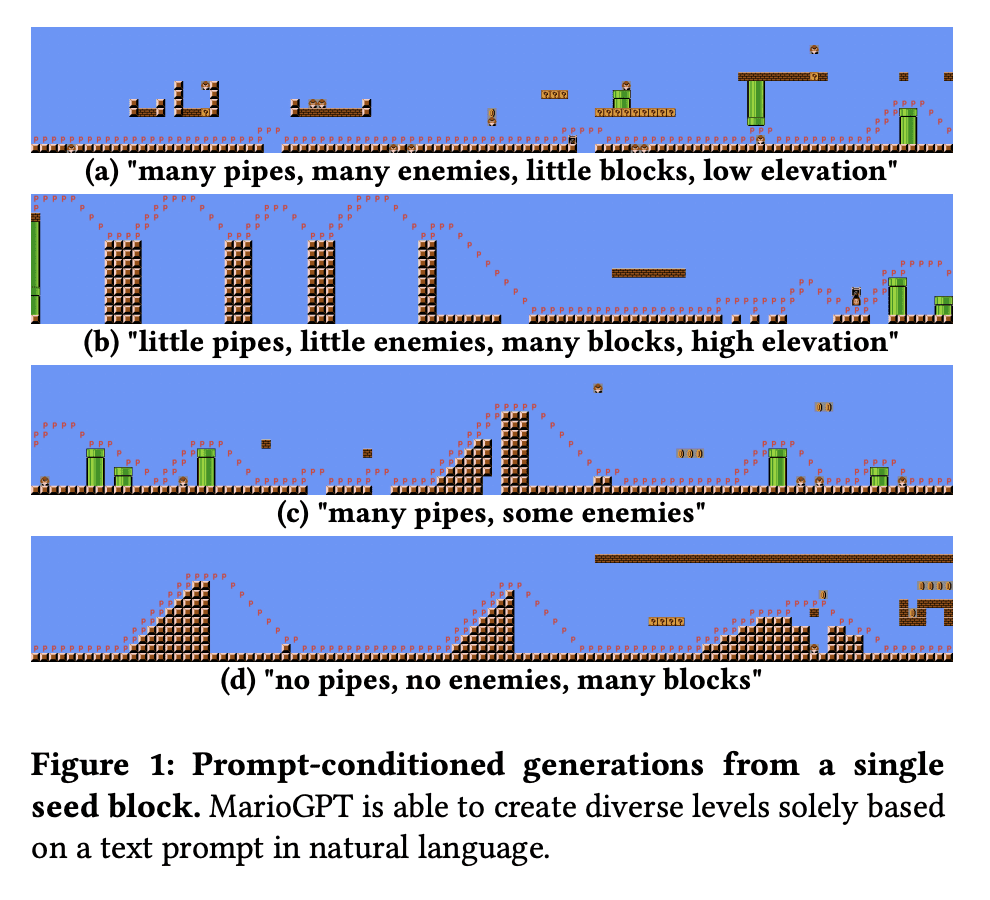
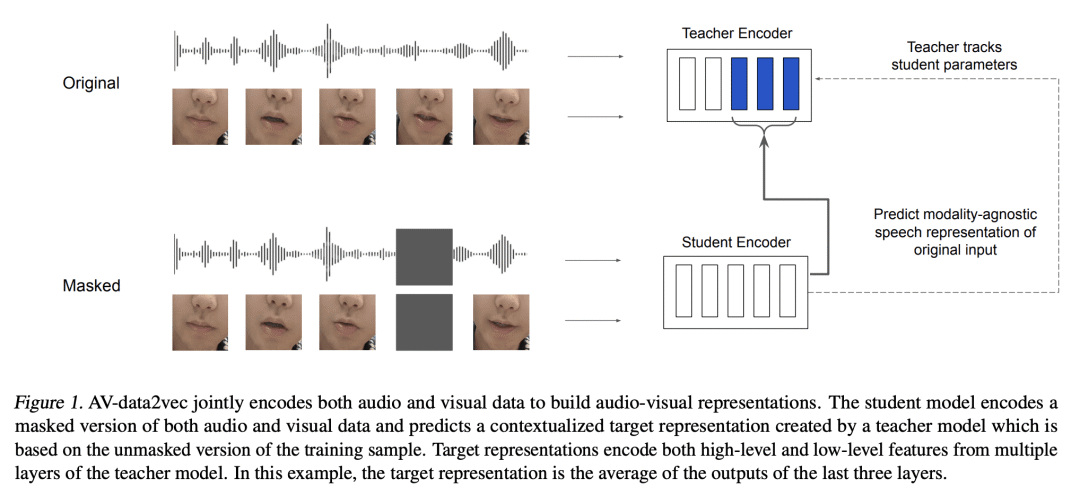
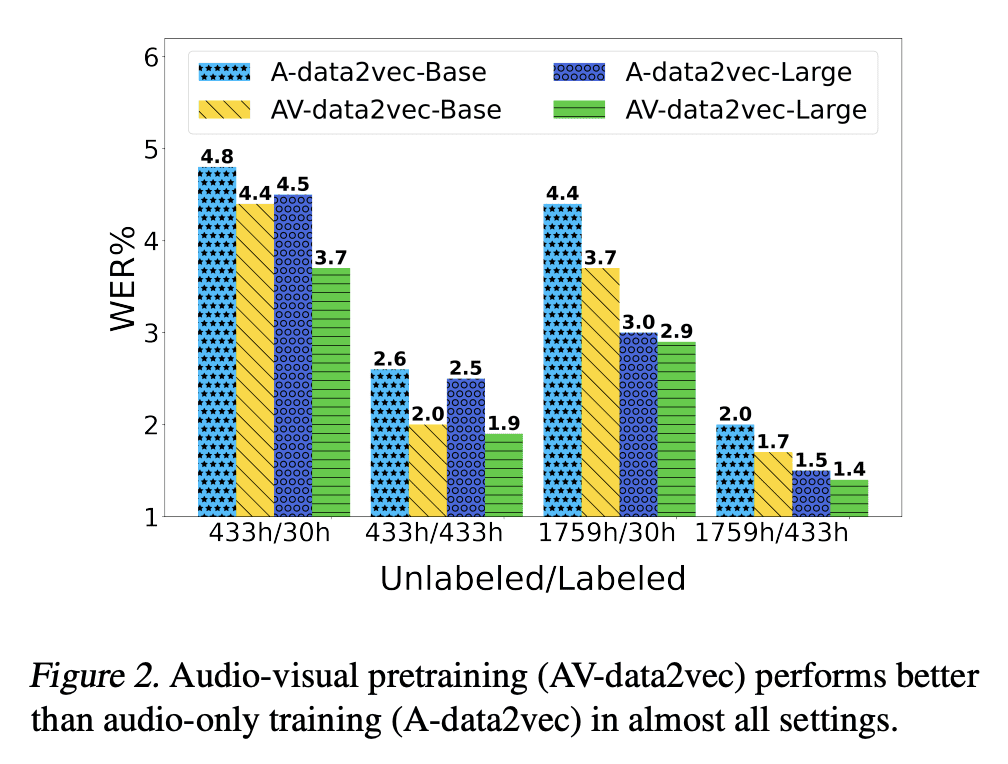
3、[AS] AV-data2vec: Self-supervised Learning of Audio-Visual Speech Representations with Contextualized Target Representations
J Lian, A Baevski, W Hsu, M Auli
[Meta AI & UC Berkeley]
AV-data2vec: 基于上下文目标表示的视觉-听觉语音表示自监督学习
要点:
-
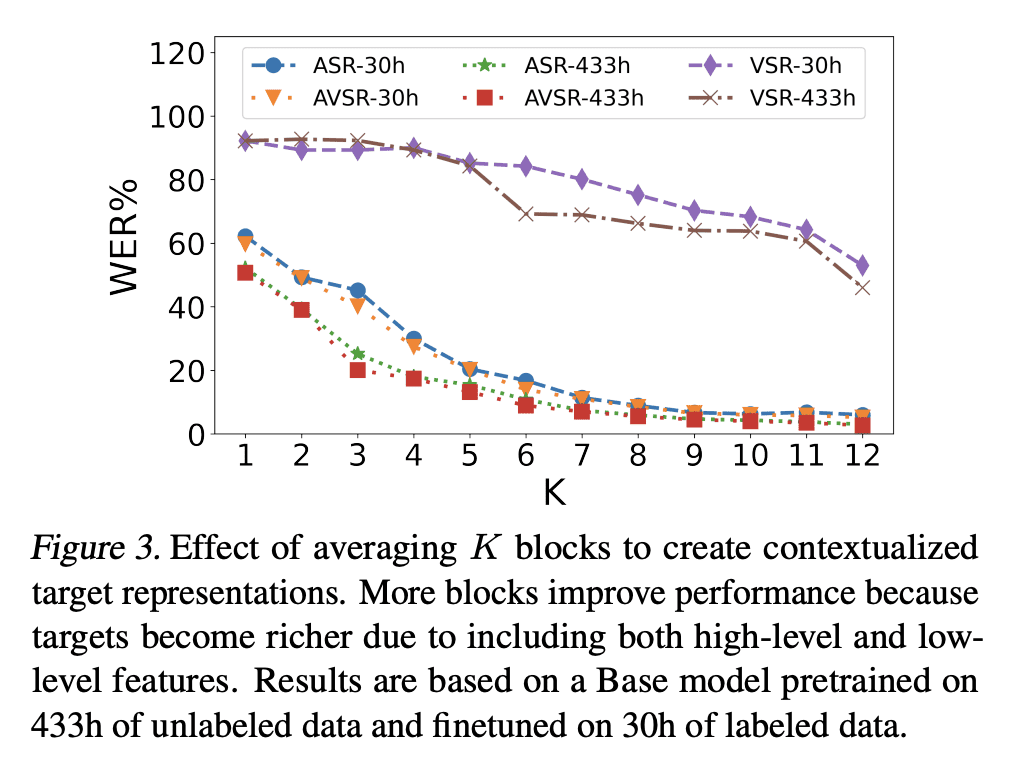
AV-data2vec 将 data2vec 从单模态扩展到联合视觉-听觉模态,并且是完全端到端的; -
AV-data2vec 对音频和视频使用一个共享的 Transformer 编码器,并能执行AVSR; -
AV-data2vec 优于 LRS3 上现有的自监督视觉-听觉学习框架。
一句话总结:
AV-data2vec 是一个自监督框架,可以联合学习视觉-听觉语音表示,并达到最先进的性能。
Self-supervision has shown great potential for audio-visual speech recognition by vastly reducing the amount of labeled data required to build good systems. However, existing methods are either not entirely end-to-end or do not train joint representations of both modalities. In this paper, we introduce AV-data2vec which addresses these challenges and builds audio-visual representations based on predicting contextualized representations which has been successful in the uni-modal case. The model uses a shared transformer encoder for both audio and video and can combine both modalities to improve speech recognition. Results on LRS3 show that AV-data2vec consistently outperforms existing methods under most settings.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06419

4、[LG] Symbolic Physics Learner: Discovering governing equations via Monte Carlo tree search
F Sun, Y Liu, J Wang, H Sun
[Northeasern University & University of Chinese Academy of Sciences & …]
符号物理学习器:基于蒙特卡洛树搜索的控制方程发现
要点:
-
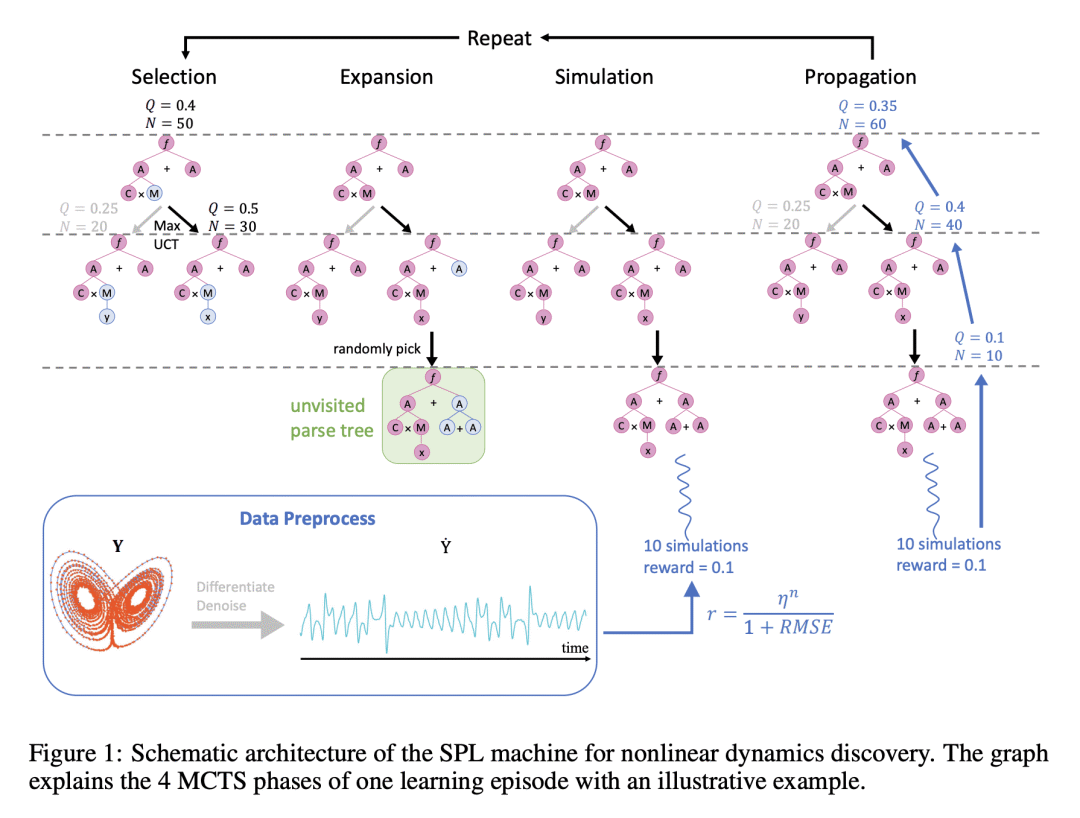
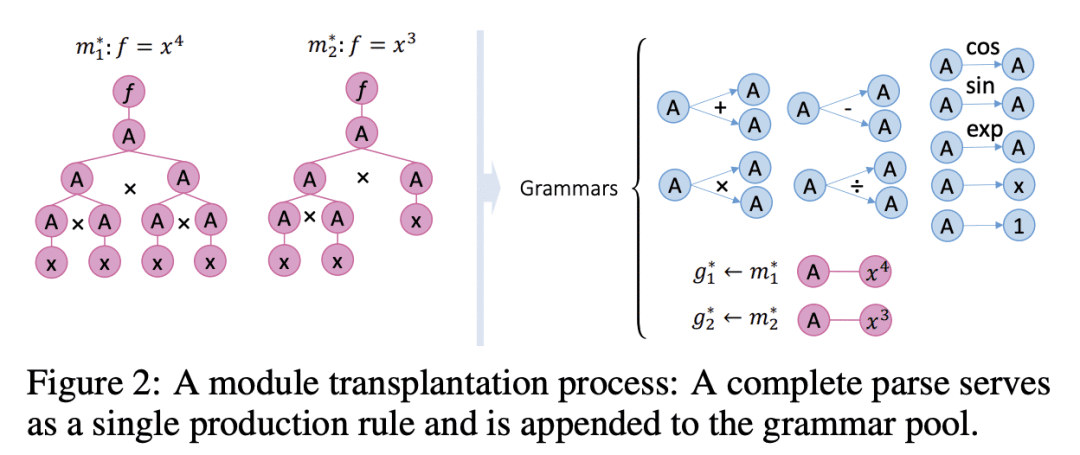
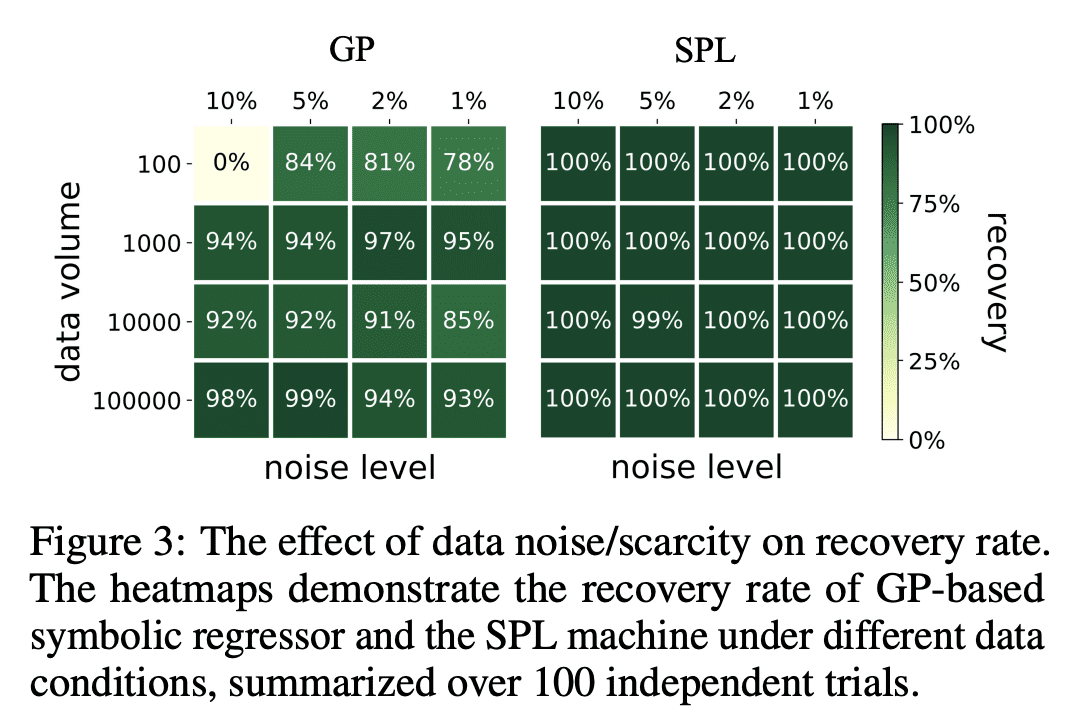
提出 SPL 通过使用计算规则和符号解释数学运算和系统状态变量,从有限数据中发现非线性动力学的数学结构,并采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)代理来探索基于测量数据的最佳表达树; -
SPL机是灵活的,对发现的方程强制执行解析,并在数值实例中被证明优于最先进的基线; -
SPL机在发现物理规律和非线性动力学方面优于最先进的符号回归方法。
一句话总结:
提出一种称为符号物理学习机(SPL)的模型,基于蒙特卡洛树形搜索,用于从有限数据中发现非线性动力学。
Nonlinear dynamics is ubiquitous in nature and commonly seen in various science and engineering disciplines. Distilling analytical expressions that govern nonlinear dynamics from limited data remains vital but challenging. To tackle this fundamental issue, we propose a novel Symbolic Physics Learner (SPL) machine to discover the mathematical structure of nonlinear dynamics. The key concept is to interpret mathematical operations and system state variables by computational rules and symbols, establish symbolic reasoning of mathematical formulas via expression trees, and employ a Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) agent to explore optimal expression trees based on measurement data. The MCTS agent obtains an optimistic selection policy through the traversal of expression trees, featuring the one that maps to the arithmetic expression of underlying physics. Salient features of the proposed framework include search flexibility and enforcement of parsimony for discovered equations. The efficacy and superiority of the SPL machine are demonstrated by numerical examples, compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.13134

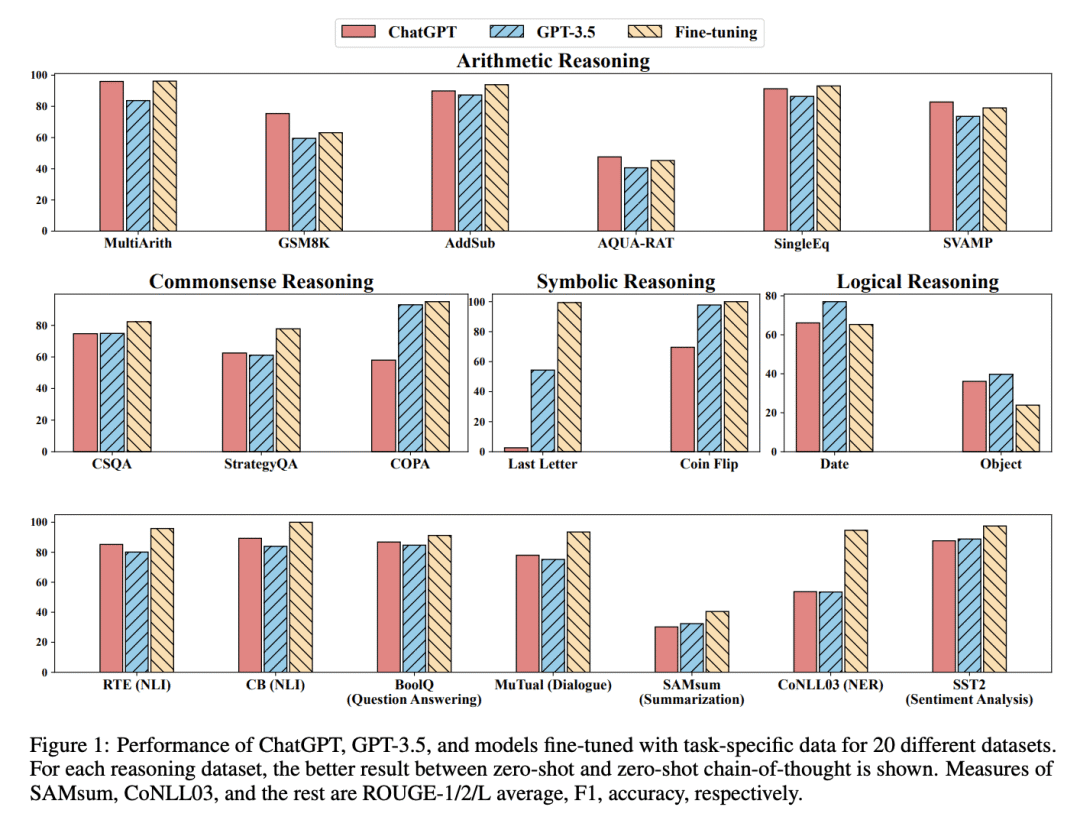
5、[CL] Is ChatGPT a General-Purpose Natural Language Processing Task Solver?
C Qin…
[Nanyang Technological University & Amazon Web Services & Shanghai Jiao Tong University & Georgia Institute of Technology & Stanford University]
ChatGPT是通用NLP任务处理器吗?
要点:
-
ChatGPT有一定的通用 NLP 能力,但往往不如特定任务的模; -
在推理和对话任务中表现出色; -
在序列标记方面很吃力; -
可生成较长的摘要,但在摘要任务中表现比 GPT-3.5 差。
一句话总结:
ChatGPT 显示了作为通用 NLP 模型的一些能力,但往往不如特定任务模型,在推理和对话任务中表现出色,而在序列标记方面略显逊色。
Spurred by advancements in scale, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated the ability to perform a variety of natural language processing (NLP) tasks zero-shot — i.e., without adaptation on downstream data. Recently, the debut of ChatGPT has drawn a great deal of attention from the natural language processing (NLP) community due to the fact that it can generate high-quality responses to human input and self-correct previous mistakes based on subsequent conversations. However, it is not yet known whether ChatGPT can serve as a generalist model that can perform many NLP tasks zero-shot. In this work, we empirically analyze the zero-shot learning ability of ChatGPT by evaluating it on 20 popular NLP datasets covering 7 representative task categories. With extensive empirical studies, we demonstrate both the effectiveness and limitations of the current version of ChatGPT. We find that ChatGPT performs well on many tasks favoring reasoning capabilities (e.g., arithmetic reasoning) while it still faces challenges when solving specific tasks such as sequence tagging. We additionally provide in-depth analysis through qualitative case studies.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06476


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CL] Gradient-Based Automated Iterative Recovery for Parameter-Efficient Tuning
M Mozes, T Bolukbasi, A Yuan, F Liu, N Thain, L Dixon
[Google Research]
面向参数高效调优的基于梯度的自动迭代恢复
要点:
-
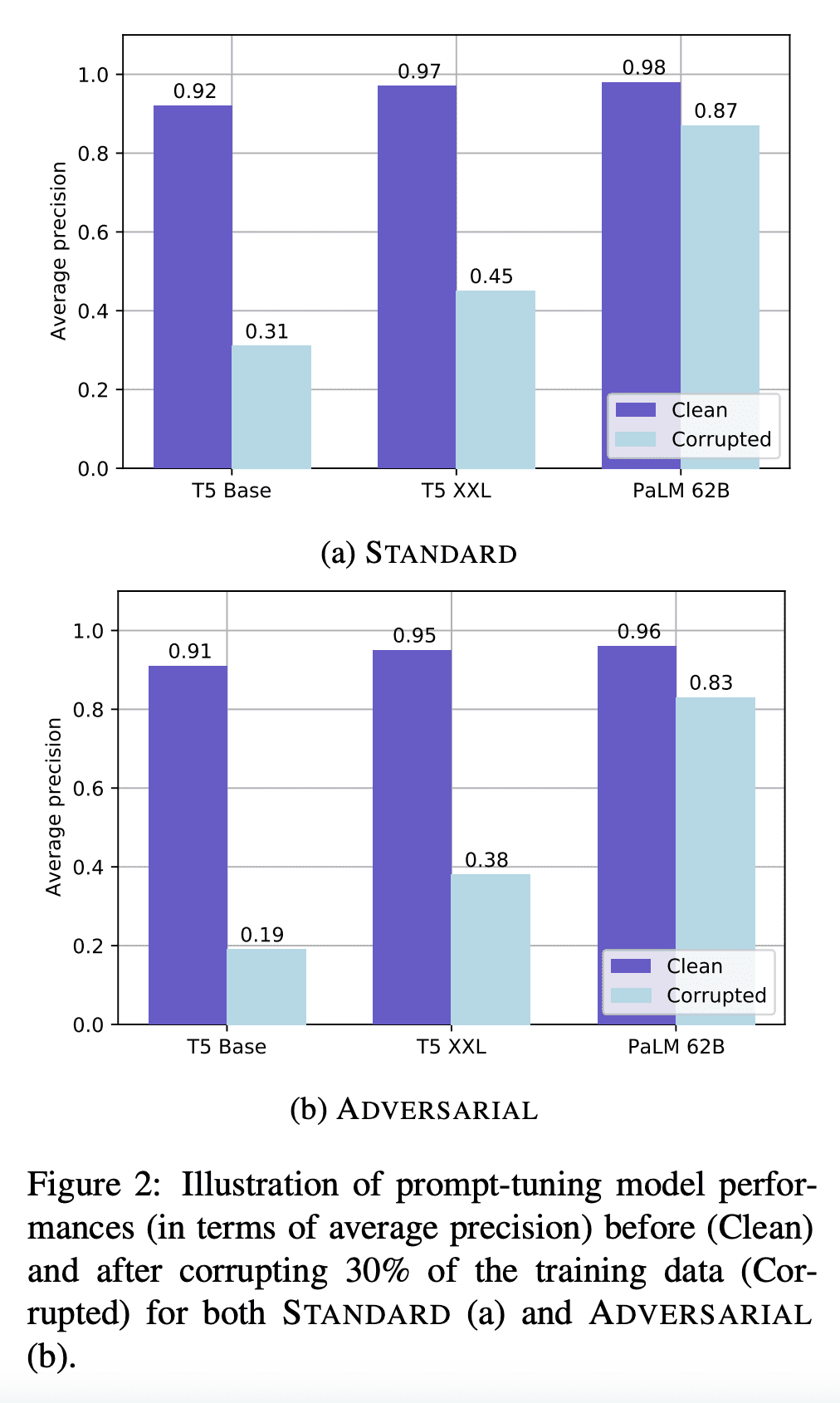
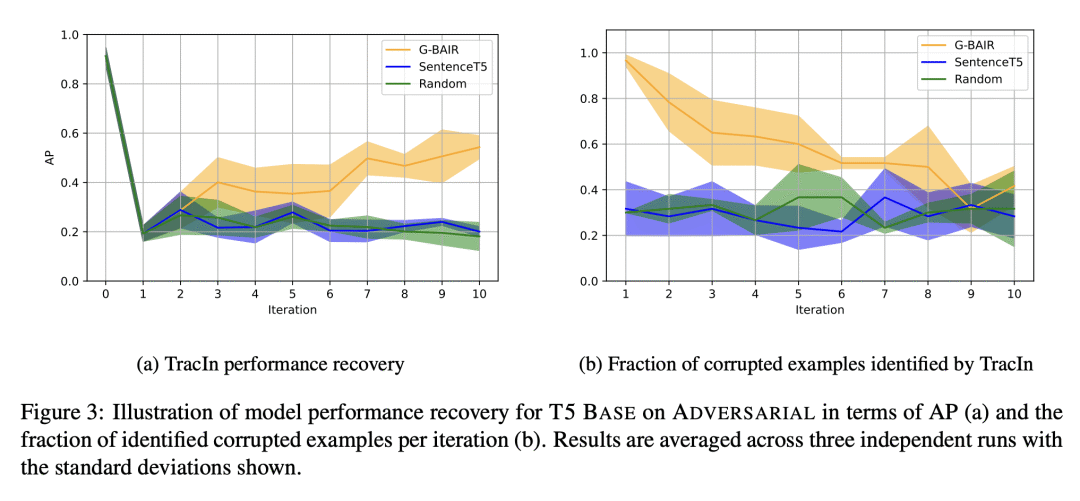
TracIn 在参数高效调优中有效地提高了模型性能; -
G-BAIR 是一个通过使用TracIn识别错误标记样本来迭代提高 LLM 性能的方案; -
TracIn 可用于自动执行数据清理,并恢复因标记损坏而损失的精度。
一句话总结:
基于梯度的可解释性技术,如TracIn,可用于自动进行数据清理,并在参数高效调优中提高模型性能。
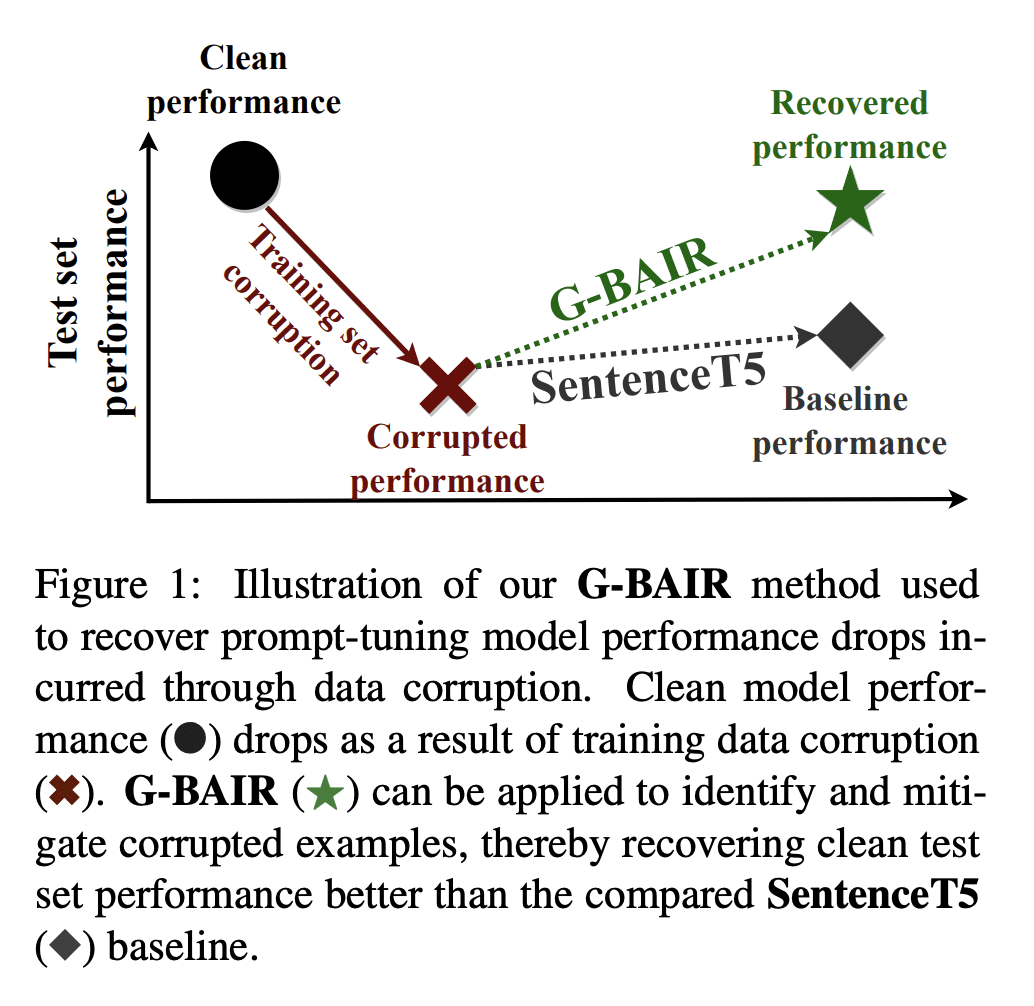
Pretrained large language models (LLMs) are able to solve a wide variety of tasks through transfer learning. Various explainability methods have been developed to investigate their decision making process. TracIn (Pruthi et al., 2020) is one such gradient-based method which explains model inferences based on the influence of training examples. In this paper, we explore the use of TracIn to improve model performance in the parameter-efficient tuning (PET) setting. We develop conversational safety classifiers via the prompt-tuning PET method and show how the unique characteristics of the PET regime enable TracIn to identify the cause for certain misclassifications by LLMs. We develop a new methodology for using gradient-based explainability techniques to improve model performance, G-BAIR: gradient-based automated iterative recovery. We show that G-BAIR can recover LLM performance on benchmarks after manually corrupting training labels. This suggests that influence methods like TracIn can be used to automatically perform data cleaning, and introduces the potential for interactive debugging and relabeling for PET-based transfer learning methods.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06598
[LG] Cross-Modal Fine-Tuning: Align then Refine
J Shen, L Li, L M. Dery, C Staten, M Khodak, G Neubig, A Talwalkar
[CMU & Hewlett Packard Enterprise]
跨模态微调:先对齐再细化
要点:
-
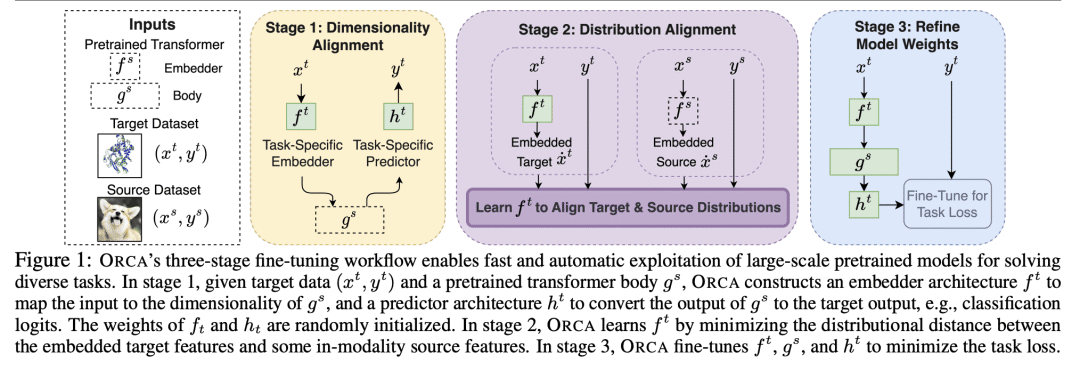
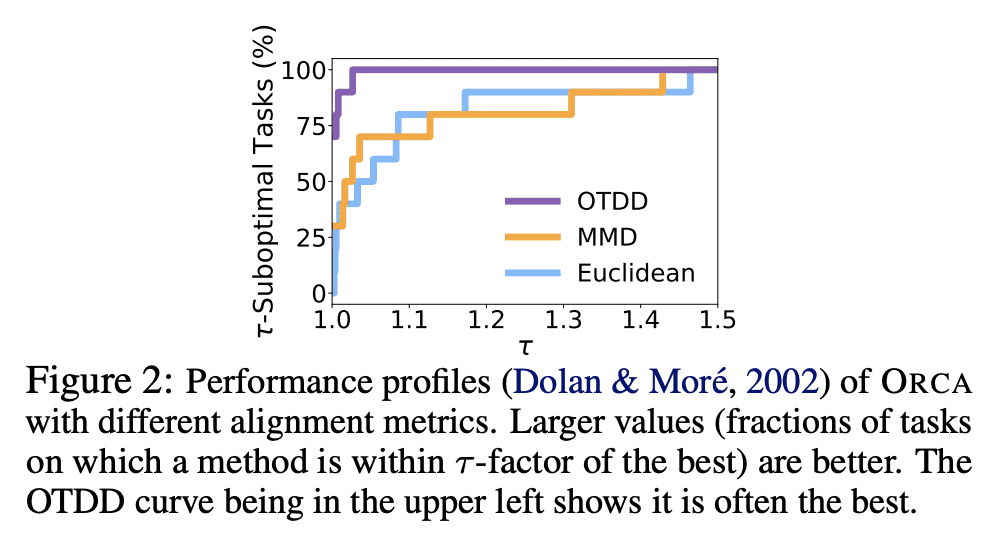
预训练模型的微调已经在视觉和NLP中取得了进展,但在许多其他模态中却没有; -
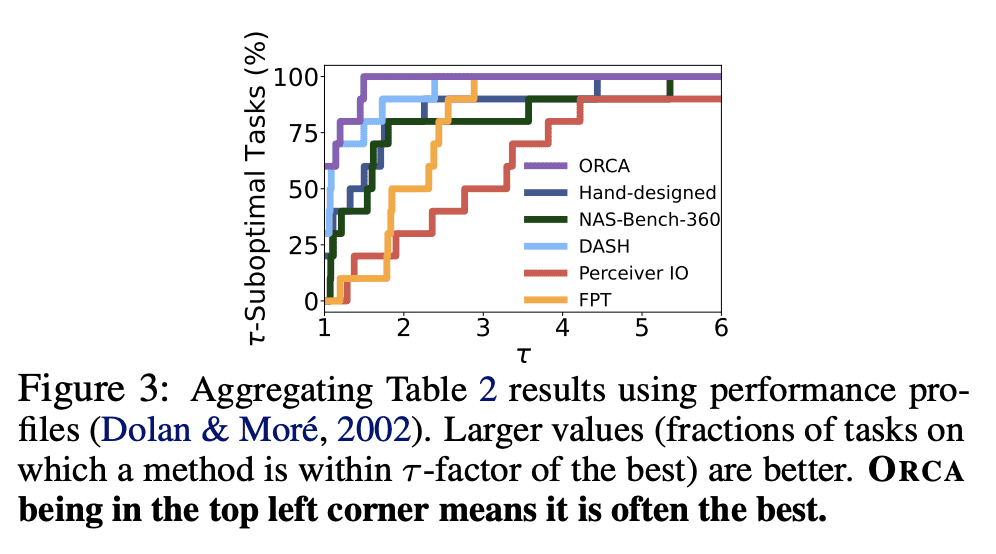
ORCA 是一个跨模态微调框架,将最终任务数据与模型的预训练模态相匹配; -
ORCA 在12种模态的60多个数据集的3个基准上的表现,优于手工设计的、AutoML的、通用的和特定任务的方法; -
ORCA 的有效性在广度、深度和与现有工作的比较上得到了验证。
一句话总结:
提出ORCA,一种跨模态微调框架,将任意模态的最终任务数据与模型的预训练模态对齐,以提高微调性能。
Fine-tuning large-scale pretrained models has led to tremendous progress in well-studied modalities such as vision and NLP. However, similar gains have not been observed in many other modalities due to a lack of relevant pretrained models. In this work, we propose ORCA, a general cross-modal fine-tuning framework that extends the applicability of a single large-scale pretrained model to diverse modalities. ORCA adapts to a target task via an align-then-refine workflow: given the target input, ORCA first learns an embedding network that aligns the embedded feature distribution with the pretraining modality. The pretrained model is then fine-tuned on the embedded data to exploit the knowledge shared across modalities. Through extensive experiments, we show that ORCA obtains state-of-the-art results on 3 benchmarks containing over 60 datasets from 12 modalities, outperforming a wide range of hand-designed, AutoML, general-purpose, and task-specific methods. We highlight the importance of data alignment via a series of ablation studies and demonstrate ORCA’s utility in data-limited regimes.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05738

[CL] Task-Specific Skill Localization in Fine-tuned Language Models
A Panigrahi, N Saunshi, H Zhao, S Arora
[Princeton University]
微调语言模型特定任务技能定位
要点:
-
微调允许模型获得特定任务的”技能”,但对这些技能在模型中的定位研究有限; -
本文提出技能定位的概念,并提出一种简单的优化方法,以确定负责模型性能的极小的参数子集,从而改善校准和分布外的泛化; -
Grafted 模型具有其他理想的属性,如校准和OD泛化,并且可以协助某些形式的持续学习。
一句话总结:
提出微调语言模型中技能定位的概念,并提出了一种简单的优化方法,以确定负责模型性能的极小参数子集,从而改进校准和分布外泛化。
Pre-trained language models can be fine-tuned to solve diverse NLP tasks, including in few-shot settings. Thus fine-tuning allows the model to quickly pick up task-specific “skills”, but there has been limited study of where these newly-learnt skills reside inside the massive model. This paper introduces the term skill localization for this problem and proposes a solution. Given the downstream task and a model fine-tuned on that task, a simple optimization is used to identify a very small subset of parameters (∼0.01% of model parameters) responsible for (>95%) of the model’s performance, in the sense that grafting the fine-tuned values for just this tiny subset onto the pre-trained model gives performance almost as well as the fine-tuned model. While reminiscent of recent works on parameter-efficient fine-tuning, the novel aspects here are that: (i) No further re-training is needed on the subset (unlike, say, with lottery tickets). (ii) Notable improvements are seen over vanilla fine-tuning with respect to calibration of predictions in-distribution (40-90% error reduction) as well as the quality of predictions out-of-distribution (OOD). In models trained on multiple tasks, a stronger notion of skill localization is observed, where the sparse regions corresponding to different tasks are almost disjoint, and their overlap (when it happens) is a proxy for task similarity. Experiments suggest that localization via grafting can assist certain forms of continual learning.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06600

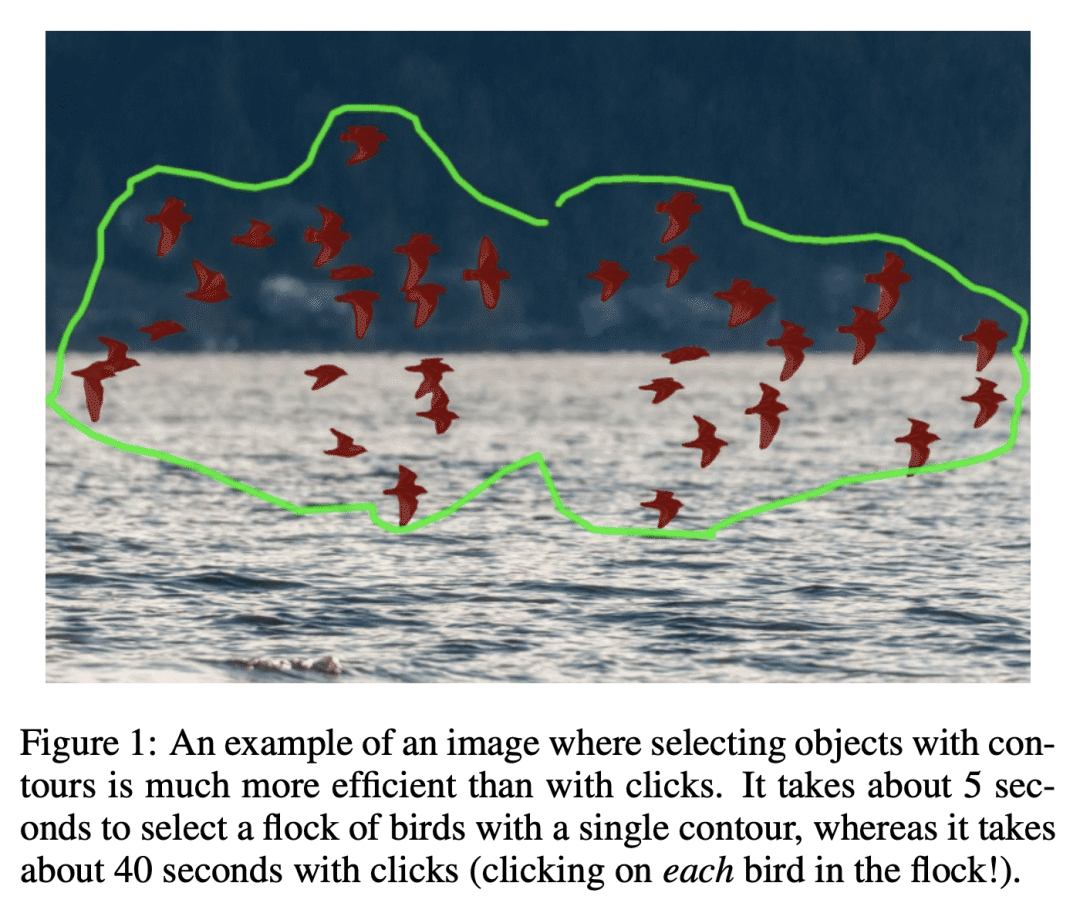
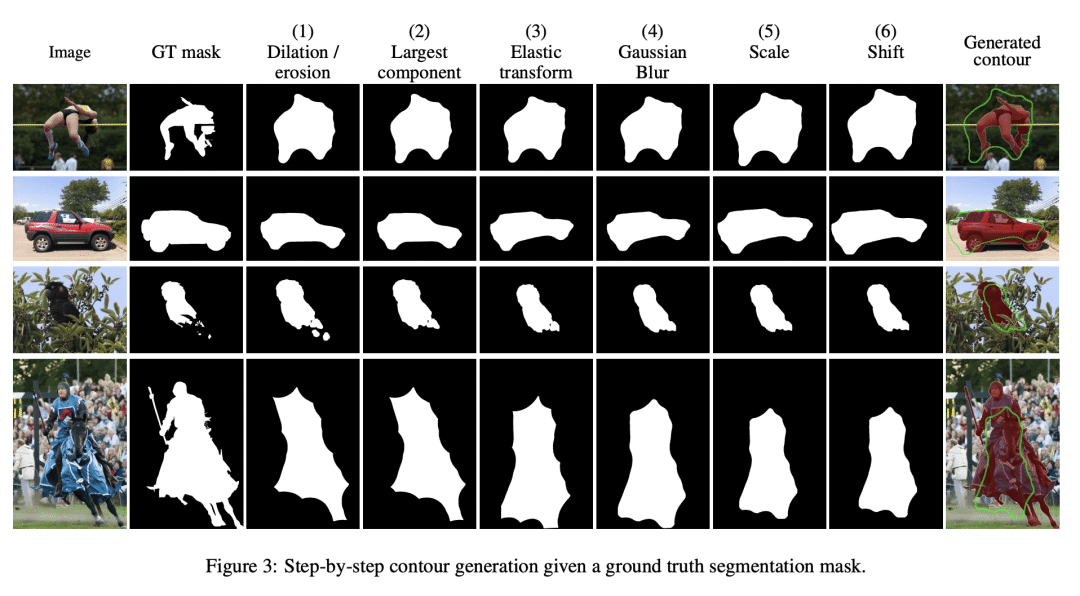
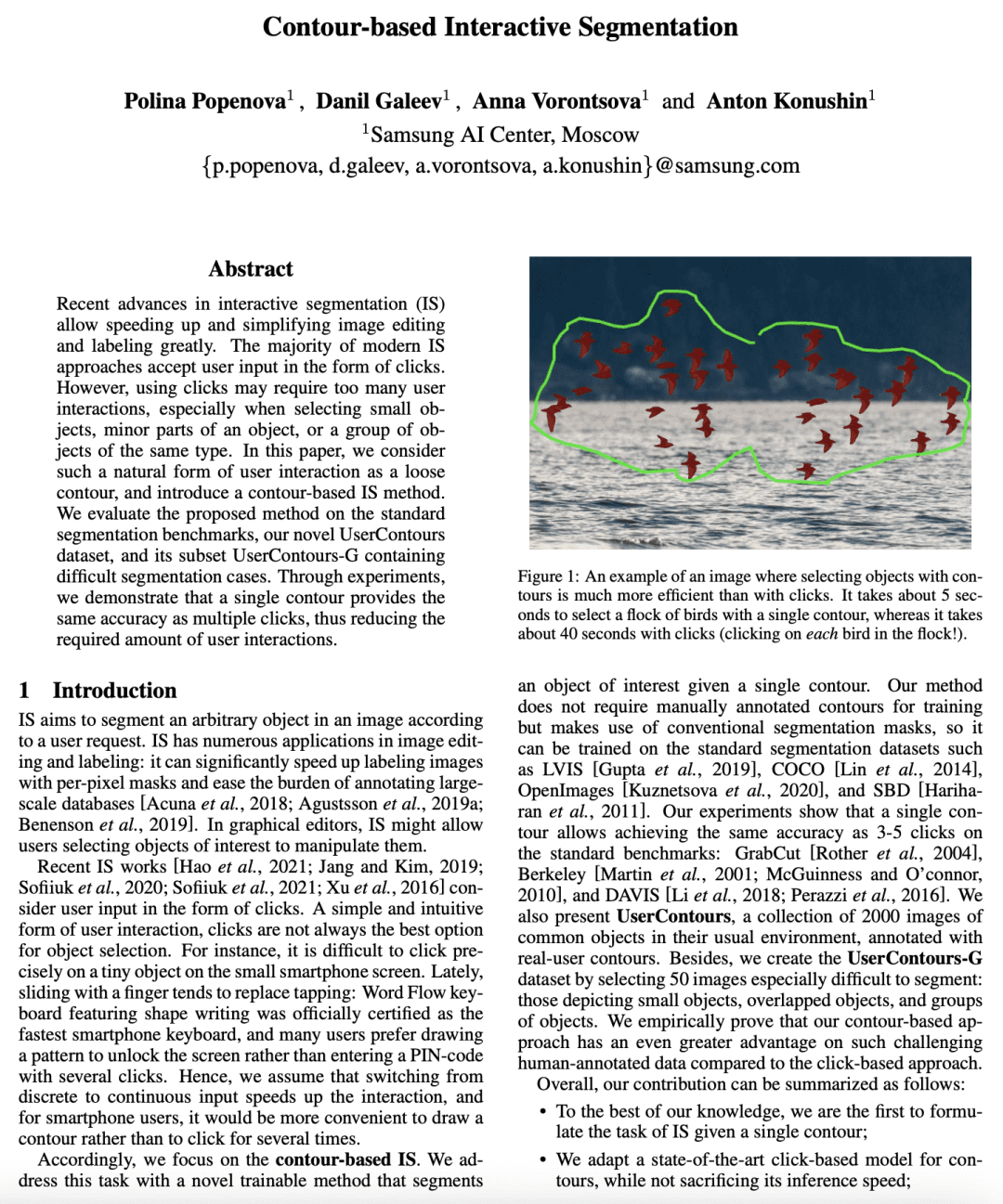
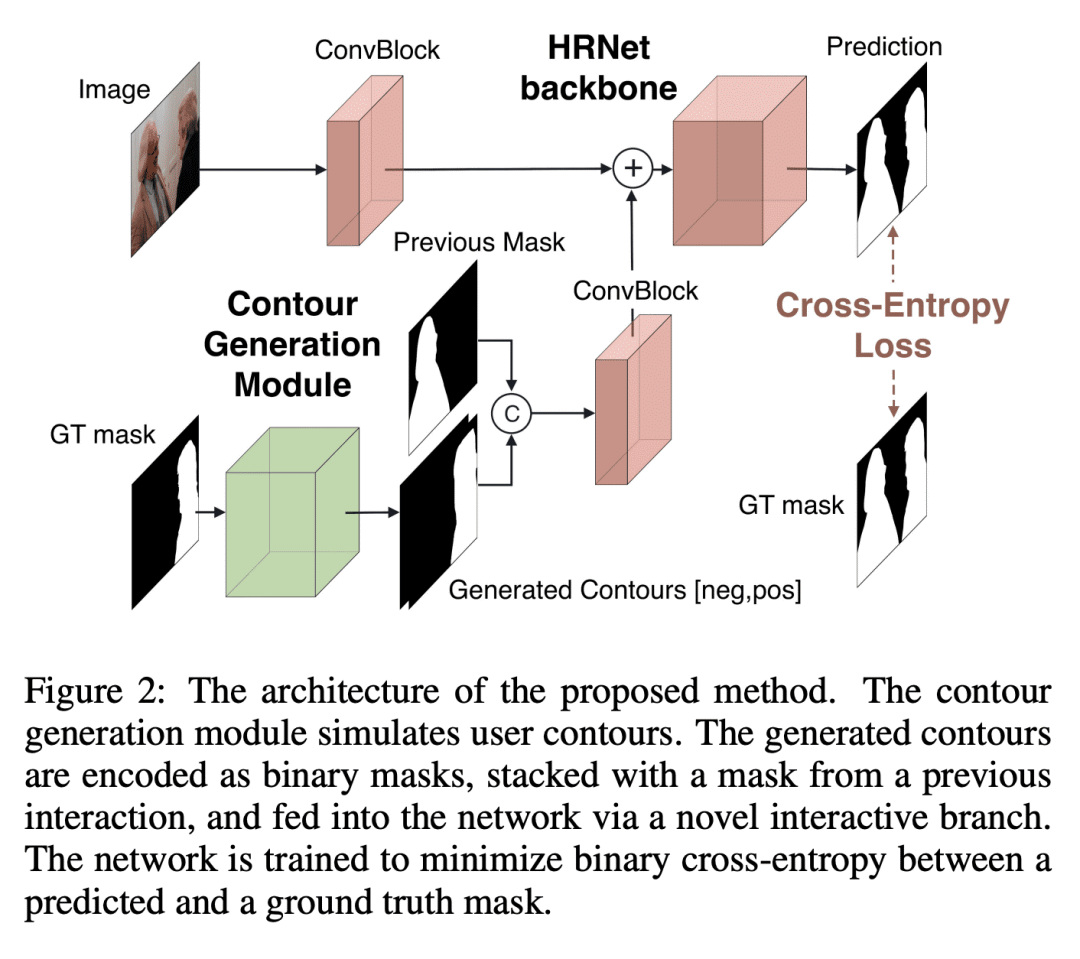
[CV] Contour-based Interactive Segmentation
D Galeev, P Popenova, A Vorontsova, A Konushin
[Samsung AI Center]
基于轮廓的交互式分割
要点:
-
提出一种基于轮廓的交互式分割方法,以松散轮廓形式接受用户输入,减少了所需的用户交互次数; -
提供了与基于点击的方法相同的准确性,同时保持了推理速度; -
提出一种新的 UserContours 数据集和一个具有挑战性的 UserContours-G,用轮廓线手动标注。 -
所提出的基于轮廓的方法在挑战性的数据上比基于点击的方法有更大的优势。
一句话总结:
提出一种新的基于轮廓的交互式分割方法,减少了所需的用户交互次数,大大简化了图像编辑和标注。
Recent advances in interactive segmentation (IS) allow speeding up and simplifying image editing and labeling greatly. The majority of modern IS approaches accept user input in the form of clicks. However, using clicks may require too many user interactions, especially when selecting small objects, minor parts of an object, or a group of objects of the same type. In this paper, we consider such a natural form of user interaction as a loose contour, and introduce a contour-based IS method. We evaluate the proposed method on the standard segmentation benchmarks, our novel UserContours dataset, and its subset UserContours-G containing difficult segmentation cases. Through experiments, we demonstrate that a single contour provides the same accuracy as multiple clicks, thus reducing the required amount of user interactions.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06353








 ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.



