1、[CV] Pic2Word: Mapping Pictures to Words for Zero-shot Composed Image Retrieval
2、[LG] Memory-Based Meta-Learning on Non-Stationary Distributions
3、[LG] Leveraging Domain Relations for Domain Generalization
4、[LG] Hard Prompts Made Easy: Gradient-Based Discrete Optimization for Prompt Tuning and Discovery
5、[LG] Probabilistic Contrastive Learning Recovers the Correct Aleatoric Uncertainty of Ambiguous Inputs
[CL] Exploring the Benefits of Training Expert Language Models over Instruction Tuning
[CL] A Categorical Archive of ChatGPT Failures
[LG] Learning a Fourier Transform for Linear Relative Positional Encodings in Transformers
[LG] The SSL Interplay: Augmentations, Inductive Bias, and Generalization
摘要: 将图映射到词进行零样本组合图像检索、基于记忆的非平稳分布元学习、基于域关系的域泛化、面向提示调优与发现的基于梯度的离散优化、用概率对比学习恢复模糊性输入的正确后验不确定性、训练专家语言模型优于指令微调的收益探索、ChatGPT失败案例的分类存档、Transformer线性相对位置编码的傅里叶变换学习、自监督学习中增强归纳偏差和泛化的相互作用
1、[CV] Pic2Word: Mapping Pictures to Words for Zero-shot Composed Image Retrieval
K Saito, K Sohn, X Zhang, C Li, C Lee, K Saenko, T Pfister
[Google Research & Google Cloud AI Research & Boston University]
Pic2Word: 将图映射到词进行零样本组合图像检索
要点:
-
提出一种新任务,即零样本组合图像检索(ZS-CIR),旨在解决不同的 CIR 任务,而不需要标记三元组训练数据集; -
提出 Pic2Word,一种新的 ZS-CIR 方法,只需使用图像描述和未标记图像数据集就可以训练; -
Pic2Word 利用预训练视觉-语言模型,将输入图像转化为语言token,以组成图像和文本查询。
一句话总结:
Pic2Word是一种新的零样本组合图像检索(ZS-CIR)方法,在弱标记图像-描述对和未标记图像数据集上进行训练,其性能优于现有的有监督 CIR 模型,并取得了与最近有标记训练数据的 CIR 方法相当或更好的结果。
摘要:
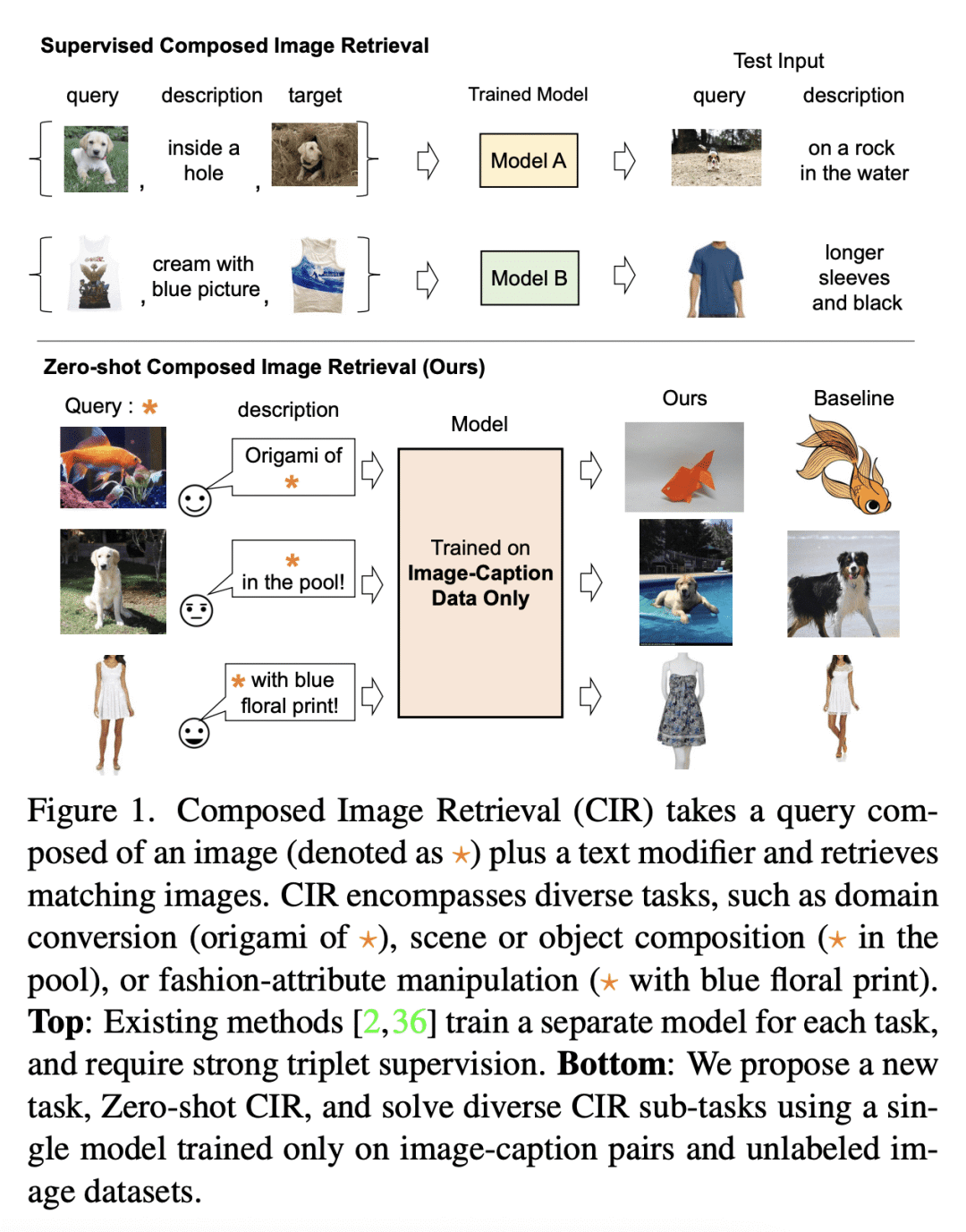
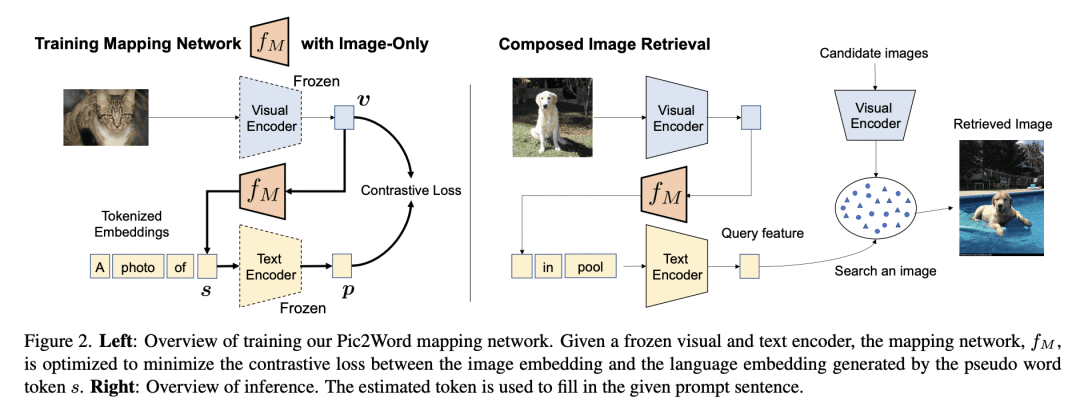
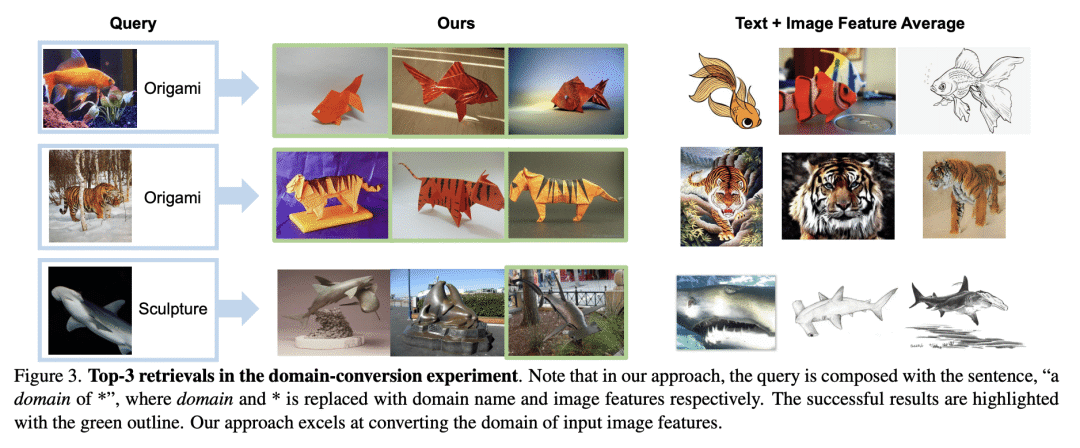
在组合图像检索(CIR)中,用户将查询图像与文本结合起来,描述他们的目标。现有的方法依赖于对 CIR 模型的监督学习,使用由查询图像、文本说明和目标图像组成的标记三元组。给这种三元组贴标签是很昂贵的,并且阻碍了 CIR 的广泛适用。本文提议研究一项重要任务,即零样本组合图像检索(ZS-CIR),其目标是建立一个不需要标记三元组的CIR模型进行训练。为此,本文提出一种新方法 Pic2Word,只需要弱标记的图像-描述对和无标记图像数据集来进行训练。与现有的监督 CIR 模型不同,本文在弱标记或无标记数据集上训练的模型在不同的 ZS-CIR 任务上显示出强大的泛化能力,例如属性编辑、对象合成和领域转换。本文方法在常见的 CIR 基准、CIRR 和 Fashion-IQ 上优于几种有监督 CIR 方法。
In Composed Image Retrieval (CIR), a user combines a query image with text to describe their intended target. Existing methods rely on supervised learning of CIR models using labeled triplets consisting of the query image, text specification, and the target image. Labeling such triplets is expensive and hinders broad applicability of CIR. In this work, we propose to study an important task, Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval (ZS-CIR), whose goal is to build a CIR model without requiring labeled triplets for training. To this end, we propose a novel method, called Pic2Word, that requires only weakly labeled image-caption pairs and unlabeled image datasets to train. Unlike existing supervised CIR models, our model trained on weakly labeled or unlabeled datasets shows strong generalization across diverse ZS-CIR tasks, e.g., attribute editing, object composition, and domain conversion. Our approach outperforms several supervised CIR methods on the common CIR benchmark, CIRR and Fashion-IQ. Code will be made publicly available at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.03084

2、[LG] Memory-Based Meta-Learning on Non-Stationary Distributions
T Genewein, G Delétang, A Ruoss, L K Wenliang, E Catt, V Dutordoir, J Grau-Moya, L Orseau, M Hutter, J Veness
[DeepMind]
基于记忆的非平稳分布元学习
要点:
-
回顾了最小化顺序预测误差、元学习及其隐贝叶斯目标之间的联系; -
记忆对最小化顺序预测误差这一目标的必要性; -
通过元学习的神经模型对两种一般非参数贝叶斯算法的匹配预测性能进行经验论证。
一句话总结:
基于记忆的元学习是一种接近贝叶斯最优预测器的技术,本文研究了当前序列预测模型和训练方案实现的有效性,结果表明,基于记忆的神经模型可以接近已知的贝叶斯最优算法,并证明学到的神经解决方案可以匹配贝叶斯算法的预测性能。
摘要:
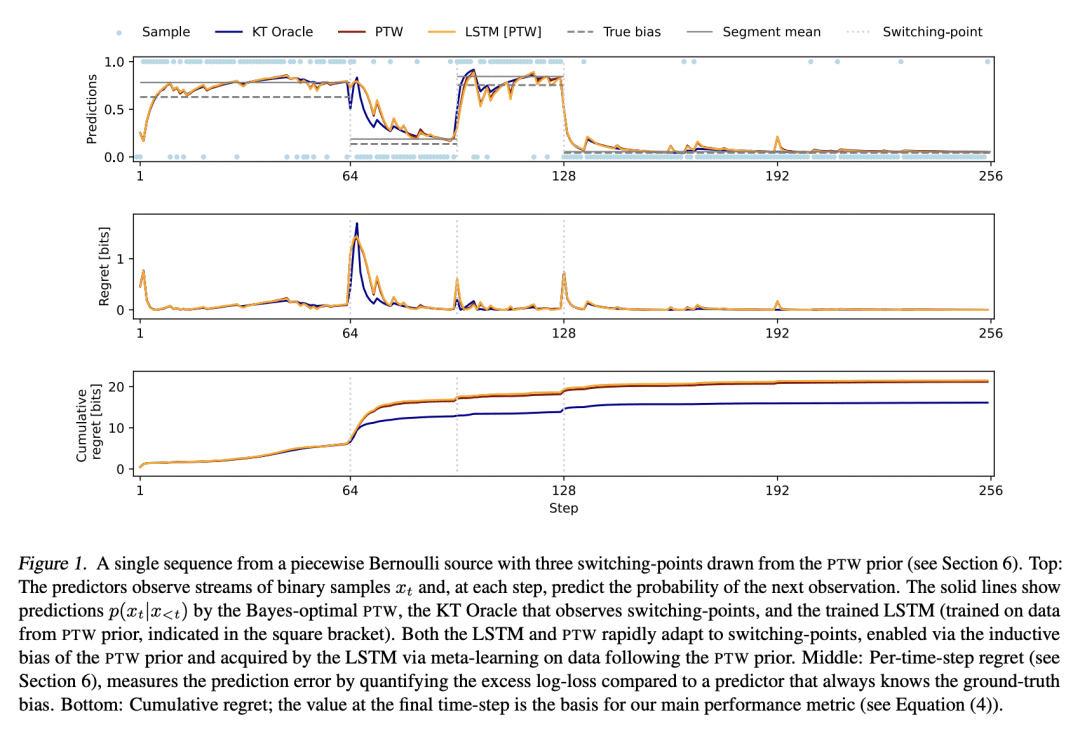
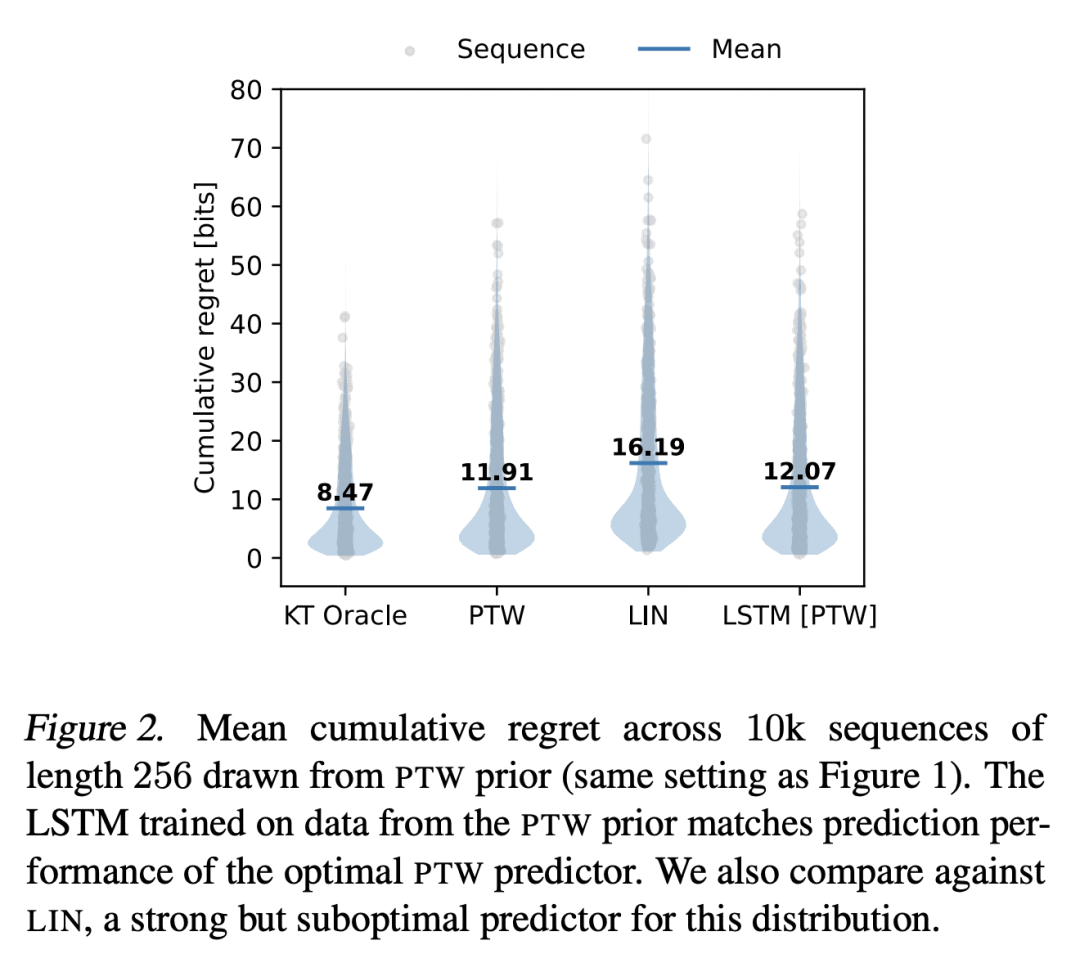
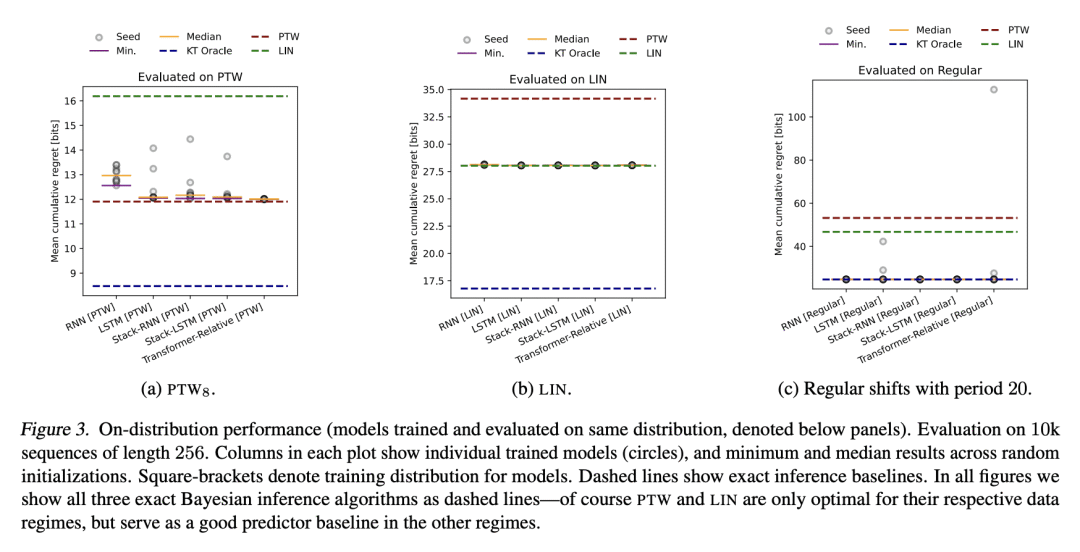
基于记忆的元学习,是一种近似贝叶斯最优预测器的技术。在相当普遍的条件下,通过对数损失来衡量的序列预测误差最小化,导致了隐性元学习。本文的目标是研究目前的序列预测模型和训练方案,在多大程度上可以实现这种解释。重点是具有未观察的切换点的片状静止源,这可以说是反映了部分可观察环境中自然语言和行动观察序列的一个重要特征。本文表明,各种类型的基于记忆的神经模型,包括 Transformer、LSTM 和 RNN 都能学会准确地接近已知的贝叶斯最优算法,并表现得像对潜在的切换点和支配每段数据分布的潜参数进行贝叶斯推理一样。
Memory-based meta-learning is a technique for approximating Bayes-optimal predictors. Under fairly general conditions, minimizing sequential prediction error, measured by the log loss, leads to implicit meta-learning. The goal of this work is to investigate how far this interpretation can be realized by current sequence prediction models and training regimes. The focus is on piecewise stationary sources with unobserved switching-points, which arguably capture an important characteristic of natural language and action-observation sequences in partially observable environments. We show that various types of memory-based neural models, including Transformers, LSTMs, and RNNs can learn to accurately approximate known Bayes-optimal algorithms and behave as if performing Bayesian inference over the latent switching-points and the latent parameters governing the data distribution within each segment.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.03067

3、[LG] Leveraging Domain Relations for Domain Generalization
H Yao, X Yang, X Pan, S Liu…
[Stanford University & Shanghai Jiao Tong University & Quebec Artificial Intelligence Institute & University of Washington]
基于域关系的域泛化
要点:
-
提出一种新方法D³G,用于解决机器学习中的域漂移问题; -
D³G 在训练阶段学习一组不同的、针对训练域的函数,并在测试阶段根据域关系对其进行重加权; -
理论分析表明,与平均相比,用域关系对训练域特定函数进行重加权会带来更好的泛化效果。 -
对各种数据集的实证评估显示,与最先进的方法相比,有一致的改进,平均改进率为10.6%。
一句话总结:
D³G 方法通过在测试阶段基于域关系对域特定函数进行重加权,提高机器学习模型对域漂移的鲁棒性。
摘要:
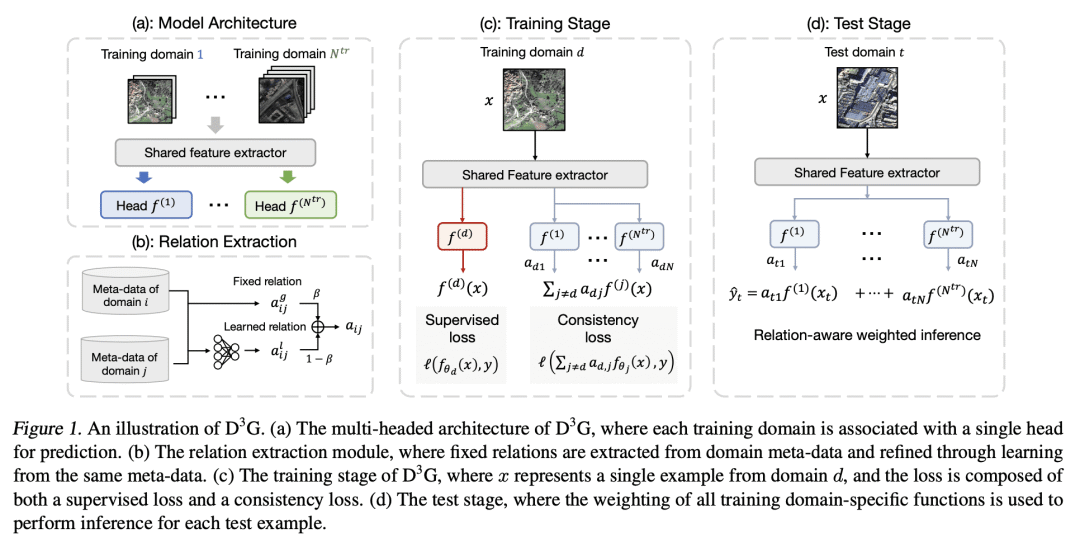
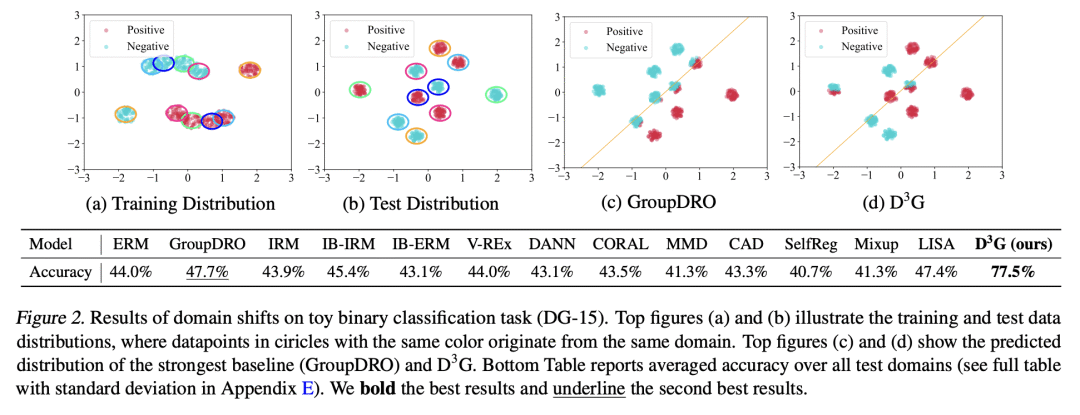
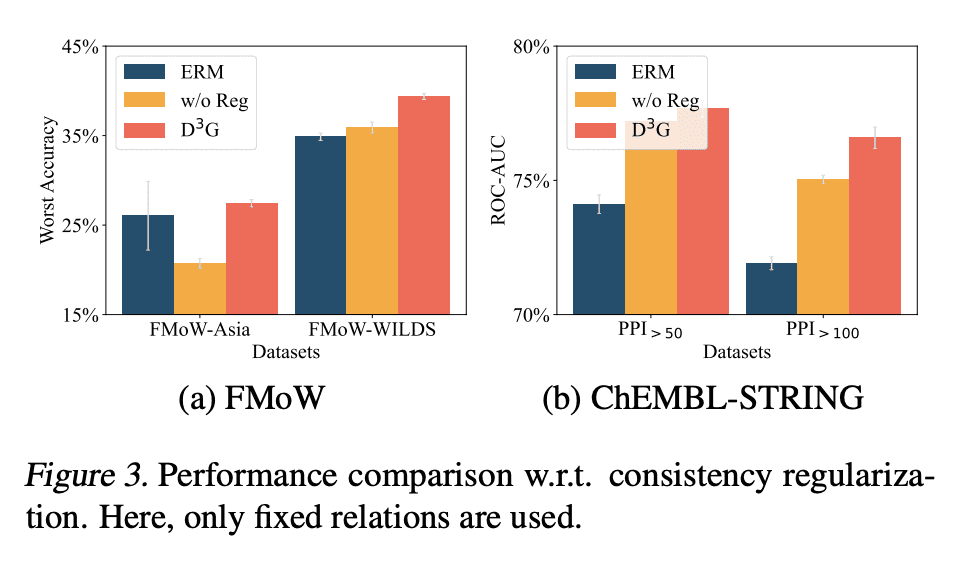
分布漂移是机器学习的一个主要挑战,如果测试分布与训练分布不同,模型在测试阶段往往表现不佳。本文专注于域漂移,即当模型被应用于与它所训练的域不同的新域时发生的漂移,并提出了一种称为 D³G 的新方法。与之前旨在学习一个域不变的单个模型的方法不同,D³G 通过利用不同域之间的关系学习特定域的模型。D³G 在训练阶段学习一组训练域特定函数,并在测试阶段基于域关系对其进行重加权。这些域关系可以直接派生或从固定的域元数据中学习。在温和假设条件下,本文从理论上证明了用域关系来重加权训练域特定函数,与平均化相比,能达到更强的泛化效果。在经验上,本文用玩具和真实世界数据集对 D³G 的有效性进行了评估,这些任务包括温度回归、土地利用分类和分子-蛋白质交互预测。结果表明,D³G 总是优于最先进的方法,其性能平均提高了10.6%。
Distribution shift is a major challenge in machine learning, as models often perform poorly during the test stage if the test distribution differs from the training distribution. In this paper, we focus on domain shifts, which occur when the model is applied to new domains that are different from the ones it was trained on, and propose a new approach called D^3G. Unlike previous approaches that aim to learn a single model that is domain invariant, D^3G learns domain-specific models by leveraging the relations among different domains. Concretely, D^3G learns a set of training-domain-specific functions during the training stage and reweights them based on domain relations during the test stage. These domain relations can be directly derived or learned from fixed domain meta-data. Under mild assumptions, we theoretically proved that using domain relations to reweight training-domain-specific functions achieves stronger generalization compared to averaging them. Empirically, we evaluated the effectiveness of D^3G using both toy and real-world datasets for tasks such as temperature regression, land use classification, and molecule-protein interaction prediction. Our results showed that D^3G consistently outperformed state-of-the-art methods, with an average improvement of 10.6% in performance.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.02609

4、[LG] Hard Prompts Made Easy: Gradient-Based Discrete Optimization for Prompt Tuning and Discovery
Y Wen, N Jain, J Kirchenbauer, M Goldblum, J Geiping…
[University of Maryland & New York University]
轻松生成硬提示: 面向提示调优与发现的基于梯度的离散优化
要点:
-
作者提出一种通过高效的基于梯度的优化学习硬文本提示的简单方案,该方案改编自梯度重投影方案和针对量化网络的大规模离散优化文献; -
所提出的方法在优化硬提示的过程中使用连续的”软”提示作为中间变量,从而实现了鲁棒的优化并促进了提示的探索和发现; -
该方法被用于文本到图像和文本到文本的应用,学到的硬提示在图像生成和语言分类任务中都表现良好。
一句话总结:
提出一种基于梯度的优化方法,为文本到图像和文本到文本的应用生成鲁棒和灵活的硬文本提示。
摘要:
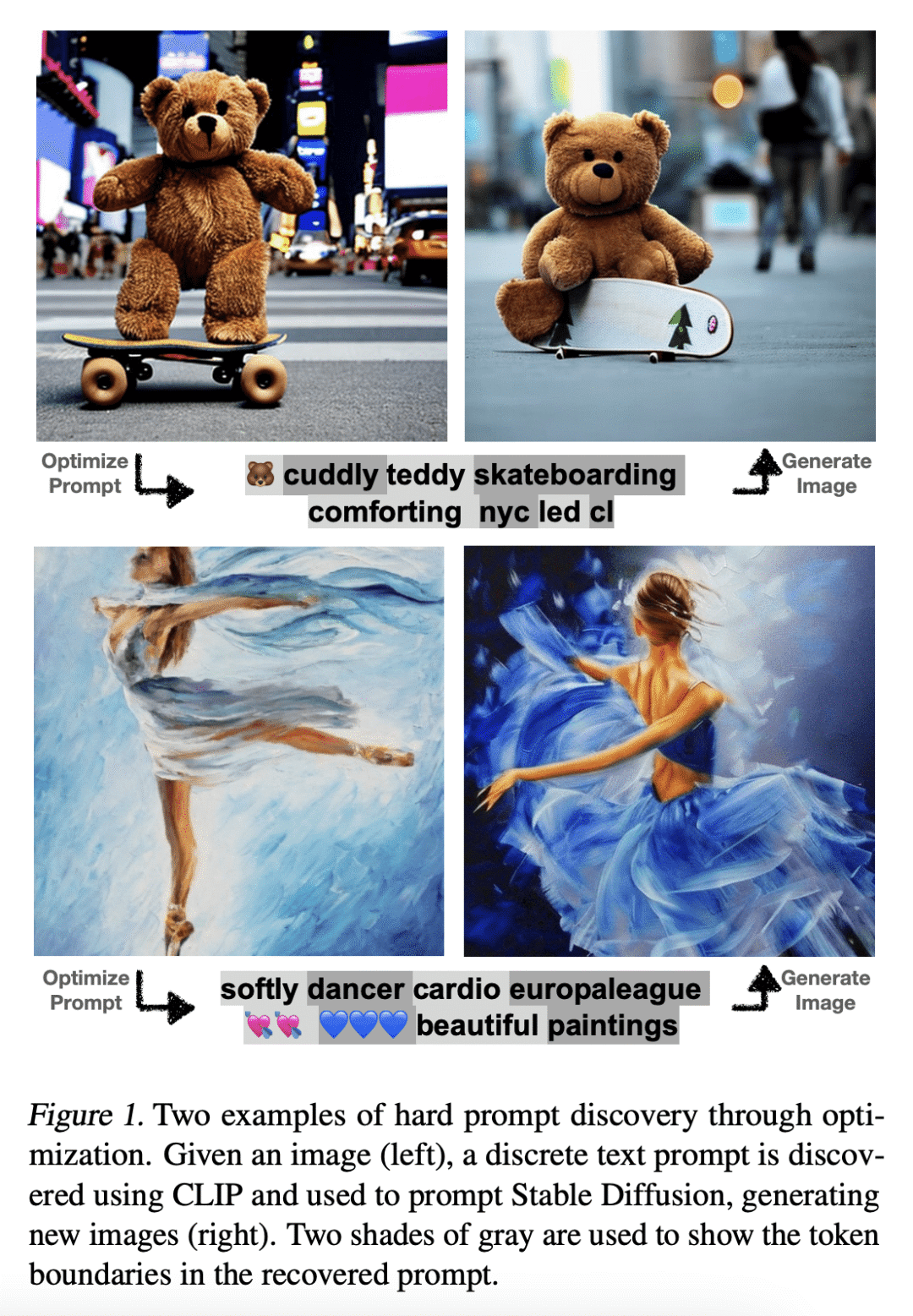
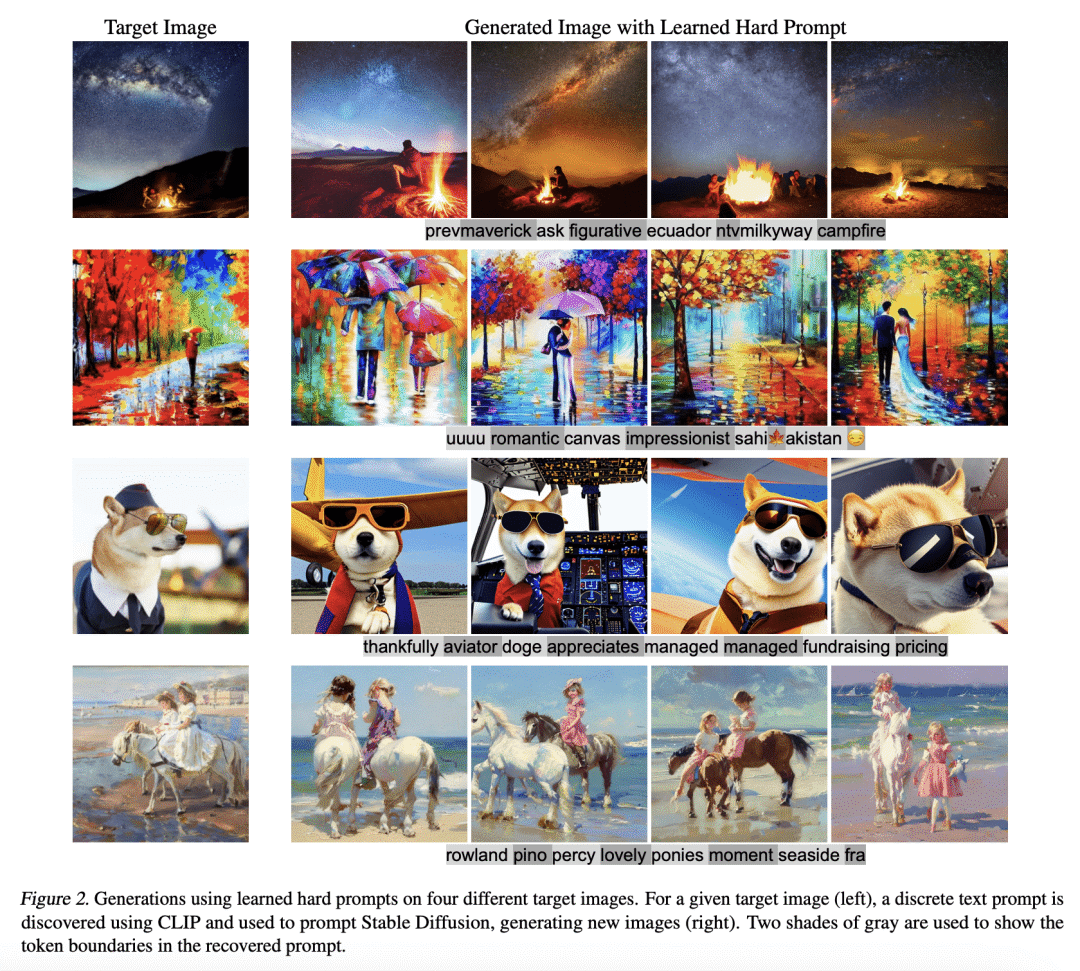
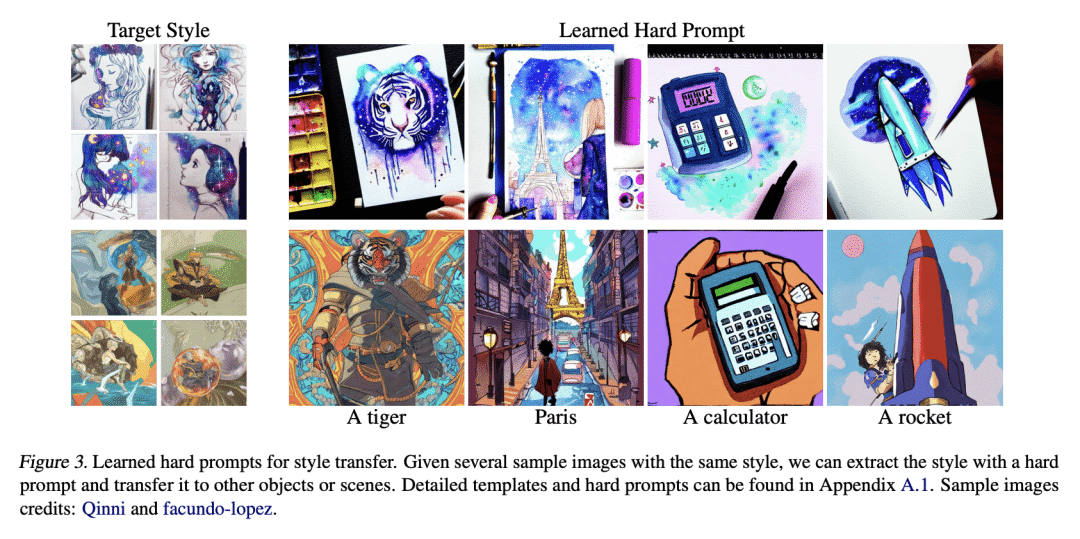
现代生成式模型的优势,在于它们能够通过基于文本的提示进行控制。典型的”硬”提示,是由可解释的词和token组成的,必须由人手工制作。也有一些”软”提示,由连续的特征向量组成。这些可以用强大的优化方法发现,但它们不容易被解释,不容易在不同的模型中重复使用,也不容易插入到基于文本的界面中。本文描述了一种通过有效的基于梯度的优化来鲁棒地优化硬文本提示的方法。该方法为文本到图像和文本到文本的应用自动生成了基于硬文本的提示语。在文本到图像的设置中,该方法为扩散模型创建了硬提示,允许API用户轻松生成、发现、混合和匹配图像概念,而无需事先了解如何提示模型。在文本到文本的设置中,本文表明硬提示可以被自动发现,从而有效地调整语言模型进行分类。
The strength of modern generative models lies in their ability to be controlled through text-based prompts. Typical “hard” prompts are made from interpretable words and tokens, and must be hand-crafted by humans. There are also “soft” prompts, which consist of continuous feature vectors. These can be discovered using powerful optimization methods, but they cannot be easily interpreted, re-used across models, or plugged into a text-based interface.We describe an approach to robustly optimize hard text prompts through efficient gradient-based optimization. Our approach automatically generates hard text-based prompts for both text-to-image and text-to-text applications. In the text-to-image setting, the method creates hard prompts for diffusion models, allowing API users to easily generate, discover, and mix and match image concepts without prior knowledge on how to prompt the model. In the text-to-text setting, we show that hard prompts can be automatically discovered that are effective in tuning LMs for classification.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.03668

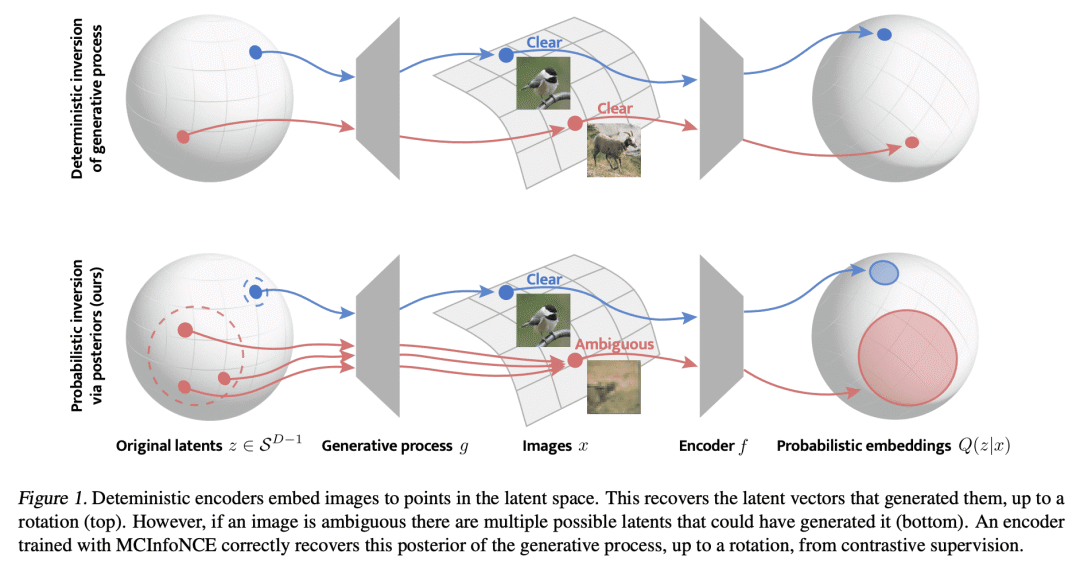
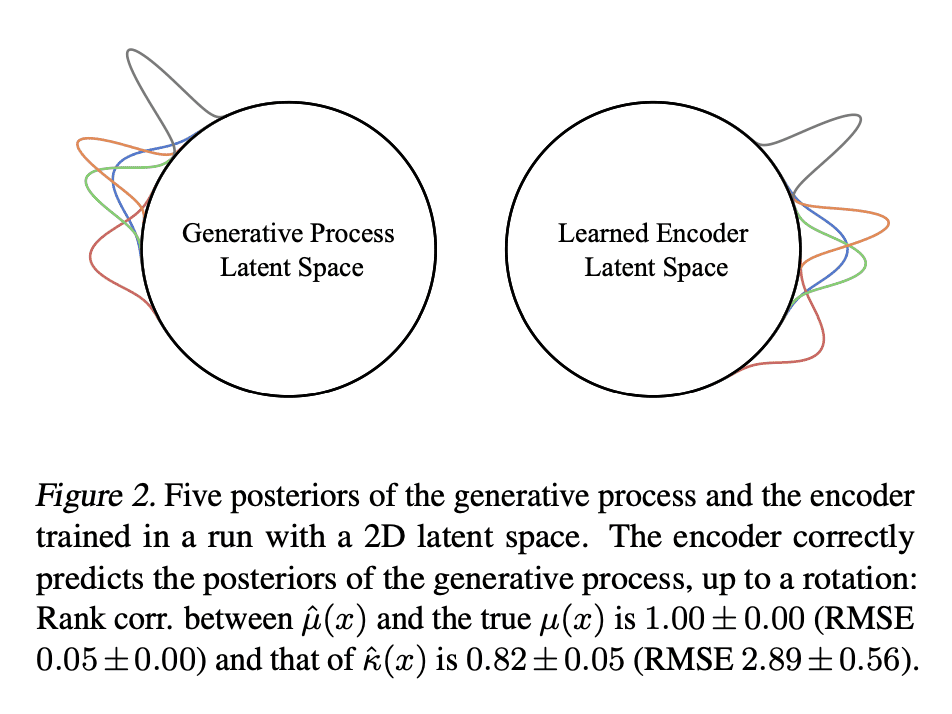
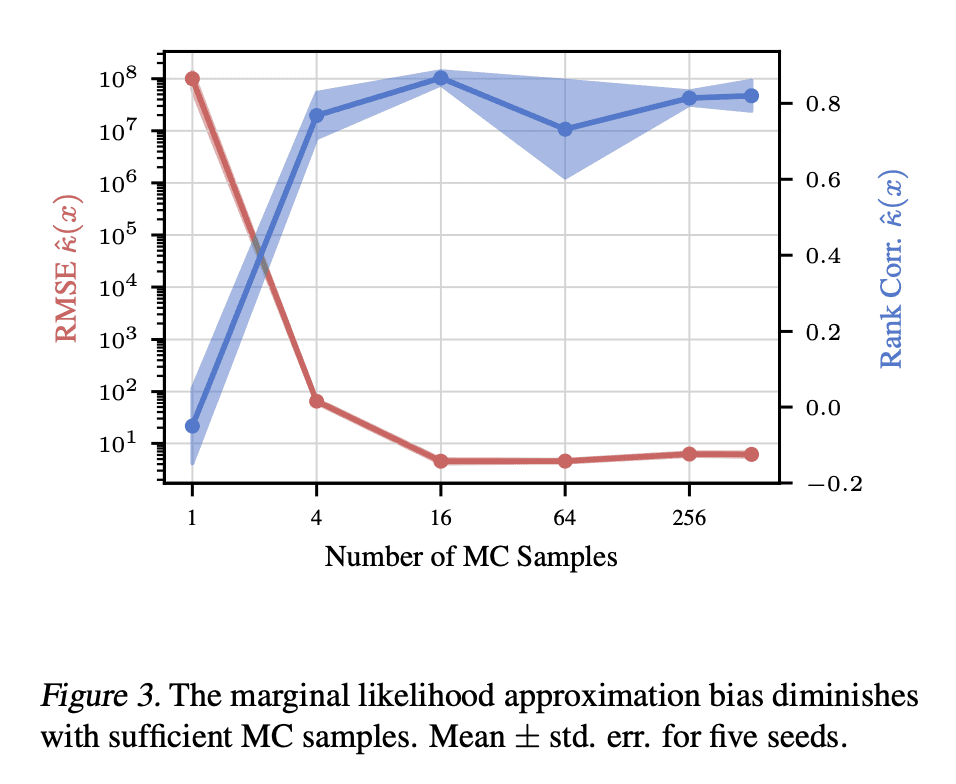
5、[LG] Probabilistic Contrastive Learning Recovers the Correct Aleatoric Uncertainty of Ambiguous Inputs
M Kirchhof, E Kasneci, S J Oh
[University of Tubingen & TUM University]
用概率对比学习恢复模糊性输入的正确后验不确定性
要点:
-
将非线性 ICA 扩展到非主观非决定性生成过程,以模拟输入的模糊性; -
提出 MCInfoNCE,用于训练预测概率嵌入的编码器; -
理论和经验证明,预测的后验是正确的,反映了真正的不确定性。
一句话总结:
提出 MCInfoNCE,一种预测数据生成过程的正确后验的概率性对比损失,并在图像检索中提供校准的不确定性估计和可信区间。
摘要:
对比训练的编码器最近被证明可以反演数据生成过程:将每个输入,例如图像,编码为生成图像的真实潜向量。然而,现实世界的观察往往具有内在的模糊性。例如,图像可能是模糊的,或者只显示一个 3D 物体的 2D 视图,所以可能有多个潜量产生了它们。这使得潜向量的真实后验具有异方差不确定性的概率。在这种情况下,本文扩展了常见的InfoNCE目标和编码器,以预测潜分布而不是点。本文证明,这些分布恢复了数据生成过程的正确后验,包括不确定性水平,直到潜空间的旋转。除了提供校准的不确定性估计外,这些后验允许计算图像检索中的可信区间。包括具有与给定查询相同的潜量的图像,受其不确定性的影响。
Contrastively trained encoders have recently been proven to invert the data-generating process: they encode each input, e.g., an image, into the true latent vector that generated the image (Zimmermann et al., 2021). However, real-world observations often have inherent ambiguities. For instance, images may be blurred or only show a 2D view of a 3D object, so multiple latents could have generated them. This makes the true posterior for the latent vector probabilistic with heteroscedastic uncertainty. In this setup, we extend the common InfoNCE objective and encoders to predict latent distributions instead of points. We prove that these distributions recover the correct posteriors of the data-generating process, including its level of aleatoric uncertainty, up to a rotation of the latent space. In addition to providing calibrated uncertainty estimates, these posteriors allow the computation of credible intervals in image retrieval. They comprise images with the same latent as a given query, subject to its uncertainty.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.02865

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CL] Exploring the Benefits of Training Expert Language Models over Instruction Tuning
J Jang, S Kim, S Ye, D Kim, L Logeswaran, M Lee, K Lee, M Seo [KAIST & LG AI Research] (2023)
训练专家语言模型优于指令微调的收益探索
要点:
-
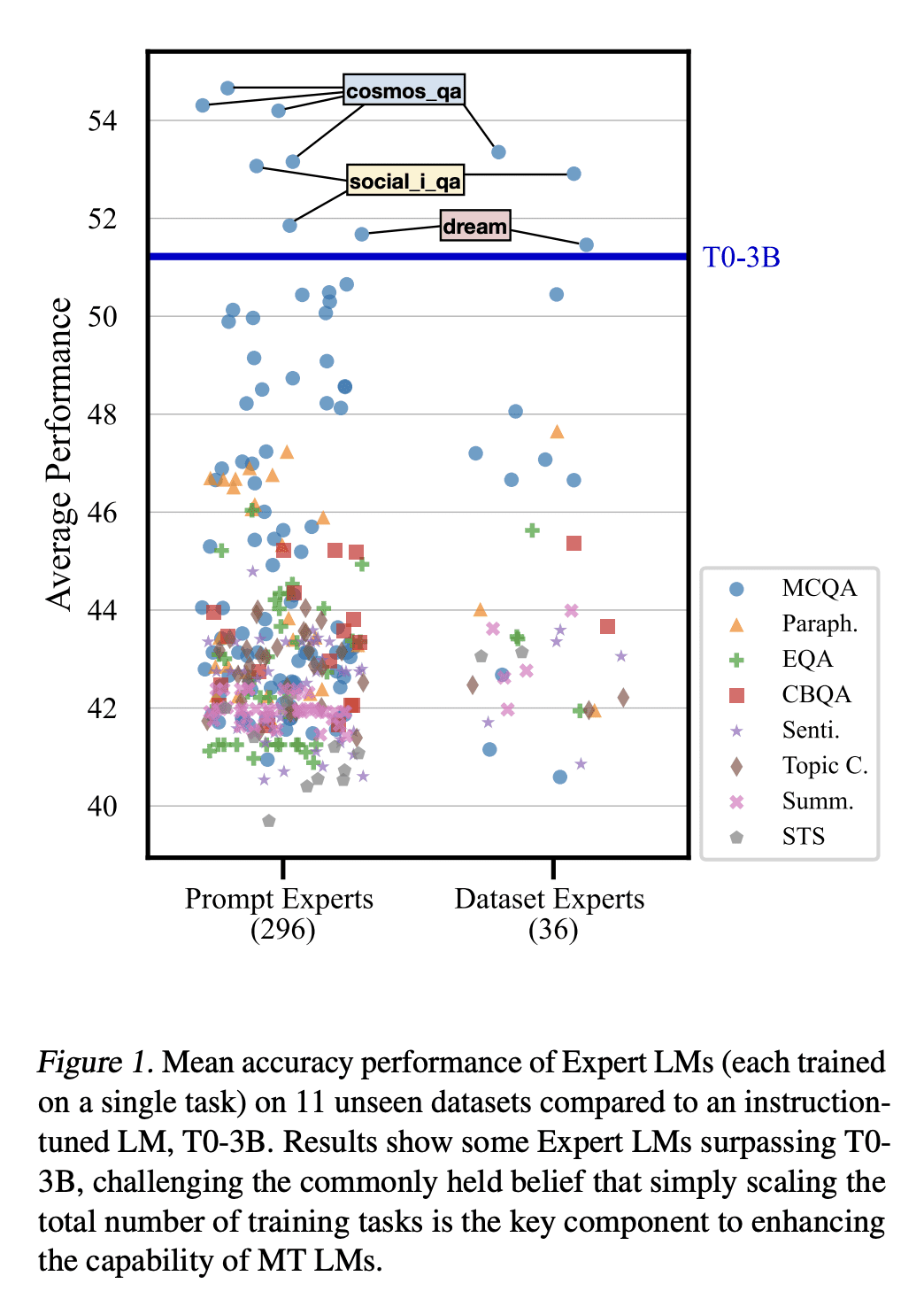
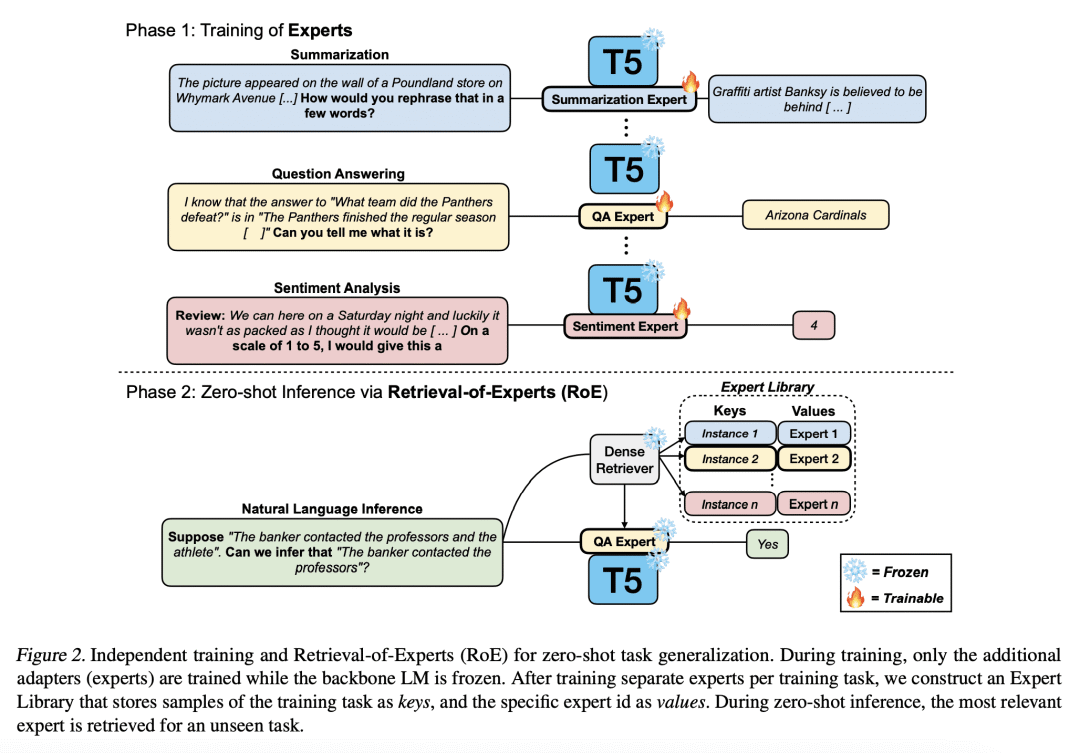
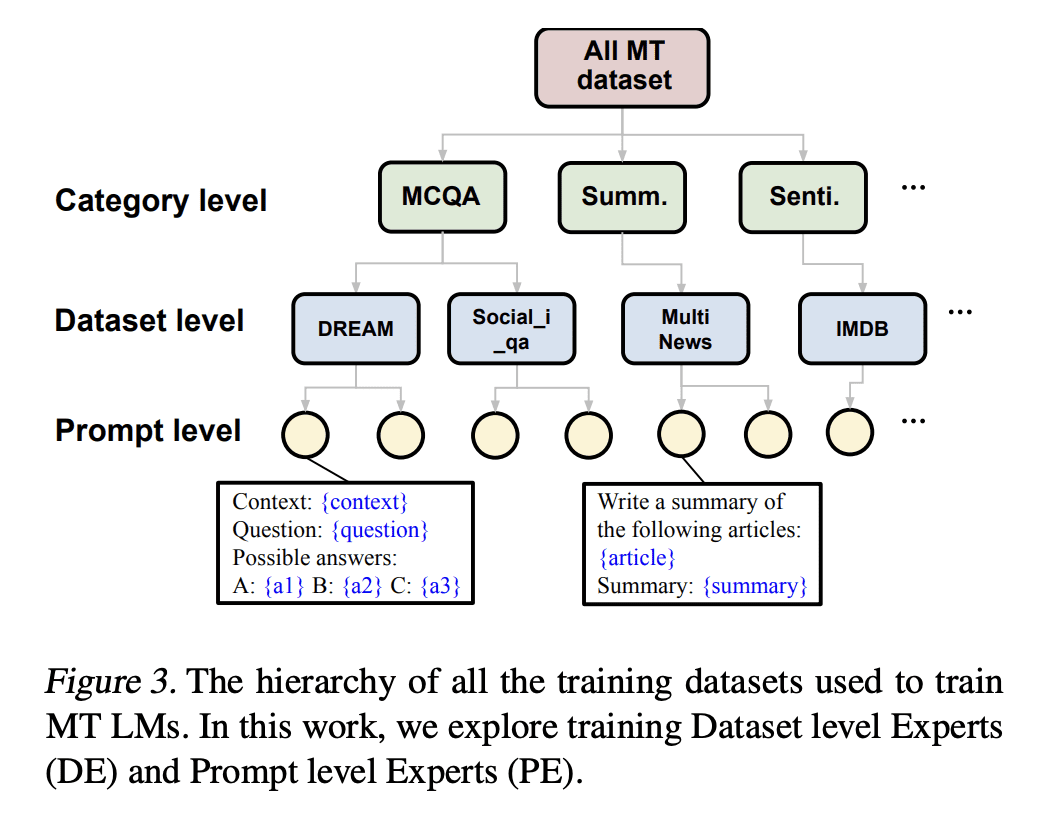
提出了一个出乎意料的发现,在单个任务上进行专家微调的语言模型(LM)可以胜过在几个未见过的数据集上对300多个任务进行训练的多任务微调(MT)LM; -
为每项任务训练一个单独的专家LM,而不是单个MT LM有多种好处,包括避免消极的任务迁移、持续学习新任务和合成能力; -
挑战了以前持有的信念,即简单地扩大训练任务的数量是制造更强大的MT LM的关键。
一句话总结:
单一任务微调 LM 优于多任务提示的微调LM,所提出的训练专家LM的分布式方法有多种好处,包括避免消极的任务迁移和实现持续学习。
Recently, Language Models (LMs) instruction-tuned on multiple tasks, also known as multitask-prompted fine-tuning (MT), have shown the capability to generalize to unseen tasks. Previous work has shown that scaling the number of training tasks is the key component in making stronger MT LMs. In this work, we report an unexpected finding that an expert LM fine-tuned on just a single task can outperform an MT LM trained with 300+ different tasks on 11 different unseen datasets and on 13 datasets of the BIG-bench benchmark by a mean accuracy of 3.20% and 1.29%, respectively. This finding casts doubt on the previously held belief that simply scaling the number of tasks makes stronger MT LMs. Leveraging this finding, we further show that this distributed approach of training a separate expert LM per training task instead of a single MT LM for zero-shot inference possesses many benefits including (1) avoiding negative task transfer that often occurs during instruction tuning, (2) being able to continually learn new tasks without having to re-train on previous tasks to avoid catastrophic forgetting, and (3) showing compositional capabilities when merging individual experts together. The code is available at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.03202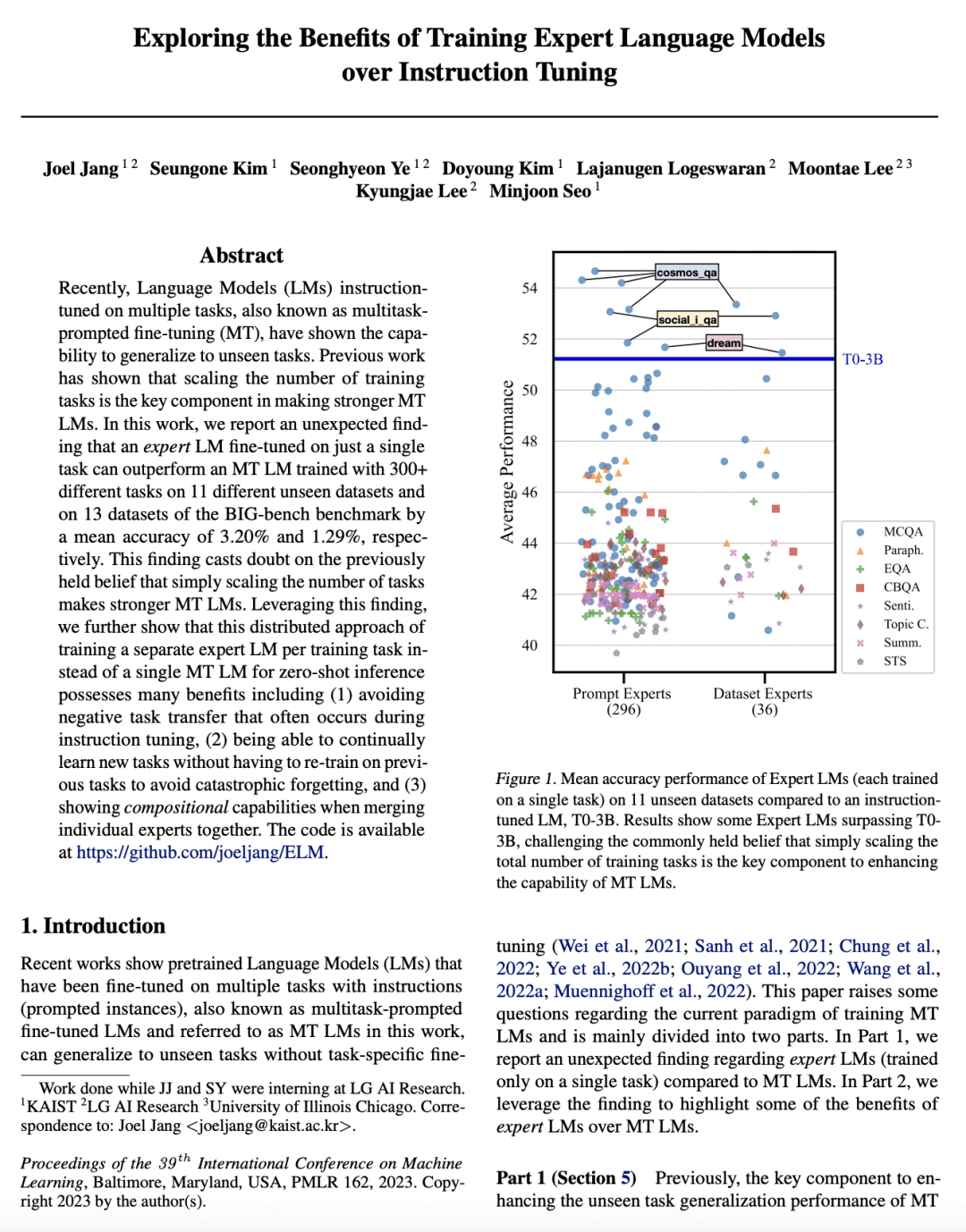
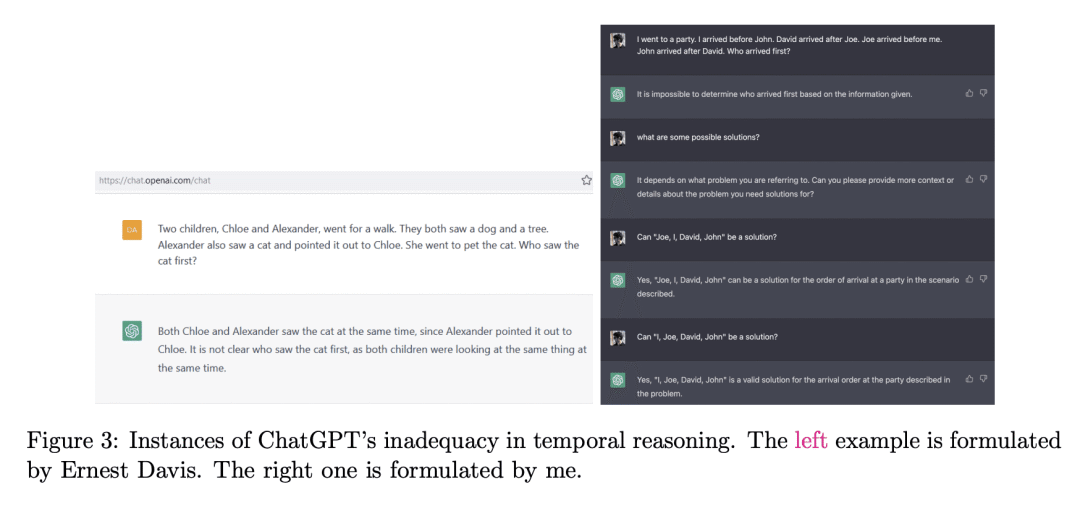
[CL] A Categorical Archive of ChatGPT Failures
A Borji (2023)
ChatGPT失败案例的分类存档
要点:
-
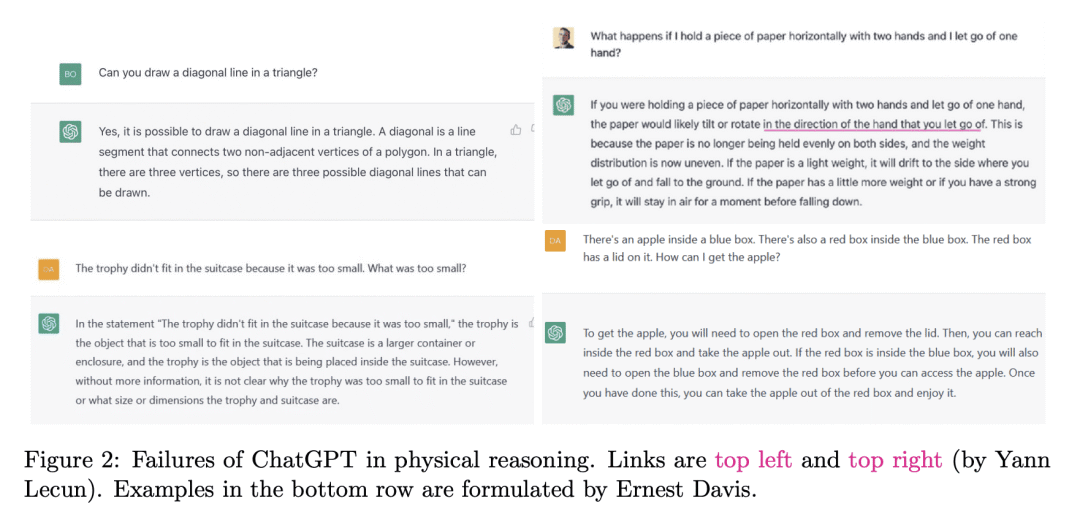
重点关注由 OpenAI 开发的大型语言模型 ChatGPT 的缺点和局限性,对其失败案例进行了全面分析; -
将 ChatGPT 的失败案例分为十个方面,包括推理、事实错误、数学、编程和偏见,并强调了使用 ChatGPT 的风险、限制和社会影响; -
提出 ChatGPT 和其他大型语言模型的可靠性和可信度,及其捕捉人类思维的能力问题。 -
强调了进一步改进 ChatGPT 的必要性,如表明其反应的可信度,探索使用这些模型的道德和社会后果,并建立一个评估聊天机器人进展的参考点。
一句话总结:
重点讨论了由OpenAI开发的语言模型ChatGPT的局限性和失败案例,分析了ChatGPT失败的各种情况,并强调了使用该模型的风险、限制和社会影响,目标是协助研究人员和开发人员加强未来的语言模型和聊天机器人。
Large language models have been demonstrated to be valuable in different fields. ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, has been trained using massive amounts of data and simulates human conversation by comprehending context and generating appropriate responses. It has garnered significant attention due to its ability to effectively answer a broad range of human inquiries, with fluent and comprehensive answers surpassing prior public chatbots in both security and usefulness. However, a comprehensive analysis of ChatGPT’s failures is lacking, which is the focus of this study. Ten categories of failures, including reasoning, factual errors, math, coding, and bias, are presented and discussed. The risks, limitations, and societal implications of ChatGPT are also highlighted. The goal of this study is to assist researchers and developers in enhancing future language models and chatbots.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.03494


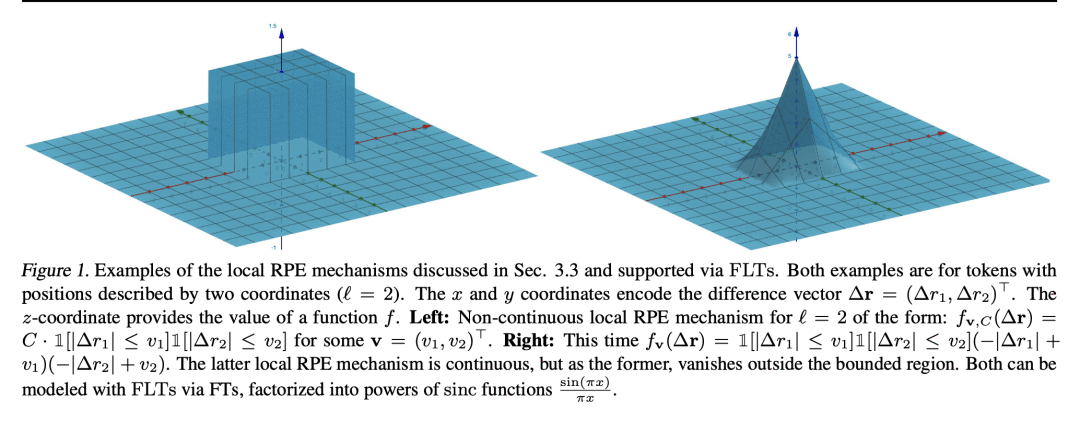
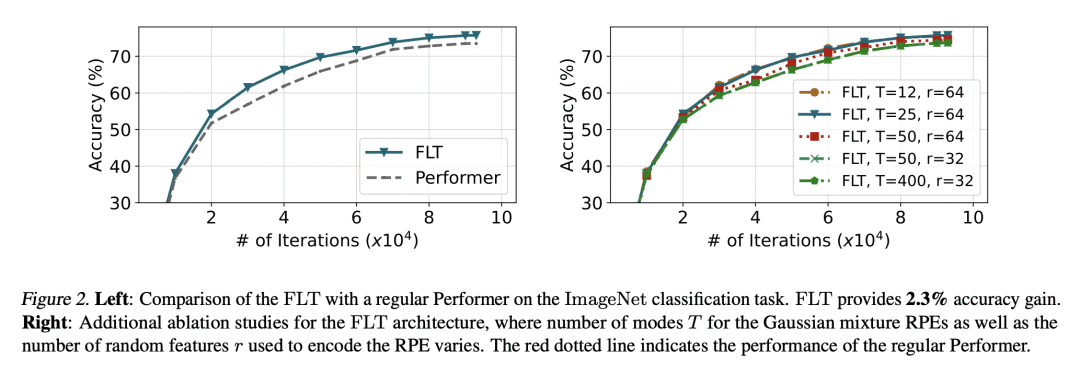
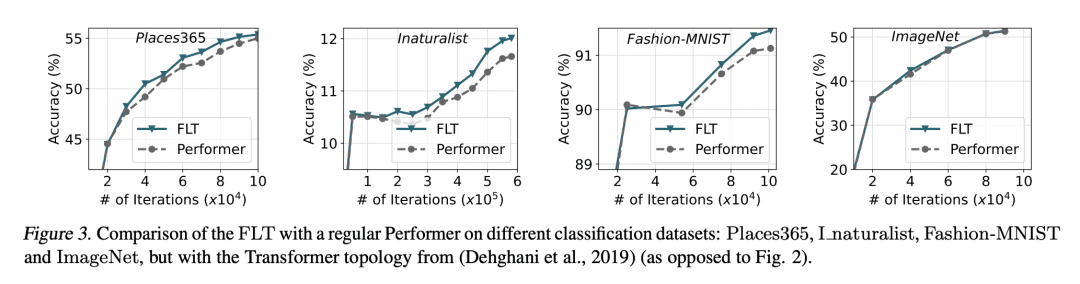
[LG] Learning a Fourier Transform for Linear Relative Positional Encodings in Transformers
K M Choromanski, S Li, V Likhosherstov, K A Dubey, S Luo, D He, Y Yang, T Sarlos, T Weingarten, A Weller [Google Research & CMU & University of Cambridge & Peking University] (2023)
Transformer线性相对位置编码的傅里叶变换学习
要点:
-
提出 FourierLearner-Transformers(FLT),一类新的线性 Transformer,包含了一系列的相对位置编码(RPE)机制; -
最优 RPE 机制是通过在 FLT 中学习其频谱表示而隐式构建的,保持了实际的内存使用,并允许使用结构性归纳偏差技术; -
在各种任务和数据模态上对 FLT 进行了广泛的经验评估,包括语言建模、图像分类和 3D 分子特性预测。 -
与其他线性 Transformer 相比,FLT 提供了准确的结果,其中局部 RPE 变体在语言建模任务中取得了最佳性能。
一句话总结:
提出 FLT,一类新的基于 RPE 增强的线性注意力的 Transformer,与其他线性 Transformer 相比,具有更好的准确性和多功能性,并且是第一个为 3D 数据提供这种能力的 Transformer。
We propose a new class of linear Transformers called FourierLearner-Transformers (FLTs), which incorporate a wide range of relative positional encoding mechanisms (RPEs). These include regular RPE techniques applied for nongeometric data, as well as novel RPEs operating on the sequences of tokens embedded in higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces (e.g. point clouds). FLTs construct the optimal RPE mechanism implicitly by learning its spectral representation. As opposed to other architectures combining efficient low-rank linear attention with RPEs, FLTs remain practical in terms of their memory usage and do not require additional assumptions about the structure of the RPE-mask. FLTs allow also for applying certain structural inductive bias techniques to specify masking strategies, e.g. they provide a way to learn the so-called local RPEs introduced in this paper and providing accuracy gains as compared with several other linear Transformers for language modeling. We also thoroughly tested FLTs on other data modalities and tasks, such as: image classification and 3D molecular modeling. For 3D-data FLTs are, to the best of our knowledge, the first Transformers architectures providing RPE-enhanced linear attention.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.01925

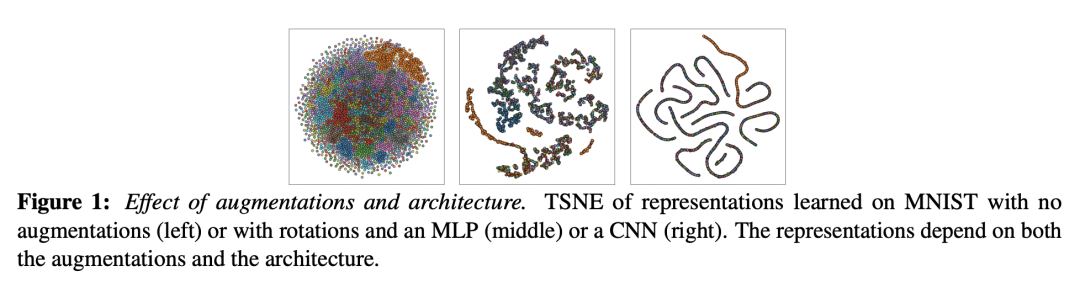
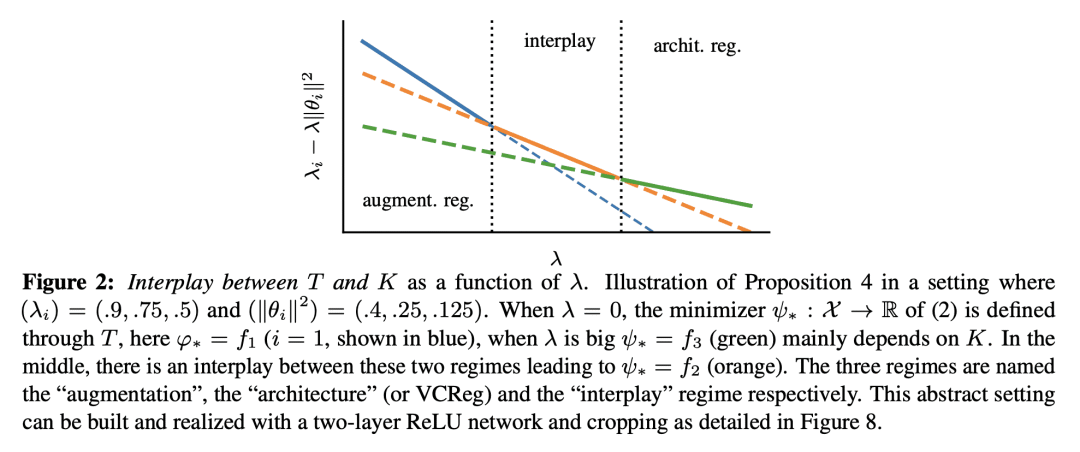
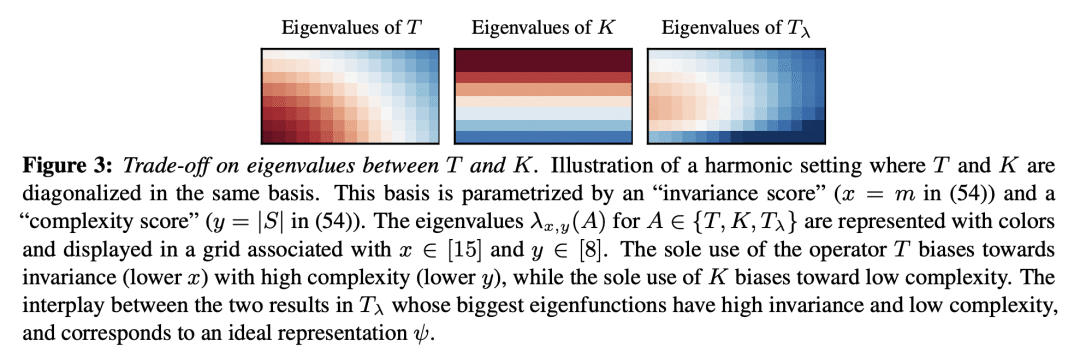
[LG] The SSL Interplay: Augmentations, Inductive Bias, and Generalization
V Cabannes, B T. Kiani, R Balestriero, Y LeCun, A Bietti [Meta AI & MIT] (2023)
自监督学习的相互作用:增强、归纳偏差和泛化
要点:
-
提出一个理论框架,用于研究自监督学习(SSL)中数据增强、网络结构和训练算法之间的相互作用; -
框架包括两个中心积分算子,一个是输入分布和增量的选择,另一个是计算模型的归纳偏差; -
对下游泛化误差提供了新的、更清晰的界,可处理分布漂移,并通过凸分析工具对预训练超额风险提供了新的泛化界。 -
为 SSL 提供了实用的见解,即预训练中的设计选择如何影响下游的性能以及如何避免表示的坍缩。
一句话总结:
提供了新的关于泛化误差和预训练超额风险的界,强调了增强、架构和正则化在形成表示中的作用,并为SSL提供了实用的见解。
Self-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged as a powerful framework to learn representations from raw data without supervision. Yet in practice, engineers face issues such as instability in tuning optimizers and collapse of representations during training. Such challenges motivate the need for a theory to shed light on the complex interplay between the choice of data augmentation, network architecture, and training algorithm. We study such an interplay with a precise analysis of generalization performance on both pretraining and downstream tasks in a theory friendly setup, and highlight several insights for SSL practitioners that arise from our theory.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.02774







 ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.



