1、[CL] Crawling the Internal Knowledge-Base of Language Models
2、[LG] Contrastive Meta-Learning for Partially Observable Few-Shot Learning
3、[RO] Emergence of Maps in the Memories of Blind Navigation Agents
4、[CV] BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models
5、[LG] PADL: Language-Directed Physics-Based Character Control
摘要:爬取语言模型内在知识库、面向部分可观察少样本学习的对比元学习、盲目导航智能体记忆中地图的涌现、基于冻结图像编码器和大语言模型的Bootstrapping语言图像预训练、语言引导的基于物理角色控制
1、[CL] Crawling the Internal Knowledge-Base of Language Models
R Cohen, M Geva, J Berant, A Globerson
[Tel Aviv University & Allen Institute for AI]
爬取语言模型内在知识库
要点:
一句话总结:
提出一种从语言模型中提取结构化知识图谱的方法,用GPT-3的高精度结果证明了其有效性。
摘要:
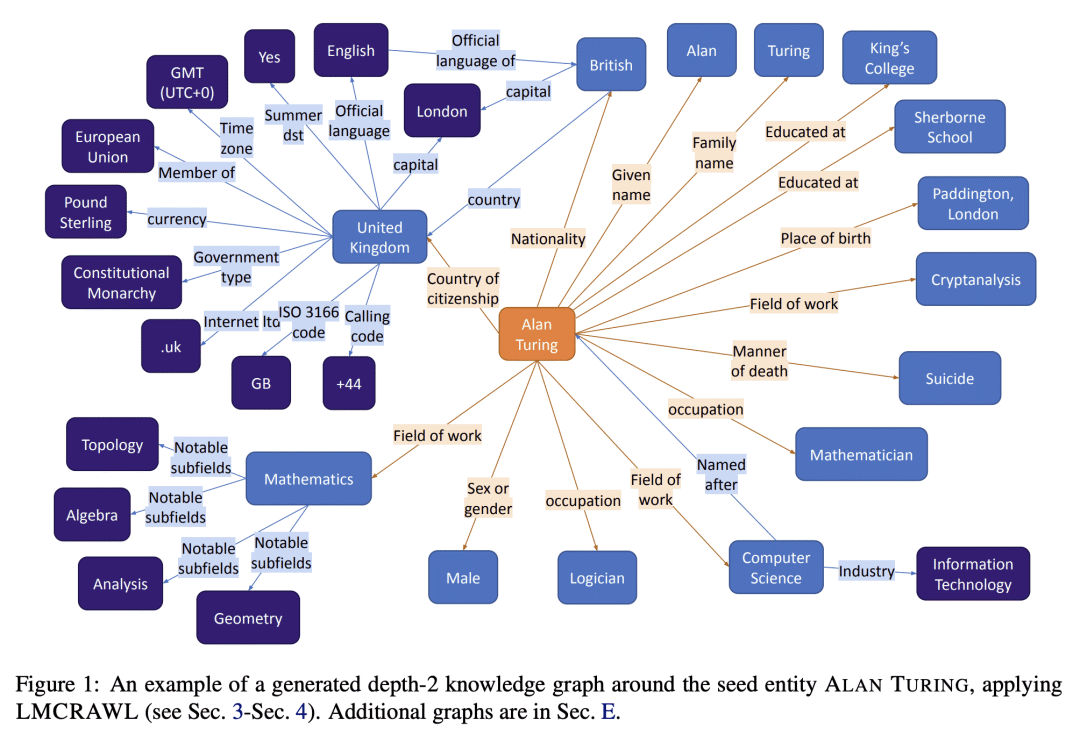
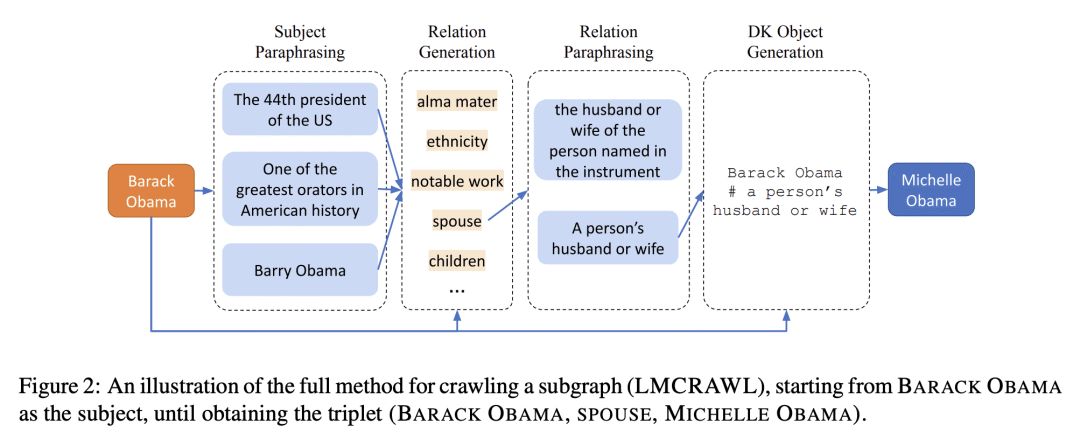
语言模型是在大量文本上训练出来的,因此它们的参数可能包含大量的事实性知识。由这些模型执行的任何下游任务都隐含地建立在这些事实的基础上,因此,非常希望有办法以可解释的方式表示这个知识体系。然而,目前还没有这样的表述机制。本文建议通过从一个给定的语言模型中提取事实的知识图谱来实现这一目标。本文描述了一个”爬取”语言模型内部知识库的程序。具体来说,给定一个种子实体,围绕它展开一个知识图谱。爬取程序被分解为子任务,通过特别设计的提示来实现,这些提示控制了精确度(即没有产生错误的事实)和召回率(即产生的事实的数量)。本文对从几十个种子实体开始抓取的图谱进行了评估,结果显示其产生了高精确度的图谱(82-92%),同时每个实体产生了合理数量的事实。
Language models are trained on large volumes of text, and as a result their parameters might contain a significant body of factual knowledge. Any downstream task performed by these models implicitly builds on these facts, and thus it is highly desirable to have means for representing this body of knowledge in an interpretable way. However, there is currently no mechanism for such a representation. Here, we propose to address this goal by extracting a knowledge-graph of facts from a given language model. We describe a procedure for “crawling” the internal knowledge-base of a language model. Specifically, given a seed entity, we expand a knowledge-graph around it. The crawling procedure is decomposed into sub-tasks, realized through specially designed prompts that control for both precision (i.e., that no wrong facts are generated) and recall (i.e., the number of facts generated). We evaluate our approach on graphs crawled starting from dozens of seed entities, and show it yields high precision graphs (82-92%), while emitting a reasonable number of facts per entity.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12810


2、[LG] Contrastive Meta-Learning for Partially Observable Few-Shot Learning
A Jelley, A Storkey, A Antoniou, S Devlin
[University of Edinburgh & Microsoft Research Cambridge]
面向部分可观察少样本学习的对比元学习
要点:
-
提出部分观察专家建模(POEM),一种对比元学习方法,用于在部分可观察的环境中进行少样本学习; -
利用表征的不确定性,使观察在POEM中只为表征向量的一部分提供信息; -
在Meta-Dataset的改编上对POEM进行了全面的实验评估,证明了它在从部分观测中进行表征学习方面比标准基线更有优势。
一句话总结:
部分观察专家建模(POEM)是一种针对少样本学习的对比元学习方法,允许使用概率形式化在部分可观察性下进行表示学习。
摘要:
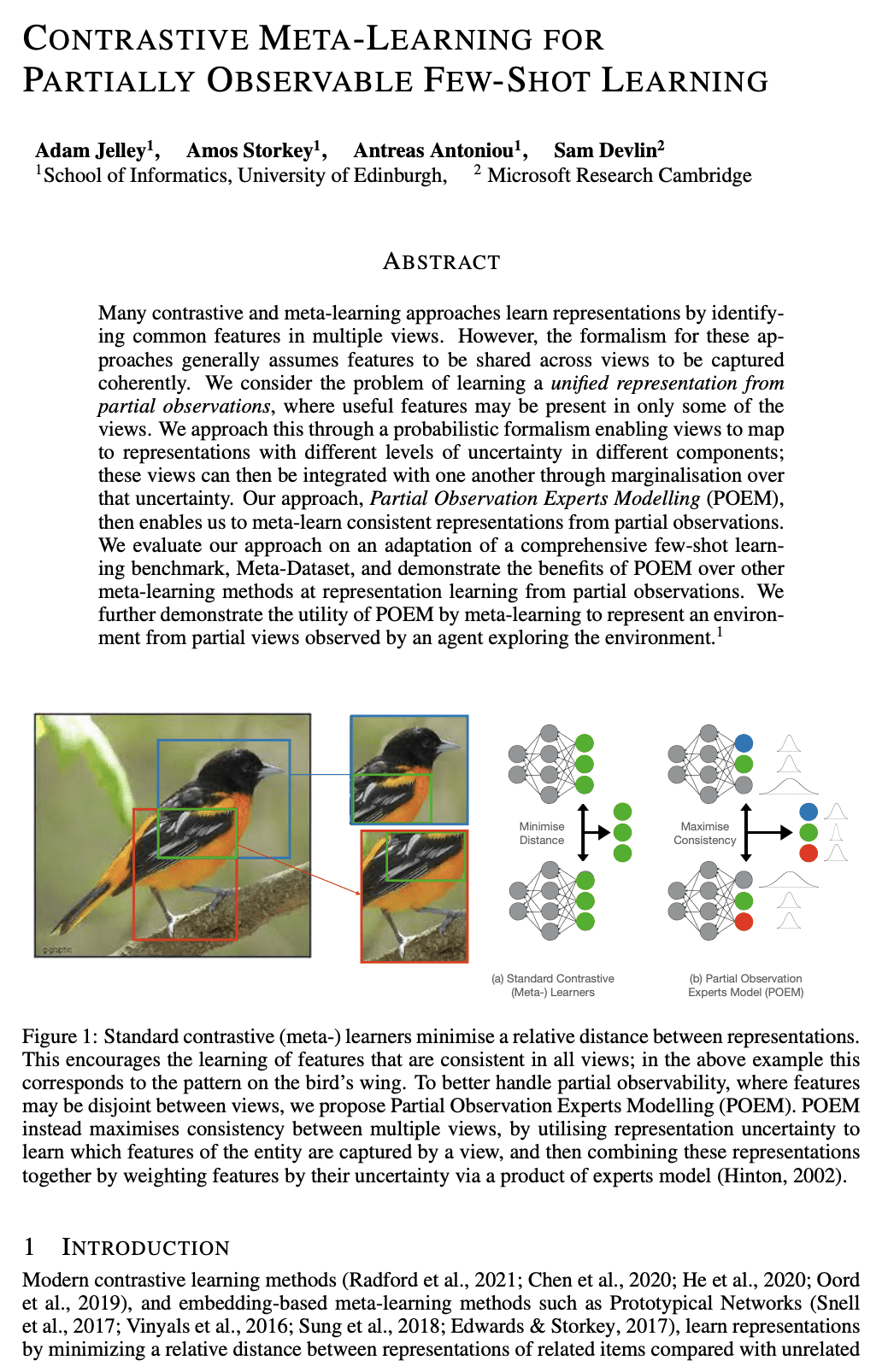
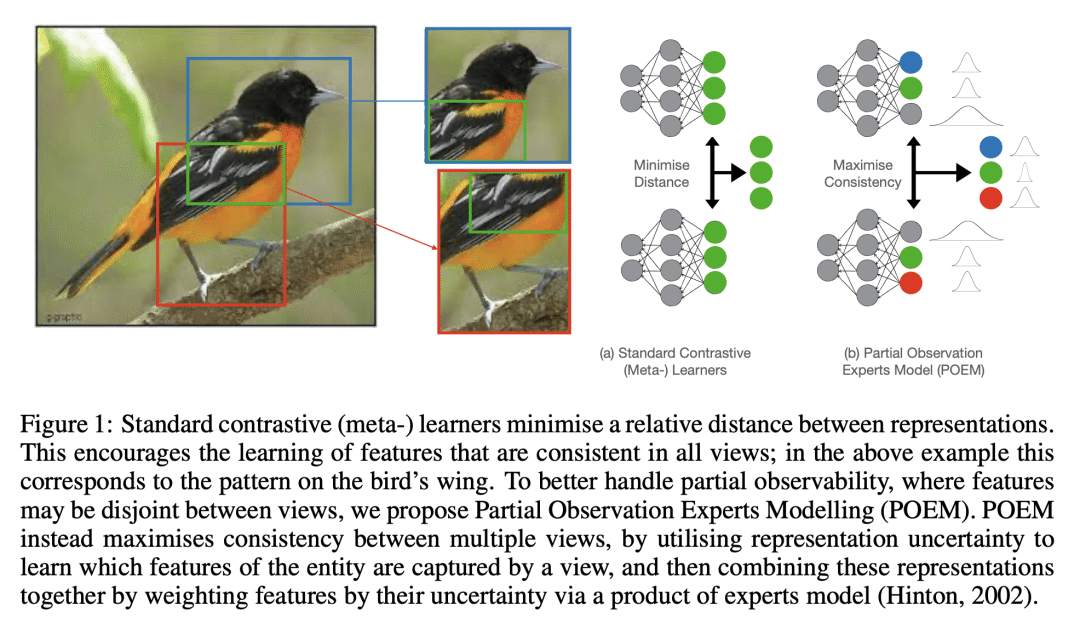
许多对比性和元学习方法,通过识别多个视图的共同特征来学习表征。然而,这些方法的形式化一般都假设不同的视图有共同的特征,以便连贯地捕获。本文考虑从部分观察中学习统一表征的问题,其中有用的特征可能只存在某些视图中。通过一个概率形式化来处理该问题,使视图能够映射到不同成分中具有不同不确定性的表示;然后这些视图可以通过对不确定性的边际化来相互整合。所提出的方法,即部分观察专家建模(POEM),使得能从部分观察中元学习一致表示。对该方法进行了评估,并证明POEM比其他元学习方法在从部分观测中学习表征方面的优势。本文进一步证明了POEM的实用性,即通过元学习从探索环境的智能体所观察到的部分视图来表示环境。
Many contrastive and meta-learning approaches learn representations by identifying common features in multiple views. However, the formalism for these approaches generally assumes features to be shared across views to be captured coherently. We consider the problem of learning a unified representation from partial observations, where useful features may be present in only some of the views. We approach this through a probabilistic formalism enabling views to map to representations with different levels of uncertainty in different components; these views can then be integrated with one another through marginalisation over that uncertainty. Our approach, Partial Observation Experts Modelling (POEM), then enables us to meta-learn consistent representations from partial observations. We evaluate our approach on an adaptation of a comprehensive few-shot learning benchmark, Meta-Dataset, and demonstrate the benefits of POEM over other meta-learning methods at representation learning from partial observations. We further demonstrate the utility of POEM by meta-learning to represent an environment from partial views observed by an agent exploring the environment.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13136

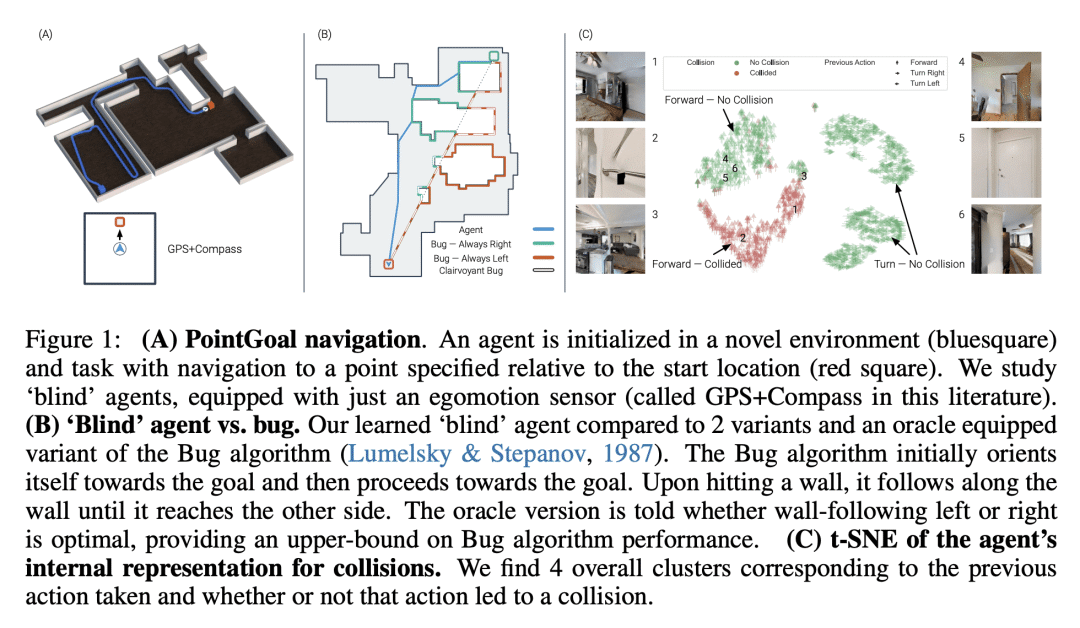
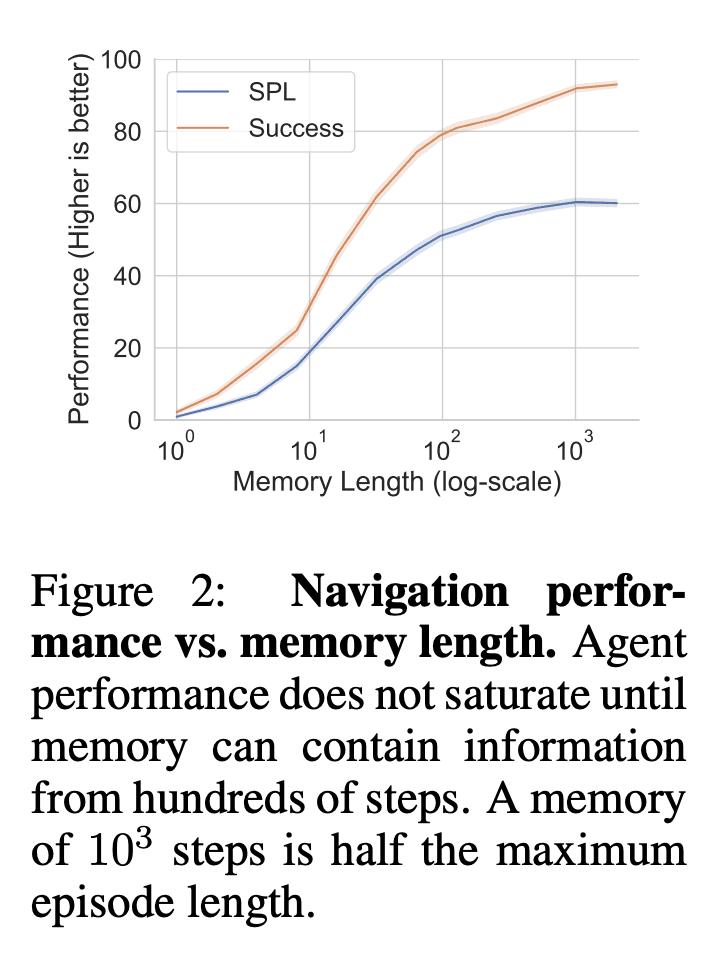
3、[RO] Emergence of Maps in the Memories of Blind Navigation Agents
E Wijmans, M Savva, I Essa, S Lee, A S. Morcos, D Batra
[Georgia Institute of Technology & Meta AI & Oregon State University]
盲目导航智能体记忆中地图的涌现
要点:
-
盲目AI导航智能体可以只使用自我运动感应,来有效地导航新环境,成功率达到95%,最佳路径效率达到62.9%; -
记忆是使这些智能体取得强大导航性能的机制。无记忆的智能体在任务中失败,而有记忆的智能体则使用储存的广大的时间和空间范围内的信息; -
盲目智能体仅通过学习导航来学习建立和使用其环境的隐性地图状表征。将偶发记忆从一个智能体移植到另一个智能体身上会带来更好的导航,因为植入记忆的探针智能体会走捷径。 -
新出现的地图是任务依赖性和选择性的,只保留与导航目标相关的环境特征。这就解释了为什么移植记忆会导致走捷径,因为偏离和绕道的情况会被遗忘。
一句话总结:
盲目AI导航智能体可以通过强化学习只用自我运动感应和记忆来有效地进行导航,其表征会涌现隐性地图,证明地图可能是智能具身智能体导航的一个自然解决方案。
摘要:
动物导航研究表明,生物体会建立并维持其环境的内在空间表征,或地图。本文要问的是,机器——特别是人工智能(AI)导航智能体——是否也会建立隐性(或“心理”)地图。对这个问题的肯定回答将 (a) 解释最近文献中令人惊讶的现象,即表面上没有地图的神经网络取得了强大的性能,以及 (b) 加强映射作为智能具身智能体导航的基本机制的证据,不管是生物还是人工。与动物导航不同的是,可以明智地设计智能体的感知系统,并控制学习范式,使其他导航机制失效。本文训练”盲目”智能体——感知仅限于自我运动,没有其他任何类型的感知——通过强化学习进行 PointGoal 导航(”去到 Δ x, Δ y”)。该智能体由导航无关的组件(全连接和递归神经网络)组成,所用实验设置没有提供对映射的归纳偏差。尽管有这些苛刻的条件,结果发现盲目智能体式是 (1) 在新环境中令人惊讶地有效的导航器(~95%的成功率);(2) 在很长的范围内利用记忆(在一轮中记住~1,000步的过往经验)。(3) 这种记忆使它们能够表现出智能行为(跟随墙壁,检测碰撞,走捷径);(4) 盲目智能体在导航时建立的环境表征中出现了地图和碰撞检测神经元;(5) 出现的地图是有选择性的,而且是依赖于任务的(例如,智能体”忘记”了探索性的迂回路线)。总的来说,本文没有提供新的技术,但提出了一个令人惊讶的发现、一个洞察力和一个解释。
Animal navigation research posits that organisms build and maintain internal spatial representations, or maps, of their environment. We ask if machines — specifically, artificial intelligence (AI) navigation agents — also build implicit (or ‘mental’) maps. A positive answer to this question would (a) explain the surprising phenomenon in recent literature of ostensibly map-free neural-networks achieving strong performance, and (b) strengthen the evidence of mapping as a fundamental mechanism for navigation by intelligent embodied agents, whether they be biological or artificial. Unlike animal navigation, we can judiciously design the agent’s perceptual system and control the learning paradigm to nullify alternative navigation mechanisms. Specifically, we train ‘blind’ agents — with sensing limited to only egomotion and no other sensing of any kind — to perform PointGoal navigation (‘go to Δ x, Δ y’) via reinforcement learning. Our agents are composed of navigation-agnostic components (fully-connected and recurrent neural networks), and our experimental setup provides no inductive bias towards mapping. Despite these harsh conditions, we find that blind agents are (1) surprisingly effective navigators in new environments (~95% success); (2) they utilize memory over long horizons (remembering ~1,000 steps of past experience in an episode); (3) this memory enables them to exhibit intelligent behavior (following walls, detecting collisions, taking shortcuts); (4) there is emergence of maps and collision detection neurons in the representations of the environment built by a blind agent as it navigates; and (5) the emergent maps are selective and task dependent (e.g. the agent ‘forgets’ exploratory detours). Overall, this paper presents no new techniques for the AI audience, but a surprising finding, an insight, and an explanation.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13261


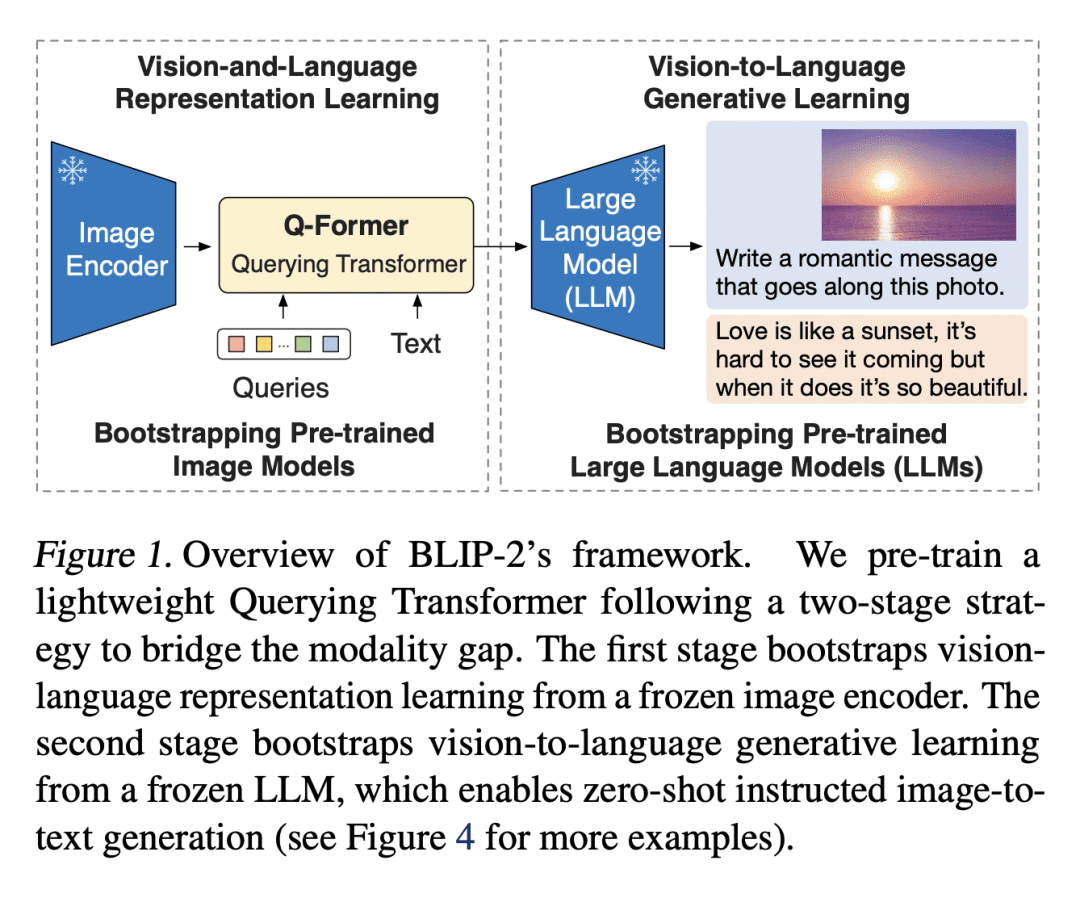
4、[CV] BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models
J Li, D Li, S Savarese, S Hoi
[Salesforce Research]
BLIP-2: 基于冻结图像编码器和大语言模型的Bootstrapping语言图像预训练
要点:
-
提出 BLIP-2,一种通用的、高效的视觉和语言预训练策略,利用了冻结的预训练图像编码器和大型语言模型(LLMs); -
使用轻量查询 Transformer(Q-Former)来弥补模态之间的差距,分两个阶段进行预训练:从冻结的图像编码器中进行表示学习,从冻结的语言模型中进行生成学习; -
在各种视觉语言任务上的最先进的表现,包括视觉问题回答、图像描述和图像-文本检索。
一句话总结:
BLIP-2是一种低成本高性能的视觉-语言预训练策略,利用了冻结的预训练图像编码器和大型语言模型,展示出在零样本图像-文本生成方面的新兴能力。
摘要:
由于大规模模型的端到端训练,视觉和语言预训练的成本已经变得越来越高。本文提出 BLIP-2,一个通用的、高效的预训练策略,从现成的冻结预训练图像编码器和冻结的大型语言模型中 bootstrap 视觉-语言预训练。BLIP-2通过一个轻量的查询 Transformer 弥补了模式上的差距,该 Transformer 分两个阶段进行预训练。第一阶段从冻结的图像编码器引导视觉-语言表示学习。第二阶段从冻结的语言模型 bootstrap 视觉到语言的生成学习。BLIP-2 在各种视觉-语言任务上取得了最先进的性能,尽管它的可训练参数比现有方法少得多。例如,所提出模型在零样本 VQAv2 上比 Flamingo80B 高出 8.7%,而可训练参数却少了54倍。本文还展示了该模型的新能力,可遵循自然语言指令的零样本图像到文本的生成。
The cost of vision-and-language pre-training has become increasingly prohibitive due to end-to-end training of large-scale models. This paper proposes BLIP-2, a generic and efficient pre-training strategy that bootstraps vision-language pre-training from off-the-shelf frozen pre-trained image encoders and frozen large language models. BLIP-2 bridges the modality gap with a lightweight Querying Transformer, which is pre-trained in two stages. The first stage bootstraps vision-language representation learning from a frozen image encoder. The second stage bootstraps vision-to-language generative learning from a frozen language model. BLIP-2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various vision-language tasks, despite having significantly fewer trainable parameters than existing methods. For example, our model outperforms Flamingo80B by 8.7% on zero-shot VQAv2 with 54x fewer trainable parameters. We also demonstrate the model’s emerging capabilities of zero-shot image-to-text generation that can follow natural language instructions.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12597



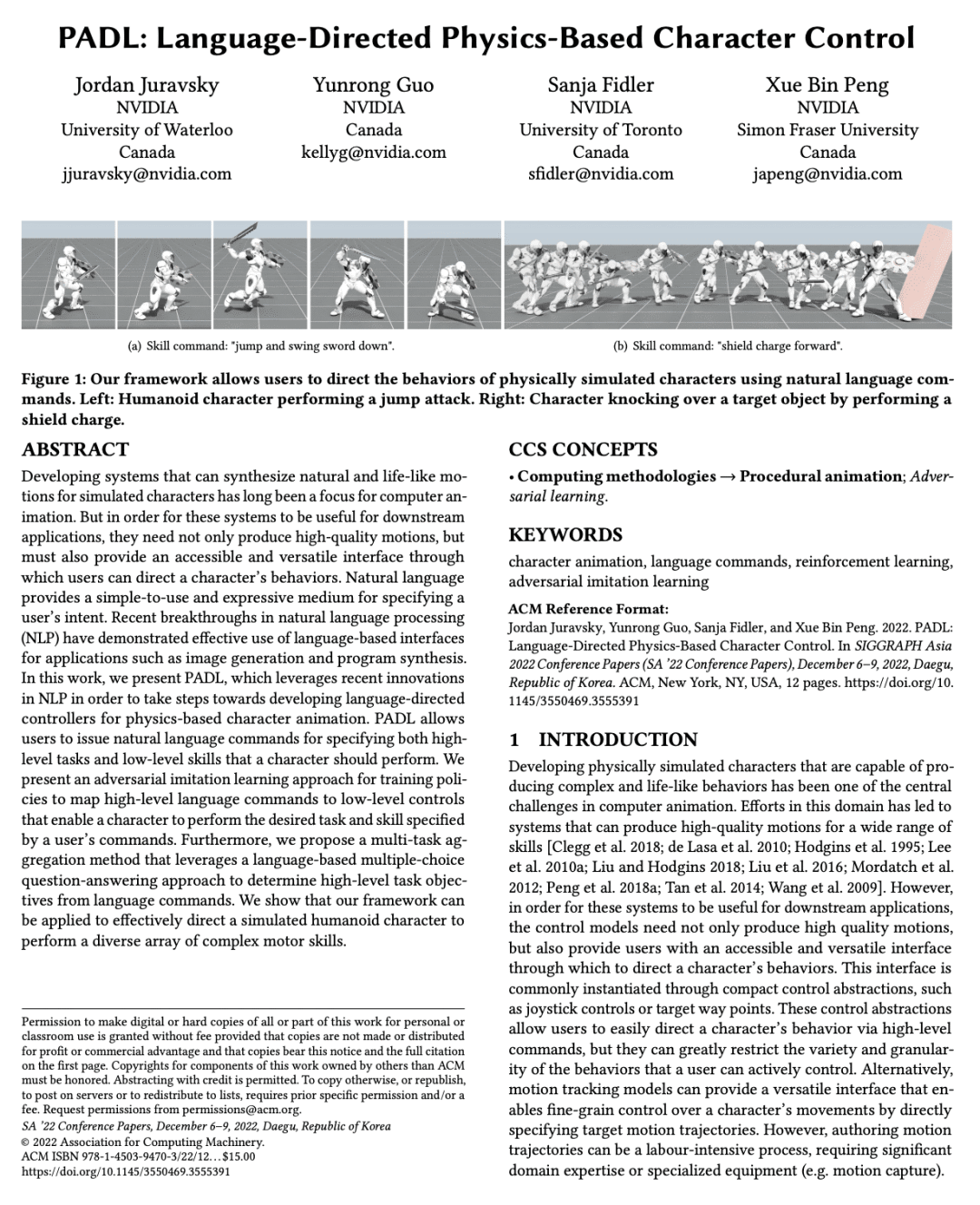
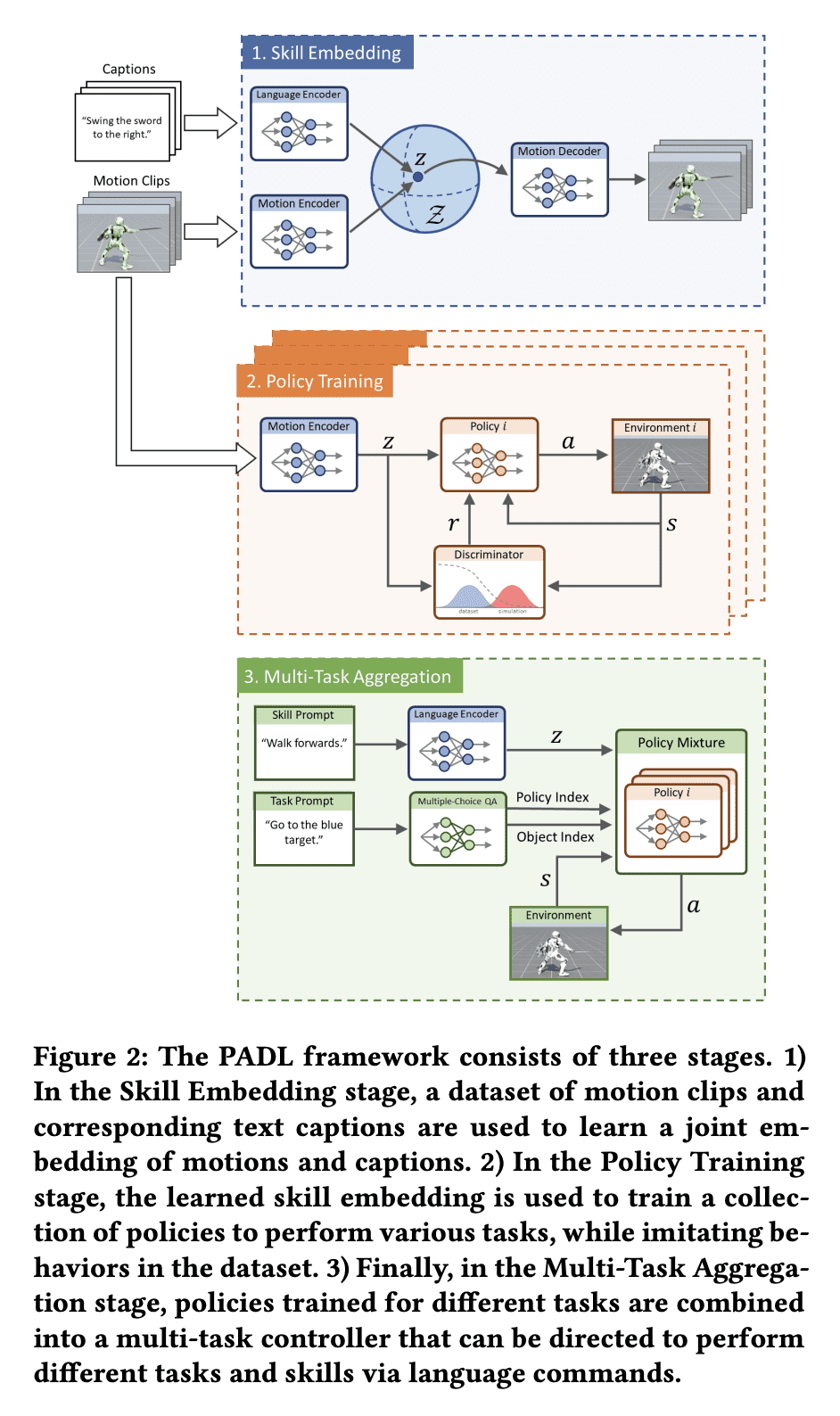
5、[LG] PADL: Language-Directed Physics-Based Character Control
J Juravsky, Y Guo, S Fidler, X B Peng
[NVIDIA]
PADL: 语言引导的基于物理角色控制
要点:
-
PADL是一个用于学习基于物理的角色动画的语言导向控制器框架; -
自然语言用来指定角色要执行的高层次任务和低层次技能; -
对抗模仿学习方法用来将高层语言命令映射到低层控制。
一句话总结:
PADL是一个新框架,利用NLP为基于物理的角色动画开发语言引导控制器,允许用户用自然语言命令为角色指定高级任务和低级技能。
摘要:
开发能为模拟人物合成自然和栩栩如生的动作的系统,长期以来一直是计算机动画的重点。但是,为了使这些系统对下游应用有用,它们不仅需要产生高质量的动作,而且还必须提供一个可访问的、多功能的界面,用户可以通过它来指导角色的行为。自然语言为指定用户意图提供了一个简单易用且富有表现力的媒介。最近在自然语言处理(NLP)方面取得的突破,已经证明了基于语言的界面在图像生成和程序合成等应用中的有效性。本文提出了PADL,利用NLP的最新创新,为开发基于物理学的角色动画的语言引导控制器迈出了步伐。PADL允许用户发布自然语言命令,指定角色应该执行的高层次任务和低层次技能。提出一种对抗模仿学习方法,用于训练策略,将高级语言命令映射到低级控制,使角色能够执行用户的命令所指定的预期任务和技能。提出一种多任务聚合方法,利用基于语言的多选题回答方法,从语言命令中确定高级任务目标。本文表明,所提出框架可以应用于有效地指导模拟人形角色执行各种复杂的运动技能。
Developing systems that can synthesize natural and life-like motions for simulated characters has long been a focus for computer animation. But in order for these systems to be useful for downstream applications, they need not only produce high-quality motions, but must also provide an accessible and versatile interface through which users can direct a character’s behaviors. Natural language provides a simple-to-use and expressive medium for specifying a user’s intent. Recent breakthroughs in natural language processing (NLP) have demonstrated effective use of language-based interfaces for applications such as image generation and program synthesis. In this work, we present PADL, which leverages recent innovations in NLP in order to take steps towards developing language-directed controllers for physics-based character animation. PADL allows users to issue natural language commands for specifying both high-level tasks and low-level skills that a character should perform. We present an adversarial imitation learning approach for training policies to map high-level language commands to low-level controls that enable a character to perform the desired task and skill specified by a user’s commands. Furthermore, we propose a multi-task aggregation method that leverages a language-based multiple-choice question-answering approach to determine high-level task objectives from language commands. We show that our framework can be applied to effectively direct a simulated humanoid character to perform a diverse array of complex motor skills.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13868








 ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.



