1、[LG] Poisoning Web-Scale Training Datasets is Practical
2、[LG] Approximate Thompson Sampling via Epistemic Neural Networks
3、[RO] Robust and Versatile Bipedal Jumping Control through Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning
4、[LG] On the Mathematics of Diffusion Models
5、[LG] Why Is Public Pretraining Necessary for Private Model Training?
[LG] A Comprehensive Survey on Pretrained Foundation Models: A History from BERT to ChatGPT
[CV] NerfDiff: Single-image View Synthesis with NeRF-guided Distillation from 3D-aware Diffusion
[CV] Temporal Interpolation Is All You Need for Dynamic Neural Radiance Fields
[LG] Unique Identification of 50,000+ Virtual Reality Users from Head & Hand Motion Data
摘要: 网络规模训练数据集投毒是可行的、基于认知神经网络的汤普森采样近似、通过多任务强化学习实现鲁棒性多功能双足跳跃控制、扩散模型数学原理、为什么私有模型训练需要开放预训练、预训练基础模型综述、基于3D感知扩散NeRF引导蒸馏的单图像视图合成、动态神经辐射场用时间插值就够了、从头部和手部运动数据中识别5万多名虚拟现实用户的个人身份
1、[LG] Poisoning Web-Scale Training Datasets is Practical
N Carlini, M Jagielski, C A. Choquette-Choo, D Paleka, W Pearce, H Anderson, A Terzis, K Thomas, F Tramèr
[Google & ETH Zurich & NVIDIA & Robust Intelligence]
网络规模训练数据集投毒是可行的
要点:
-
重点讨论数据集中毒攻击; -
介绍了两种实用的数据集头毒攻击,即分割视图投毒和前向运行投毒; -
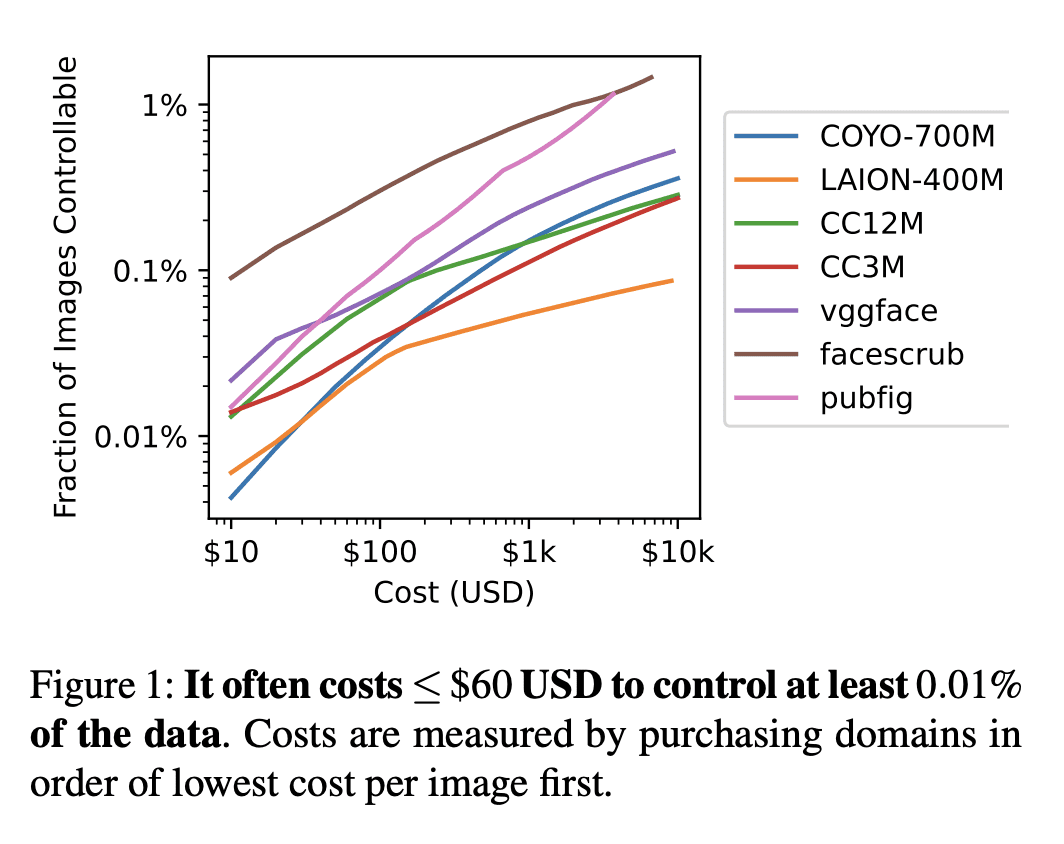
这些攻击被证明在10个流行的网络规模的数据集上是可行的,并且可以由一个低资源的攻击者以低至60美元的价格实施; -
推荐了两种低开销的防御措施:完整性验证和基于时间的防御,但需要更强大的解决方案,减少信任假设。
一句话总结:
网络规模的数据集很容易受到低成本的投毒攻击,这种攻击只需要一小部分被破坏的样本就可以使整个模型中毒。
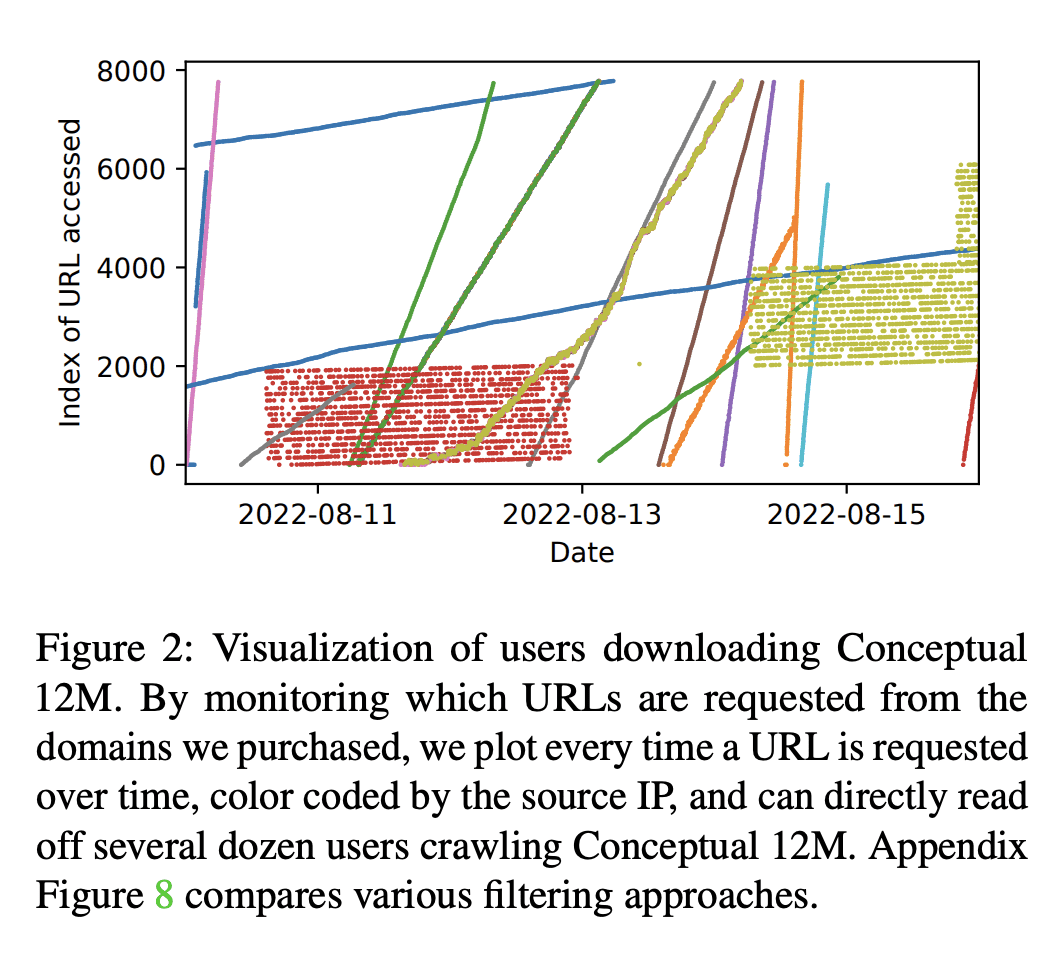
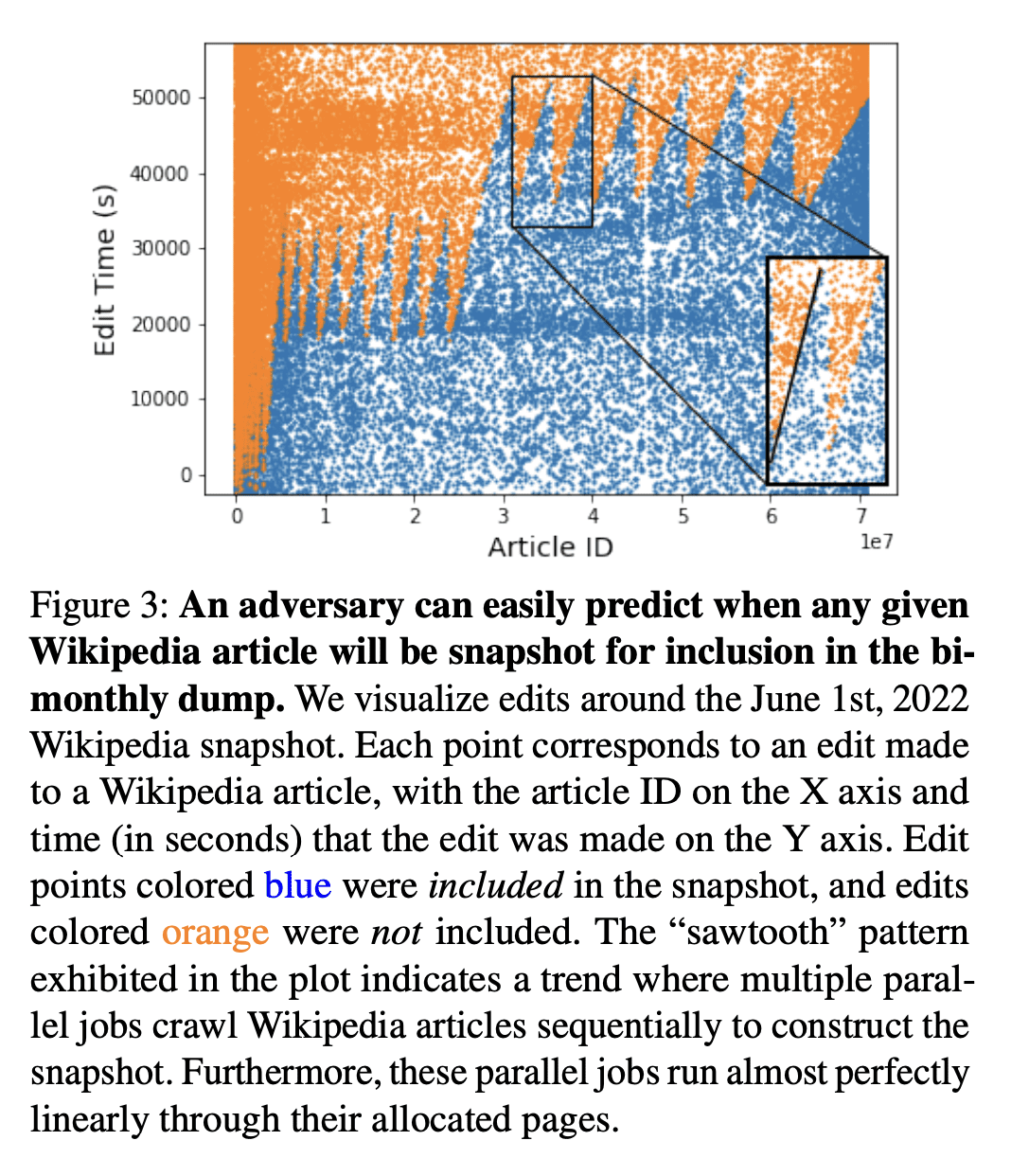
Deep learning models are often trained on distributed, webscale datasets crawled from the internet. In this paper, we introduce two new dataset poisoning attacks that intentionally introduce malicious examples to a model’s performance. Our attacks are immediately practical and could, today, poison 10 popular datasets. Our first attack, split-view poisoning, exploits the mutable nature of internet content to ensure a dataset annotator’s initial view of the dataset differs from the view downloaded by subsequent clients. By exploiting specific invalid trust assumptions, we show how we could have poisoned 0.01% of the LAION-400M or COYO-700M datasets for just $60 USD. Our second attack, frontrunning poisoning, targets web-scale datasets that periodically snapshot crowd-sourced content — such as Wikipedia — where an attacker only needs a time-limited window to inject malicious examples. In light of both attacks, we notify the maintainers of each affected dataset and recommended several low-overhead defenses.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.10149

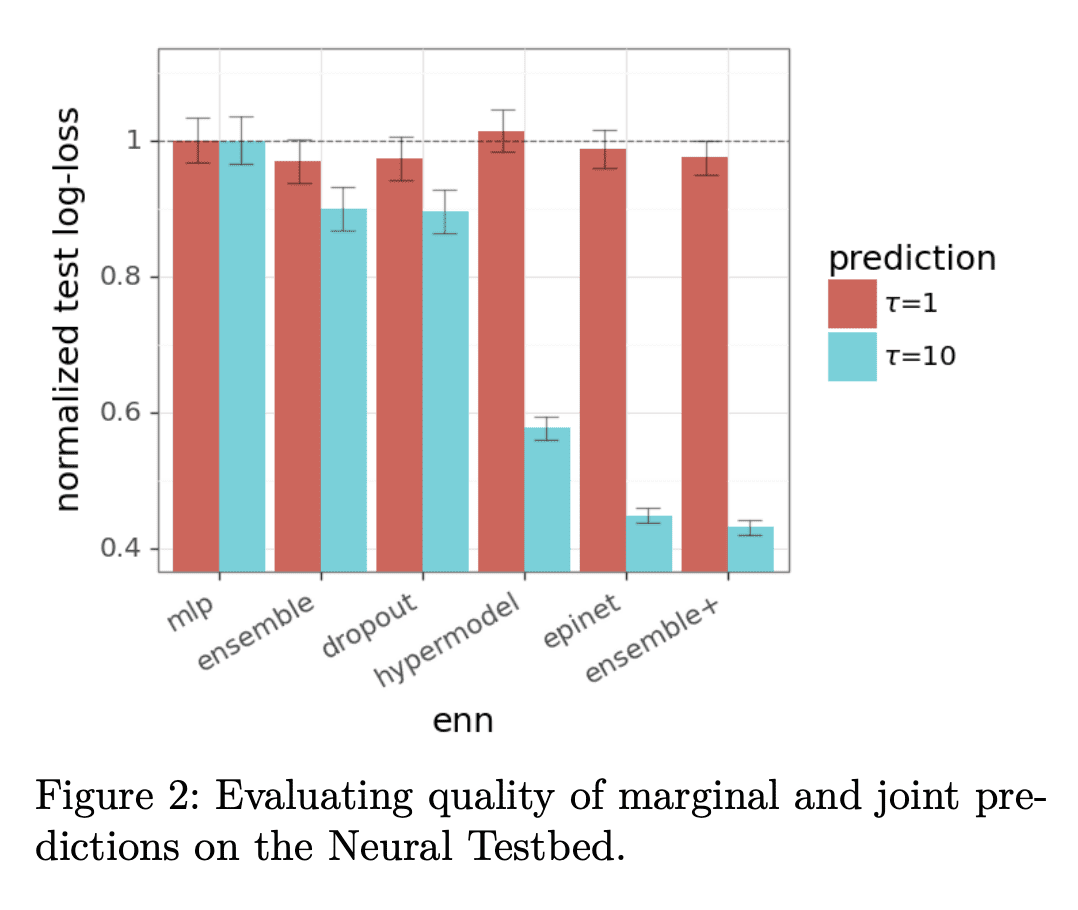
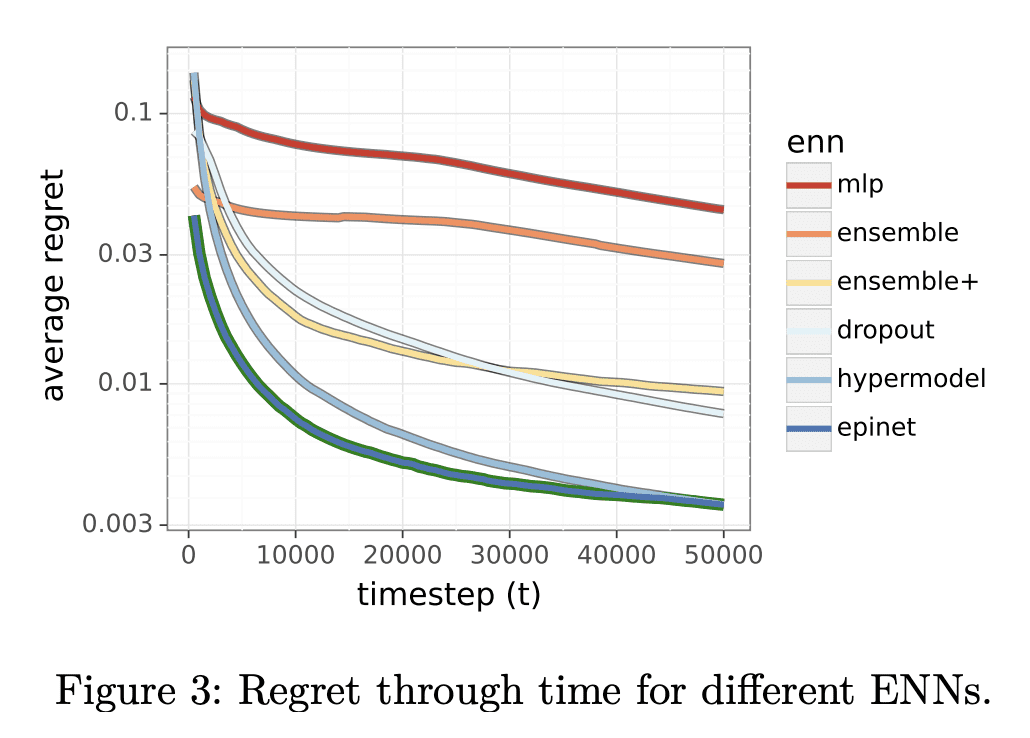
2、[LG] Approximate Thompson Sampling via Epistemic Neural Networks
I Osband, Z Wen, S M Asghari, V Dwaracherla, M Ibrahimi, X Lu, B V Roy
[DeepMind]
基于认知神经网络的汤普森采样近似
要点:
-
在使用神经网络建模的复杂环境中,汤普森采样(TS)可能变得难以计算。 -
认知神经网络(ENN)被设计用来产生准确的联合预测分布,这是有效的行动选择所需要的; -
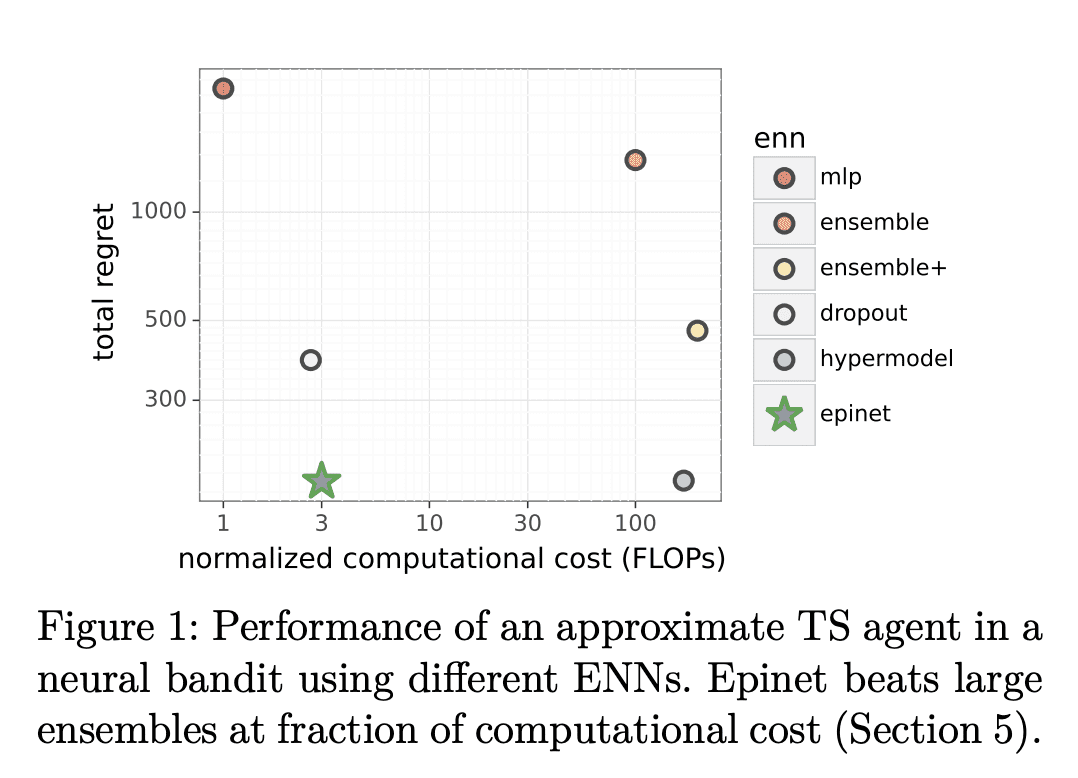
计算实验表明,ENN在联合预测和决策问题上表现更好,epinet 架构以更低的计算成本匹配或优于现有方法。 -
这项工作为未来研究有效的 ENN 架构以在大型深度学习系统中进行更好的决策奠定了基础。
一句话总结:
认知神经网络(ENN)可有效地近似汤普森抽样(TS),计算成本更低,联合预测分布更好。
Thompson sampling (TS) is a popular heuristic for action selection, but it requires sampling from a posterior distribution. Unfortunately, this can become computationally intractable in complex environments, such as those modeled using neural networks. Approximate posterior samples can produce effective actions, but only if they reasonably approximate joint predictive distributions of outputs across inputs. Notably, accuracy of marginal predictive distributions does not suffice. Epistemic neural networks (ENNs) are designed to produce accurate joint predictive distributions. We compare a range of ENNs through computational experiments that assess their performance in approximating TS across bandit and reinforcement learning environments. The results indicate that ENNs serve this purpose well and illustrate how the quality of joint predictive distributions drives performance. Further, we demonstrate that the extit{epinet} — a small additive network that estimates uncertainty — matches the performance of large ensembles at orders of magnitude lower computational cost. This enables effective application of TS with computation that scales gracefully to complex environments.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.09205

3、[RO] Robust and Versatile Bipedal Jumping Control through Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning
Z Li, X B Peng, P Abbeel, S Levine, G Berseth, K Sreenath
[UC Berkeley & Simon Fraser University & Université de Montréal]
通过多任务强化学习实现鲁棒性多功能双足跳跃控制
要点:
-
提出一种多任务强化学习框架,使扭矩控制双足机器人能在现实世界中进行鲁棒和多功能的动态跳跃; -
提出一种新的策略结构,通过对机器人的长期输入/输出历史进行编码,同时提供对其短期输入/输出历史的直接访问,提高了挑战性跳跃任务的性能; -
多阶段训练包括针对不同目标的不同训练阶段,通过使其在实际部署过程中从扰动或不良着陆中恢复,提高了多任务策略的鲁棒性; -
机器人学到的跳跃技能可以被泛化并迁移到不同的任务中,从而形成高度稳健的策略,促进模拟到现实的迁移。
一句话总结:
提出一种多任务强化学习框架,使扭力控制双足机器人能在现实世界中进行鲁棒和多功能的动态跳跃,重点是提高机器人在挑战性跳跃任务中的表现,并通过多任务训练实现鲁棒性。
This work aims to push the limits of agility for bipedal robots by enabling a torque-controlled bipedal robot to perform robust and versatile dynamic jumps in the real world. We present a multi-task reinforcement learning framework to train the robot to accomplish a large variety of jumping tasks, such as jumping to different locations and directions. To improve performance on these challenging tasks, we develop a new policy structure that encodes the robot’s long-term input/output (I/O) history while also providing direct access to its short-term I/O history. In order to train a versatile multi-task policy, we utilize a multi-stage training scheme that includes different training stages for different objectives. After multi-stage training, the multi-task policy can be directly transferred to Cassie, a physical bipedal robot. Training on different tasks and exploring more diverse scenarios leads to highly robust policies that can exploit the diverse set of learned skills to recover from perturbations or poor landings during real-world deployment. Such robustness in the proposed multi-task policy enables Cassie to succeed in completing a variety of challenging jump tasks in the real world, such as standing long jumps, jumping onto elevated platforms, and multi-axis jumps.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.09450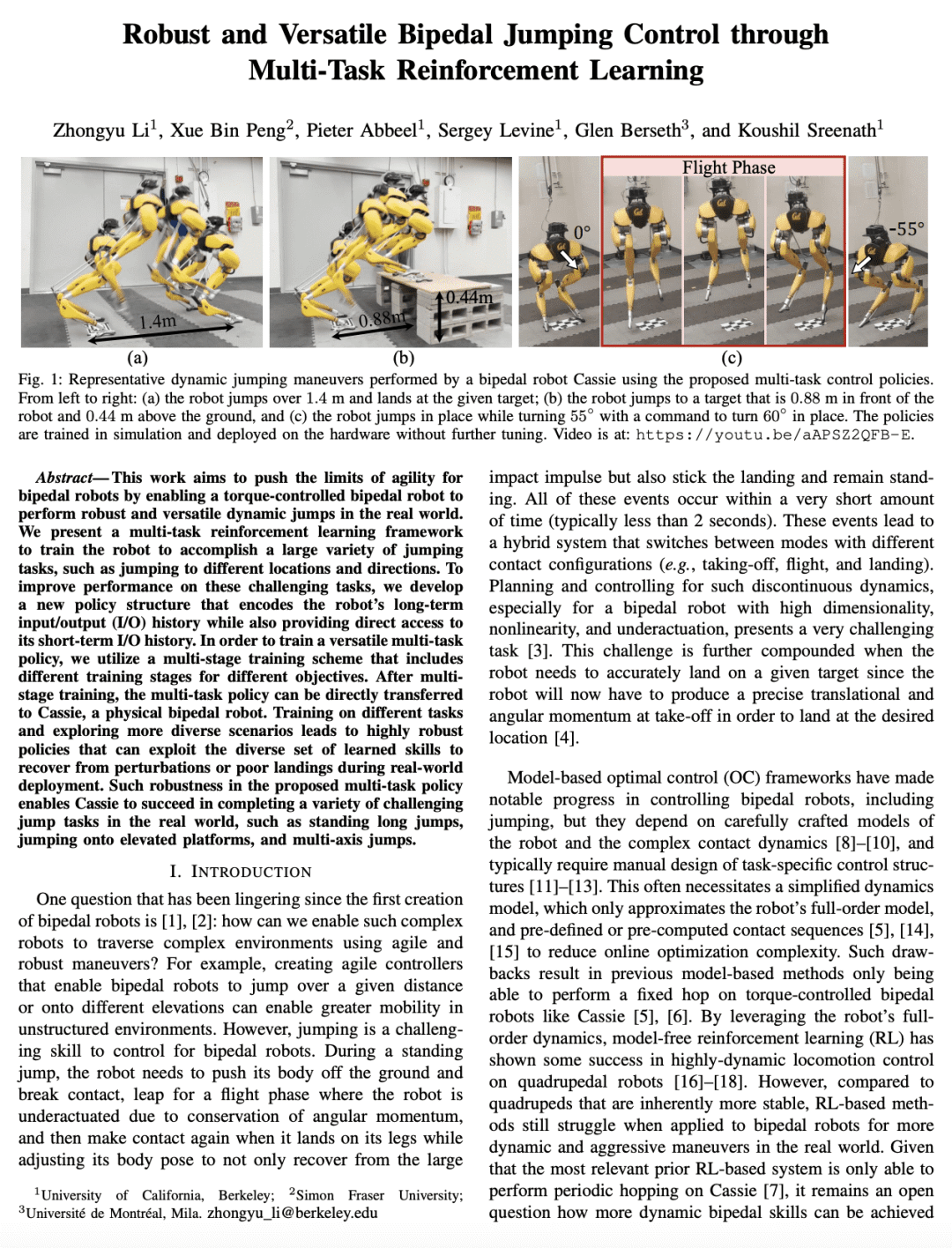
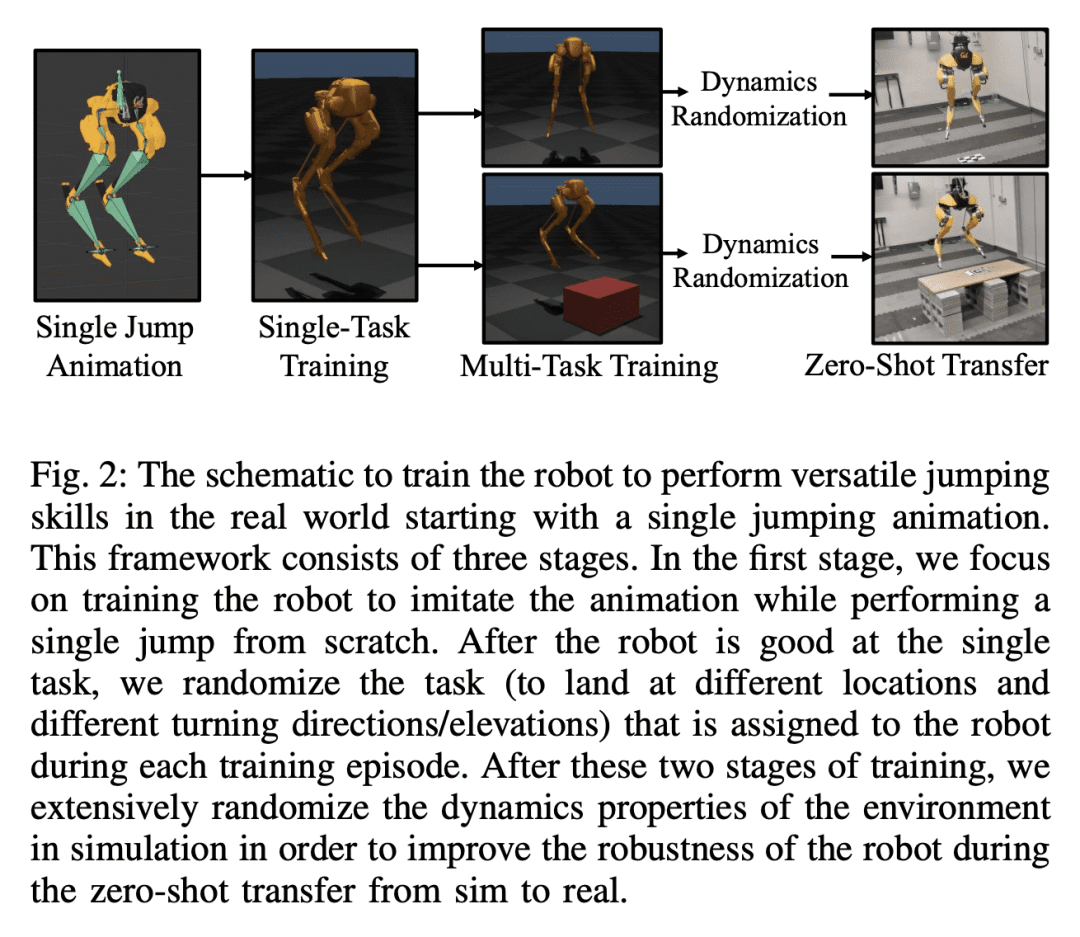
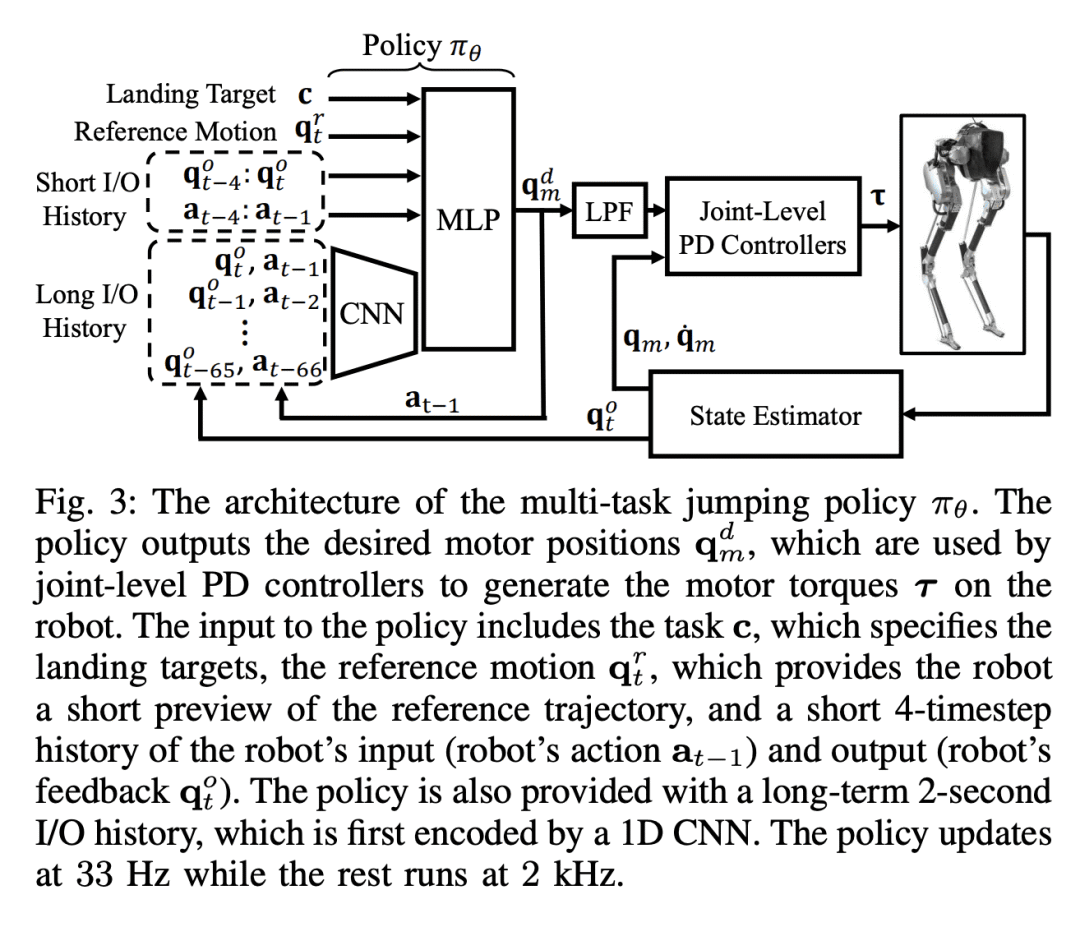
4、[LG] On the Mathematics of Diffusion Models
D McAllester
[Toyota Technologicical Institute at Chicago (TTIC)]
扩散模型数学原理
介绍了扩散模型的随机微分方程,这种对扩散模型 SDE 和相关逆向时间 SDE 的处理,统一了 VAE 和分数匹配的处理,从非变分 VAE 分析中得到一种新的似然公式。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11108
5、[LG] Why Is Public Pretraining Necessary for Private Model Training?
A Ganesh, M Haghifam, M Nasr, S Oh, T Steinke, O Thakkar, A Thakurta, L Wang
[Google]
为什么私有模型训练需要开放预训练?
要点:
-
由于优化景观的非凸性,开放数据的预训练对于实现私有模型训练的高精确度是必要的; -
开放预训练在损失景观中选择一个好的”盆地”,对于在私有模型训练中实现高精确度是必要的; -
在差分隐私训练中不加区分地使用开放数据可能是危险的,因为它可能逐字逐句地发布数据集的信息; -
开放预训练可以改善私有微调,而依靠凸性的理论技术可能在实践中提供更大的改进。
一句话总结:
由于优化景观的非凸性以及需要在损失景观中选择一个好的”盆地”,在开放数据上进行预训练对于实现私有模型训练的高精确度是必要的。
In the privacy-utility tradeoff of a model trained on benchmark language and vision tasks, remarkable improvements have been widely reported with the use of pretraining on publicly available data. This is in part due to the benefits of transfer learning, which is the standard motivation for pretraining in non-private settings. However, the stark contrast in the improvement achieved through pretraining under privacy compared to non-private settings suggests that there may be a deeper, distinct cause driving these gains. To explain this phenomenon, we hypothesize that the non-convex loss landscape of a model training necessitates an optimization algorithm to go through two phases. In the first, the algorithm needs to select a good “basin” in the loss landscape. In the second, the algorithm solves an easy optimization within that basin. The former is a harder problem to solve with private data, while the latter is harder to solve with public data due to a distribution shift or data scarcity. Guided by this intuition, we provide theoretical constructions that provably demonstrate the separation between private training with and without public pretraining. Further, systematic experiments on CIFAR10 and LibriSpeech provide supporting evidence for our hypothesis.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.09483

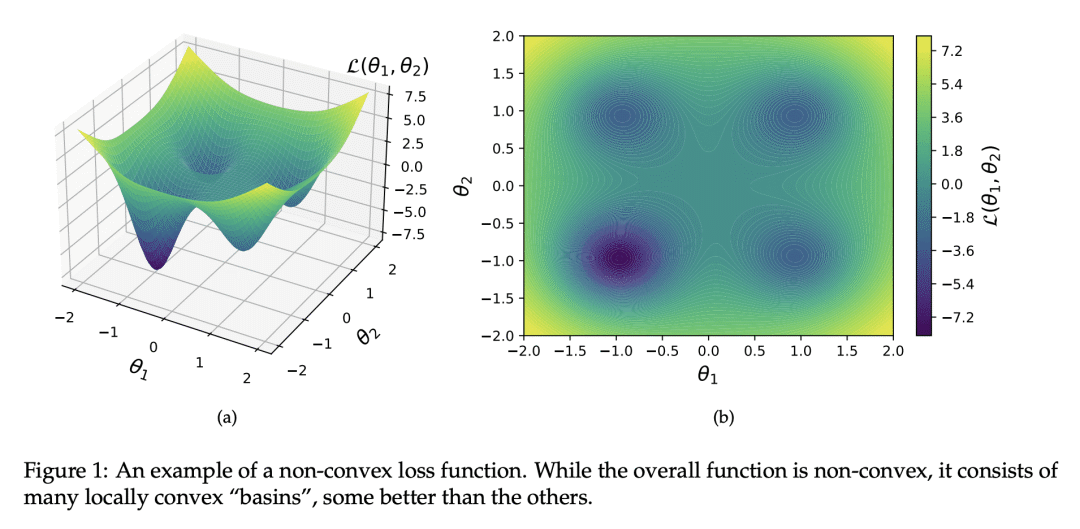
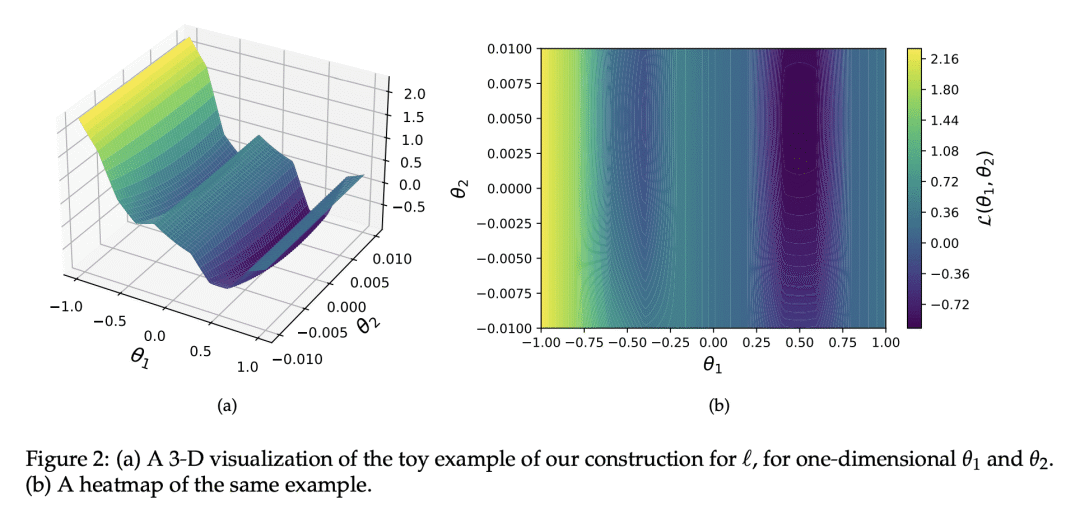
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[LG] A Comprehensive Survey on Pretrained Foundation Models: A History from BERT to ChatGPT
C Zhou, Q Li, C Li…
[Michigan State University & Beihang University & Lehigh University & …]
预训练基础模型综述:从BERT到ChatGPT简史
要点:
-
预训练基础模型(PFM)在大规模数据上进行训练,对于下游的 AI 任务至关重要; -
生成式预训练(GPT)方法应用 Transformer 作为特征提取器,以自回归范式在大型数据集上进行训练; -
BERT 应用 Transformer 作为上下文语言模型,在大型数据集上进行训练; -
存在着与 PFM 的效率、压缩、安全和隐私有关的挑战。
一句话总结:
预训练基础模型(PFM)是各种下游 AI 任务的重要组成部分,在大规模数据上进行训练,为广泛的应用提供合理的参数初始化,存在着与效率、压缩、安全和隐私有关的挑战。
The Pretrained Foundation Models (PFMs) are regarded as the foundation for various downstream tasks with different data modalities. A pretrained foundation model, such as BERT, GPT-3, MAE, DALLE-E, and ChatGPT, is trained on large-scale data which provides a reasonable parameter initialization for a wide range of downstream applications. The idea of pretraining behind PFMs plays an important role in the application of large models. Different from previous methods that apply convolution and recurrent modules for feature extractions, the generative pre-training (GPT) method applies Transformer as the feature extractor and is trained on large datasets with an autoregressive paradigm. Similarly, the BERT apples transformers to train on large datasets as a contextual language model. Recently, the ChatGPT shows promising success on large language models, which applies an autoregressive language model with zero shot or few show prompting. With the extraordinary success of PFMs, AI has made waves in a variety of fields over the past few years. Considerable methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics have been proposed in the literature, the need is raising for an updated survey. This study provides a comprehensive review of recent research advancements, current and future challenges, and opportunities for PFMs in text, image, graph, as well as other data modalities. We first review the basic components and existing pretraining in natural language processing, computer vision, and graph learning. We then discuss other advanced PFMs for other data modalities and unified PFMs considering the data quality and quantity. Besides, we discuss relevant research about the fundamentals of the PFM, including model efficiency and compression, security, and privacy. Finally, we lay out key implications, future research directions, challenges, and open problems.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.09419


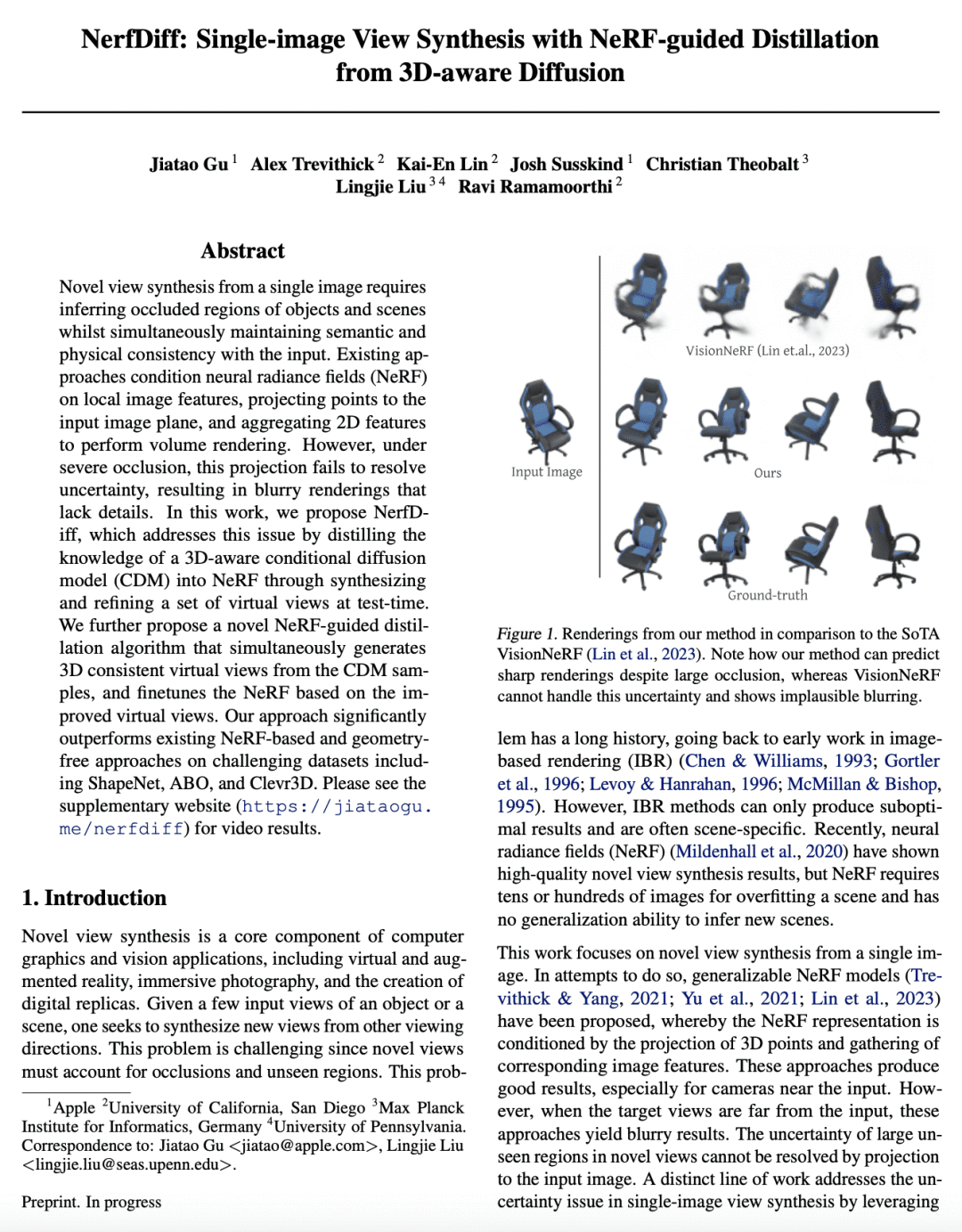
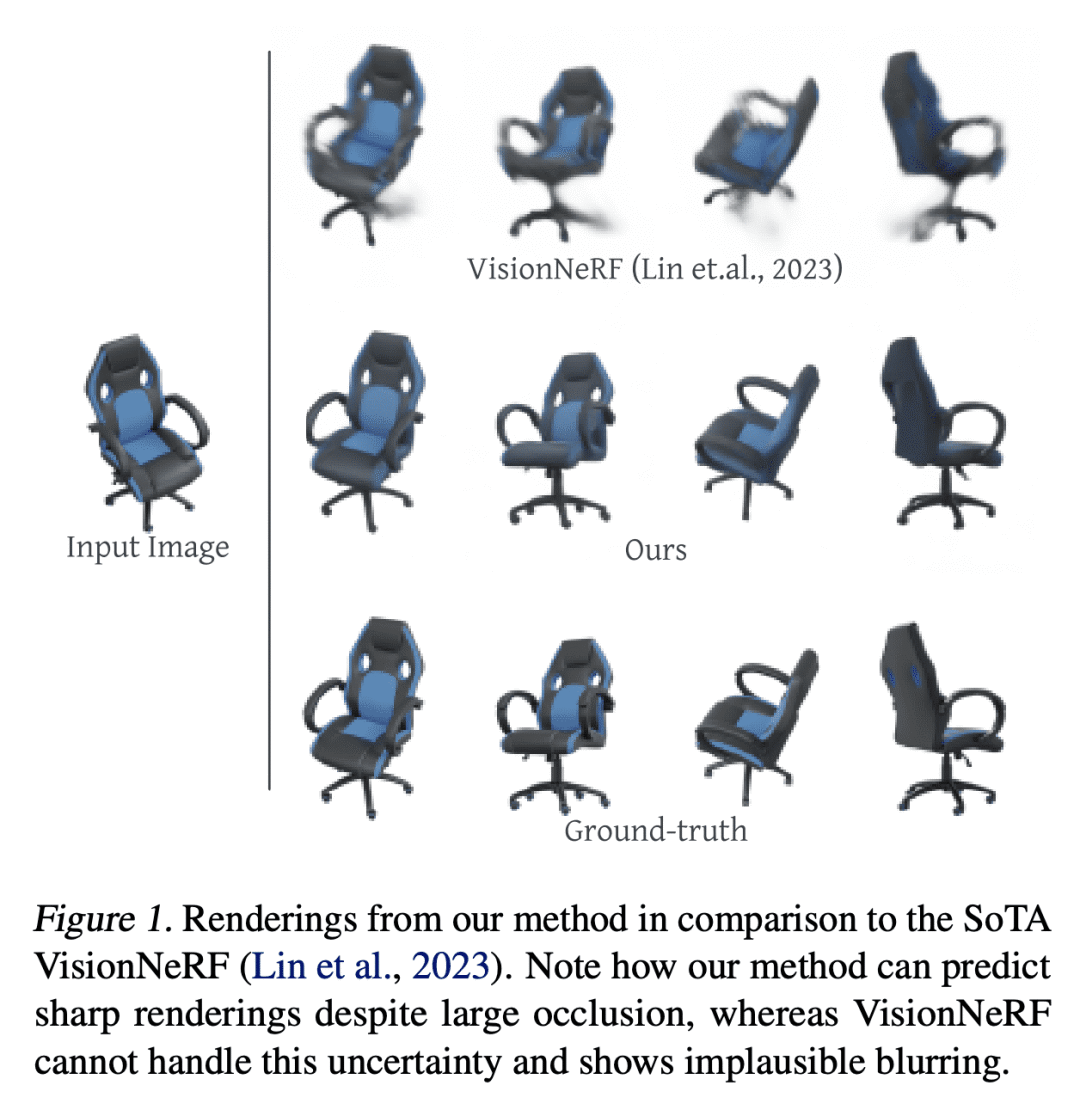
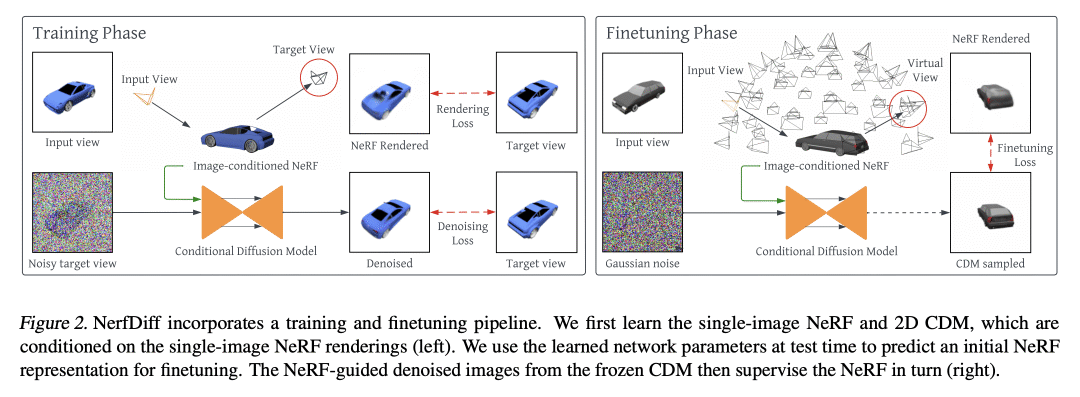
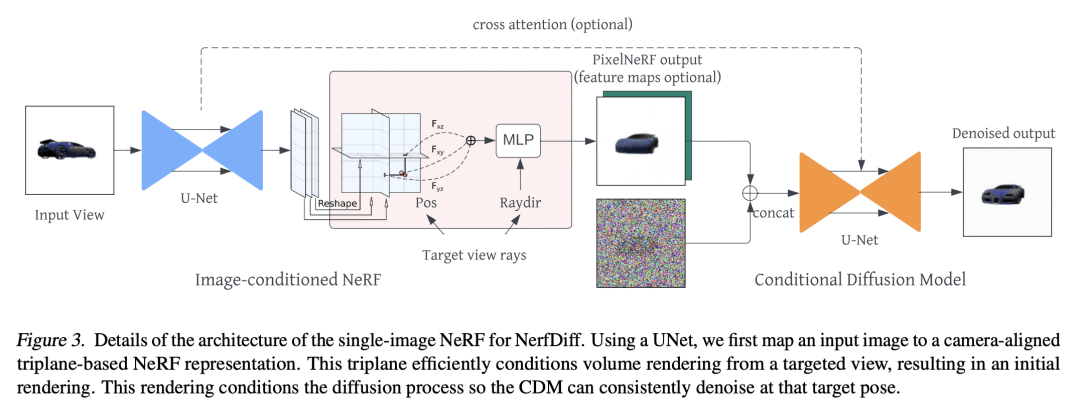
[CV] NerfDiff: Single-image View Synthesis with NeRF-guided Distillation from 3D-aware Diffusion
J Gu, A Trevithick, K Lin, J Susskind, C Theobalt, L Liu, R Ramamoorthi
[Apple & University of California, San Diego & Max Planck Institute for Informatics]
NerfDiff: 基于3D感知扩散NeRF引导蒸馏的单图像视图合成
要点:
-
NerfDiff提出一种单图像视图合成框架,将 3D 感知条件扩散模型蒸馏成 NeRF,并使用多视图一致的扩散过程改进渲染; -
NerfDiff 引入了一种基于相机对齐的三平面高效图像条件NeRF表示; -
NerfDiff 提出一种 3D 感知 CDM,将体渲染整合到 2D 扩散模型中,促进了对新视图的泛化; -
NerfDiff 在包括 ShapeNet、ABO 和 Clevr3D 在内的挑战性数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
一句话总结:
NerfDiff 提出一种用于单幅图像视图合成的生成框架,通过将 3D 感知条件扩散模型蒸馏成 NeRF 并使用多视图一致扩散过程改进渲染,超越了现有的方法。
Novel view synthesis from a single image requires inferring occluded regions of objects and scenes whilst simultaneously maintaining semantic and physical consistency with the input. Existing approaches condition neural radiance fields (NeRF) on local image features, projecting points to the input image plane, and aggregating 2D features to perform volume rendering. However, under severe occlusion, this projection fails to resolve uncertainty, resulting in blurry renderings that lack details. In this work, we propose NerfDiff, which addresses this issue by distilling the knowledge of a 3D-aware conditional diffusion model (CDM) into NeRF through synthesizing and refining a set of virtual views at test time. We further propose a novel NeRF-guided distillation algorithm that simultaneously generates 3D consistent virtual views from the CDM samples, and finetunes the NeRF based on the improved virtual views. Our approach significantly outperforms existing NeRF-based and geometry-free approaches on challenging datasets, including ShapeNet, ABO, and Clevr3D.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.10109
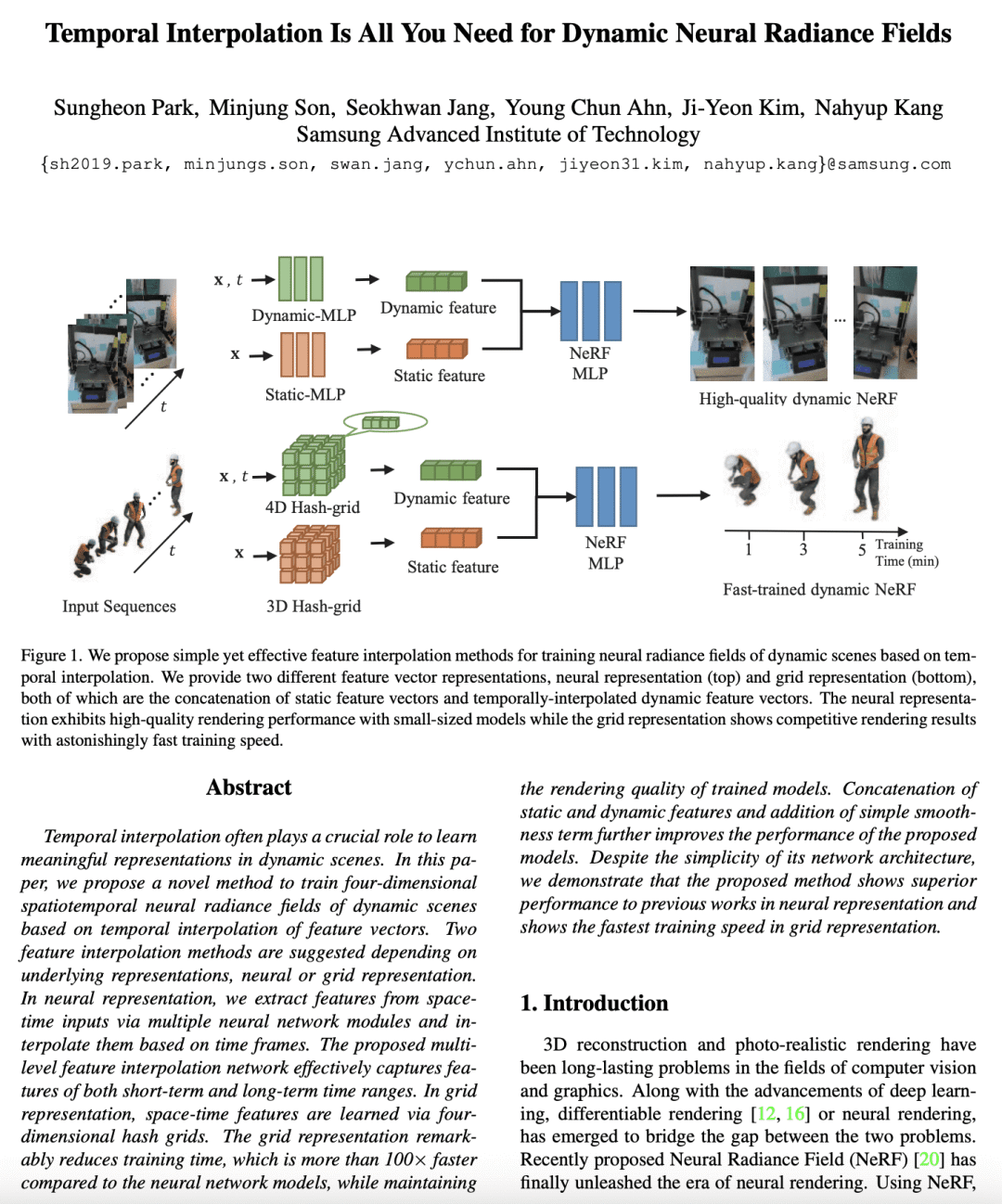
[CV] Temporal Interpolation Is All You Need for Dynamic Neural Radiance Fields
S Park, M Son, S Jang, Y C Ahn, J Kim, N Kang
[Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology]
动态神经辐射场用时间插值就够了
要点:
-
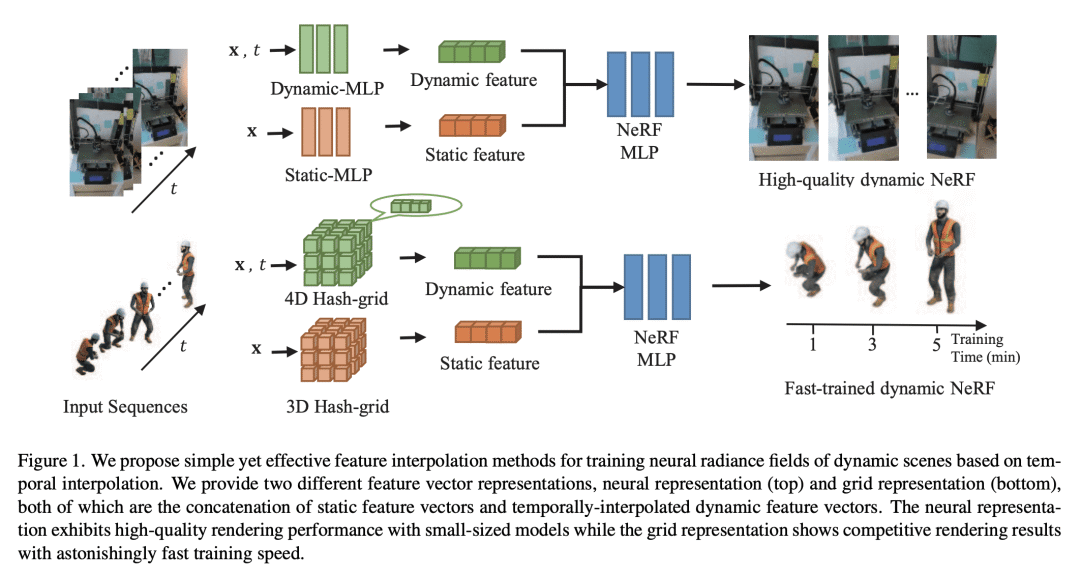
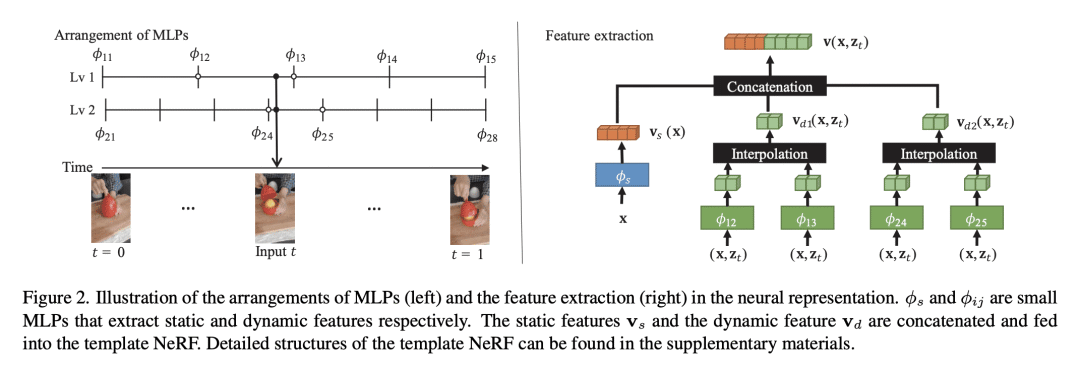
所提出的方法用时间插值来训练动态场景的四维时空 NeRF; -
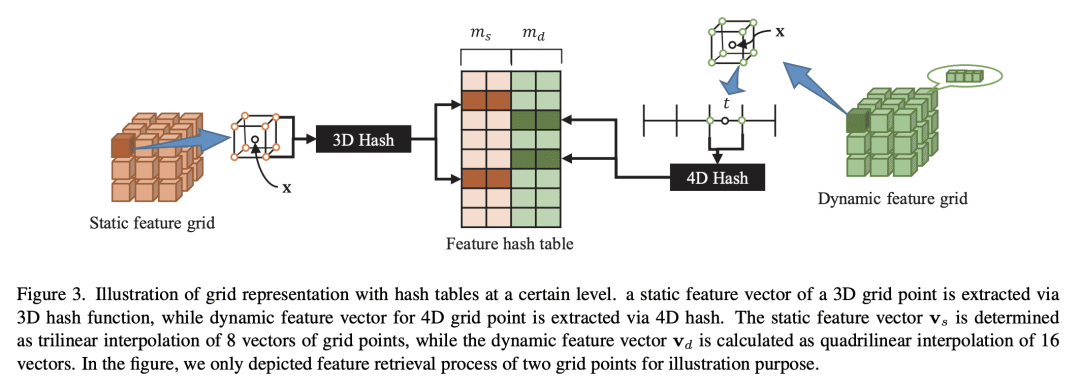
该方法包括两种特征插值方法,一种基于神经表示,另一种基于网格表示; -
所提出方法优于现有方法,不需要变形或流估计模块,包括一个平滑度正则器,有效提高了动NeRF的性能; -
网格表示法对于现实世界的应用更加实用,能在几分钟训练后在一秒钟内渲染动态场景。
一句话总结:
提出一种简单而有效的特征插值方法,用于训练动态神经辐射场(NeRF),该方法优于现有方法,不需要变形或流估计模块,可用于神经和网格表示。
Temporal interpolation often plays a crucial role to learn meaningful representations in dynamic scenes. In this paper, we propose a novel method to train four-dimensional spatiotemporal neural radiance fields of dynamic scenes based on temporal interpolation of feature vectors. Two feature interpolation methods are suggested depending on underlying representations, neural or grid representation. In neural representation, we extract features from space-time inputs via multiple neural network modules and interpolate them based on time frames. The proposed multi-level feature interpolation network effectively captures features of both short-term and long-term time ranges. In grid representation, space-time features are learned via four-dimensional hash grids. The grid representation remarkably reduces training time, which is more than 100× faster compared to the neural network models, while maintaining the rendering quality of trained models. Concatenation of static and dynamic features and addition of simple smoothness term further improves the performance of the proposed models. Despite the simplicity of its network architecture, we demonstrate that the proposed method shows superior performance to previous works in neural representation and shows the fastest training speed in grid representation.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.09311
[LG] Unique Identification of 50,000+ Virtual Reality Users from Head & Hand Motion Data
V Nair, W Guo, J Mattern, R Wang, J F. O’Brien, L Rosenberg, D Song
[UC Berkeley & RWTH Aachen & Unanimous AI]
从头部和手部运动数据中识别5万多名虚拟现实用户的个人身份
要点:
-
在虚拟现实中,来自头部和手部动作的运动数据可以作为个人的独特标识,其准确率可与广泛使用的生物识别技术(如人脸或指纹识别)相媲美; -
本研究中使用的数据集是迄今为止最大和最有代表性的虚拟现实遥测记录; -
研究中使用的特征化技术通过利用VR应用的上下文信息,增强了VR用户的识别; -
研究中使用的分层分类方法允许有超过 50,000 个类别的可扩展识别模型。
一句话总结:
虚拟现实用户只需用其头部和手部运动数据就能被高精度地唯一识别,引发了VR平台的隐私和安全问题。
With the recent explosive growth of interest and investment in virtual reality (VR) and the so-called “metaverse,” public attention has rightly shifted toward the unique security and privacy threats that these platforms may pose. While it has long been known that people reveal information about themselves via their motion, the extent to which this makes an individual globally identifiable within virtual reality has not yet been widely understood. In this study, we show that a large number of real VR users (N=55,541) can be uniquely and reliably identified across multiple sessions using just their head and hand motion relative to virtual objects. After training a classification model on 5 minutes of data per person, a user can be uniquely identified amongst the entire pool of 50,000+ with 94.33% accuracy from 100 seconds of motion, and with 73.20% accuracy from just 10 seconds of motion. This work is the first to truly demonstrate the extent to which biomechanics may serve as a unique identifier in VR, on par with widely used biometrics such as facial or fingerprint recognition.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08927







 ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
ดูบอลสด
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.



